|
Flag
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the maritime environment, where semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as " vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or " banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equivalent to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Flag
A national flag is a flag that represents and symbolizes a given nation. It is Fly (flag), flown by the government of that nation, but usually can also be flown by its citizens. A national flag is typically designed with specific meanings for its colours and symbols, which may also be used separately from the flag as a symbol of the nation. The design of a national flag is sometimes altered after the occurrence of important historical events. The Flag desecration, burning or destruction of a national flag is a greatly symbolic act. History Historically, flags originated as military standards, used as field signs. Throughout history, various examples of such proto-flags exist: the white cloth banners of the Zhou dynasty's armies in the 11th century BC, the ''vexillum'' standards flown by the armies of the Roman Empire, the Black Standard famously carried by Muhammad which later became the flag of the Abbasid Caliphate, and the various "Raven banners" flown by Viking chieftains. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Families
Flag families are sets of national flags with similarities in their design, often based on a shared history, culture, or influence. Families do not include flags with coincidental similarities. Flags may be in multiple flag families. Only twelve current national flags existed before the 19th century, when large-scale flag use began. Seven of these flags (Flag of Denmark, Denmark, Flag of France, France, Flag of the Netherlands, the Netherlands, Flag of Russia, Russia, Flag of Turkey, Turkey, Flag of the United Kingdom, the United Kingdom, and Flag of the United States, the United States of America) are the inspiration for more than 130 current national flags and ensigns. Christian cross A Christian cross flag is any flag with a cross or crosses as a central element of its design (as opposed to flags like those of Flag of Malta, Malta and Flag of Serbia, Serbia, which use crosses as smaller embellishments). It is the oldest flag family. The first flag purported to have such a cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Flag
A maritime flag is a flag designated for use on ships, boats, and other watercraft. Naval flags are considered important at sea and the rules and regulations for the flying of flags are strictly enforced. The flag flown is related to the country of registration: so much so that the word "flag" is often used symbolically as a metonym for "country of registration". Types of flag Ensigns Ensigns are usually required to be worn when entering and leaving harbour, when sailing through foreign waters, and when the ship is signalled to do so by a warship. Warships usually wear their ensigns between the morning colours ceremony and sunset when moored or at anchor, at all times when underway, and at all times when engaged in battle—the " battle ensign". When engaged in battle a warship often wears multiple battle ensigns. This tradition dates from the era of sailing vessels. Tradition dictated that if a ship lowered its ensign it was deemed to have surrendered. Masts were targets o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Semaphore
Flag semaphore (from the Ancient Greek () 'sign' and - (-) '-bearer') is a semaphore system conveying information at a distance by means of visual signals with hand-held flags, rods, disks, paddles, or occasionally bare or gloved hands. Information is encoded by the position of the flags; it is read when the flag is in a fixed position. Semaphores were adopted and widely used (with hand-held flags replacing the mechanical arms of shutter semaphores) in the maritime world in the 19th century. It is still used during underway replenishment at sea and is acceptable for emergency communication in daylight or using lighted wands instead of flags, at night. Contemporary semaphore flag system The current flag semaphore system uses two short poles with square flags, which a signal person holds in different positions to signal letters of the alphabet and numbers. The signaller holds one pole in each hand, and extends each arm in one of eight possible directions. Except for in the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vexillology
Vexillology ( ) is the study of the history, symbolism and usage of flags or, by extension, any interest in flags in general.Smith, Whitney. ''Flags Through the Ages and Across the World'' New York: McGraw-Hill, 1975. Print. The word is a synthesis of the Latin word (which refers to a kind of square flag which was carried by Roman cavalry) and the Greek suffix ("study"). The first known usage of the word ''vexillology'' was in 1959. A person who studies flags is a vexillologist, one who designs flags is a vexillographer, and the art of designing flags is called vexillography. One who is a hobbyist or general admirer of flags is a vexillophile. History The study of flags, or vexillology, was formalized by the U.S. scholar and student of flags Whitney Smith in 1961 with the publication of ''The Flag Bulletin''. During his lifetime, Smith organized various flag organizations and meetings including the first International Congress of Vexillology (ICV), the North American Ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
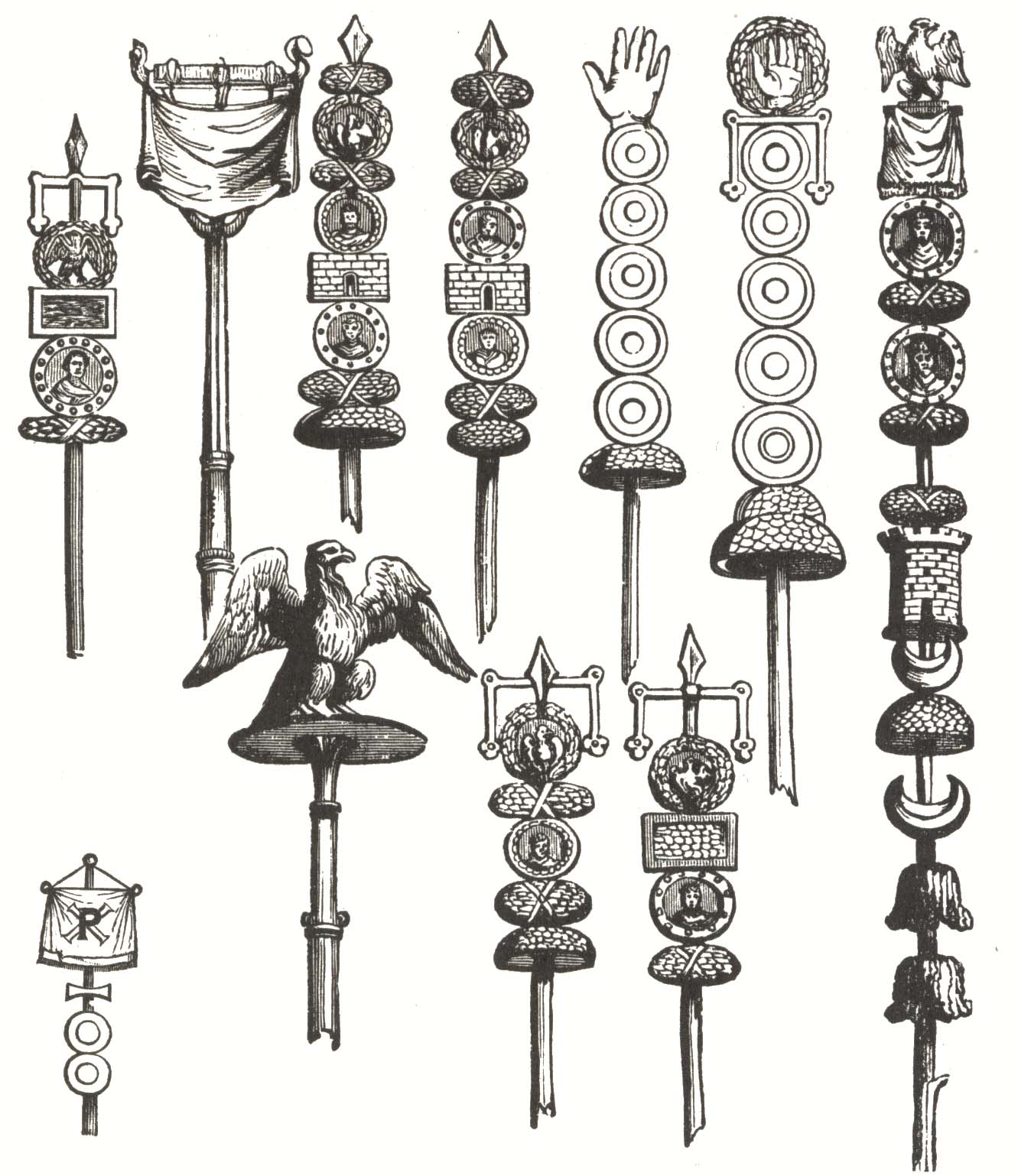
Vexilloid
A vexilloid is any flag-like (vexillary) object used by countries, organisations, or individuals as a form of representation other than flags. American vexillologist Whitney Smith coined the term ''vexilloid'' in 1958, defining it as This includes vexilla, banderoles, pennons, streamers, heraldic flags, standards, and gonfalons. Examples include the Sassanid battle standard Derafsh Kaviani, and the standards of the Roman legions such as the eagle of Augustus Caesar's Xth legion and the dragon standard of the Sarmatians; the latter was allowed to fly freely in the wind, carried by a horseman, but depictions suggest that it bore more similarity to an elongated dragon kite than to a simple flag. The use of flags replaced the use of vexilloids for general purposes during late medieval times between about 1100 to about 1400. However, vexilloids still remain in use for specialised purposes, such as for some military units or to symbolise various organisations such as fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's milit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derafsh Kaviani
Derafsh Kaviani ( fa, درفش کاویانی) was the legendary royal standard Derafsh (in Latin: vexilloid) of Iran (Persia) used since ancient times until the fall of the Sasanian Empire. The banner was also sometimes called the "Standard of Jamshid" (''Drafš-ī Jamshid'' ), the "Standard of Fereydun" (''Drafš-ī Freydun'' ) and the "Royal Standard" (''Drafš-ī Kayi'' ). Meaning and origins The name ''Drafš-e Kāvīān'' means "the standard of the kay(s)" (i.e., "kings", ''kias'', ''kavis'' ) or "of Kāva." The latter meaning is an identification with an Iranian legend in which the ''Derafš-e Kāvīān'' was the standard of a mythological Persian blacksmith-turned-hero named Kaveh ( Persian: کاوه), who led a popular uprising against the foreign demon-like ruler Zahhak ( Persian: ضحاک). Recalling the legend, the 10th-century epic '' Shahnameh'' recasts Zahhak as an evil and tyrannical ruler, against whom Kaveh called the people to arms, using his leather blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banner
A banner can be a flag or another piece of cloth bearing a symbol, logo, slogan or another message. A flag whose design is the same as the shield in a coat of arms (but usually in a square or rectangular shape) is called a banner of arms. Also, a bar-shaped piece of non-cloth advertising material sporting a name, slogan, or other marketing message is also a banner. Banner-making is an ancient craft. Church banners commonly portray the saint to whom the church is dedicated. The word derives from Old French ''baniere'' (modern french: bannière), from Late Latin ''bandum'', which was borrowed from a Germanic languages, Germanic source (compare got, 𐌱𐌰𐌽𐌳𐍅𐌰, translit=bandwa). Cognates include Italian language, Italian ''bandiera'', Portuguese language, Portuguese ''bandeira'', and Spanish language, Spanish ''bandera''. Vexillum The vexillum was a flag-like object used as a military standard by units in the Ancient Roman army. The word ''vexillum'' itself is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named after the House of Sasan, it endured for over four centuries, from 224 to 651 AD, making it the longest-lived Persian imperial dynasty. The Sasanian Empire succeeded the Parthian Empire, and re-established the Persians as a major power in late antiquity alongside its neighbouring arch-rival, the Roman Empire (after 395 the Byzantine Empire).Norman A. Stillman ''The Jews of Arab Lands'' pp 22 Jewish Publication Society, 1979 International Congress of Byzantine Studies ''Proceedings of the 21st International Congress of Byzantine Studies, London, 21–26 August 2006, Volumes 1–3'' pp 29. Ashgate Pub Co, 2006 The empire was founded by Ardashir I, an Iranian ruler who rose to power as Parthia weakened from internal strife and wars wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Legion
For centuries, Spain recruited foreign soldiers to its army, forming the Foreign Regiments () - such as the Regiment of Hibernia (formed in 1709 from Irishmen who fled their own country in the wake of the Flight of the Earls and the penal laws). However, the specific unit of the Spanish Army and Spain's Rapid Reaction Force, now known as the Spanish Legion (), and informally known as the Tercio or the Tercios, is a 20th-century creation. It was raised in the 1920s to serve as part of Spain's Army of Africa. The unit, which was established in January 1920 as the Spanish equivalent of the French Foreign Legion, was initially known as the (" Tercio of foreigners"), the name under which it began fighting in the Rif War of 1920–1926. Although foreign recruitment spans the Spanish-speaking nations, the majority of recruits are Spaniards. Over the years, the force's name has changed from to (when the field of operations targeted Morocco), and by the end of the Rif War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)