|
First Aceh Expedition
The First Aceh Expedition was a punitive expedition of the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army against Aceh. Early in 1873, the American Consul in Singapore had discussions with an Achenese emissary about a possible Acehnese-American treaty, which the Dutch saw as justification for intervention. In March 1873, the Dutch bombed the Acehnese capital Banda Aceh (Kutaraja) and in April they landed 3,000 troops led by Johan Harmen Rudolf Köhler. Having misjudged their Acehnese opposition, the Dutch were forced to withdraw losing Köhler and eighty men. They then established a blockade and Acehnese troops (estimates of whom range from 10,000 to 100,000) prepared for battle. This was followed by the Second Aceh Expedition in late 1873. See also * History of Indonesia *Second Aceh Expedition The Dutch dispatched a second expedition in Aceh in late 1873 during the Aceh War following the failed First Aceh Expedition of the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army to Aceh. At that ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aceh War
The Aceh War ( id, Perang Aceh), also known as the Dutch War or the Infidel War (1873–1913), was an armed military conflict between the Sultanate of Aceh and the Kingdom of the Netherlands which was triggered by discussions between representatives of Aceh and the United States in Singapore during early 1873.Ricklefs (2001), p. 185–88 The war was part of a series of conflicts in the late 19th century that consolidated Dutch rule over modern-day Indonesia. The campaign drew controversy in the Netherlands as photographs and accounts of the death toll were reported. Isolated bloody insurgencies continued as late as 1914 and less violent forms of Acehnese resistance continued to persist until World War II and the Japanese occupation. Background For much of the 19th century, Aceh's independence had been guaranteed by the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824 and its status as a protectorate of the Ottoman Empire since the 16th century. During the 1820s, Aceh became a regional political ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Aceh
The Sultanate of Aceh, officially the Kingdom of Aceh Darussalam ( ace, Keurajeuën Acèh Darussalam; Jawoë: كاورجاون اچيه دارالسلام), was a sultanate centered in the modern-day Indonesian province of Aceh. It was a major regional power in the 16th and 17th centuries, before experiencing a long period of decline. Its capital was Kutaraja, the present-day Banda Aceh. At its peak it was a formidable enemy of the Sultanate of Johor and Portuguese-controlled Malacca, both on the Malayan Peninsula, as all three attempted to control the trade through the Strait of Malacca and the regional exports of pepper and tin with fluctuating success. In addition to its considerable military strength, the court of Aceh became a noted center of Islamic scholarship and trade. History Foundation and rise The sultanate was founded by Ali Mughayat Syah, who began campaigns to extend his control over northern Sumatra in 1520. His conquests included Deli, Pedir, and Pasai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johan Harmen Rudolf Köhler
{{disambiguation ...
Johan * Johan (given name) * ''Johan'' (film), a 1921 Swedish film directed by Mauritz Stiller * Johan (band), a Dutch pop-group ** ''Johan'' (album), a 1996 album by the group * Johan Peninsula, Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada * Jo-Han, a manufacturer of plastic scale model kits See also * John (name) John (; ') is a common male given name in the English language of Hebrew origin. The name is the English form of ''Iohannes'' and ''Ioannes'', which are the Latin forms of the Greek name Ioannis (Ιωάννης), originally borne by Hellenized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panglima Polim
Panglima is a military title used in Indonesia and Malaysia, and historically in the Philippines. It means 'a commander of a body of troops'. In the past it is used to call some prominent military leaders in several kingdoms, such as Panglima Polem from Aceh. In modern times it is reserved for the chiefs of the armed forces of Indonesia and Malaysia and some other posts. Use in Indonesia Panglima Tertinggi Angkatan Bersenjata Republik Indonesia As stipulated in article 10 of Indonesian Constitution, the President of Indonesia is the Supreme Commander of Indonesian Armed Forces (). Essentially it is parallel to the title 'Commander-in-Chief' in other countries, ''e.g.'' the United States. During the Old Order era, this title is included into many honorific titles that were often mentioned each time Sukarno's name was written or read in speeches, edicts, or news. Panglima TNI In Indonesian National Armed Forces the highest position overseeing the three branches - Army, Navy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alauddin Mahmud Syah II
Sultan Alauddin Mahmud Syah II (died 28 January 1874) was the thirty-fourth sultan of Aceh in northern Sumatra. He reigned from 1870 to 1874 and was the last sultan to rule Aceh before the colonial invasion. Rivalries at the court He was the son of Sultan Alauddin Sulaiman Ali Iskandar Syah (d. 1857) and a commoner wife. When his granduncle Alauddin Ibrahim Mansur Syah died in 1870 without living sons, Alauddin Mahmud Syah was enthroned, still a minor. He married Pocut Meurah Awan as his main wife. His main councilors were Panglima Tibang and the Arab Habib Abdurrahman Az-Zahir. The latter had exerted influence on the late sultan and was appointed guardian to the young successor who greatly admired his tutor. The two councilors were at odds with each other; Habib Abdurrahman realized that Aceh could not stay isolated from the world and favoured an understanding with the Dutch colonial state, while Panglima Tibang was averse to any compromise with Aceh's independent position. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punitive Expedition
A punitive expedition is a military journey undertaken to punish a political entity or any group of people outside the borders of the punishing state or union. It is usually undertaken in response to perceived disobedient or morally wrong behavior by miscreants, as revenge or corrective action, or to apply strong diplomatic pressure without a formal declaration of war (e.g. surgical strike). In the 19th century, punitive expeditions were used more commonly as pretexts for colonial adventures that resulted in annexations, regime changes or changes in policies of the affected state to favour one or more colonial powers. Stowell (1921) provides the following definition: When the territorial sovereign is too weak or is unwilling to enforce respect for international law, a state which is wronged may find it necessary to invade the territory and to chastise the individuals who violate its rights and threaten its security. Historical examples *In the 5th century BC, the Achaem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Netherlands East Indies Army
The Royal Netherlands East Indies Army ( nl, Koninklijk Nederlands Indisch Leger; KNIL, ) was the military force maintained by the Kingdom of the Netherlands in its colony of the Dutch East Indies, in areas that are now part of Indonesia. The KNIL's air arm was the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army Air Force. Elements of the Royal Netherlands Navy and Government Navy were also stationed in the Netherlands East Indies. History 1814–1942 The KNIL was formed by royal decree on 14 September 1814. It was not part of the Royal Netherlands Army, but a separate military arm specifically formed for service in the Netherlands East Indies. Its establishment coincided with the Dutch drive to expand colonial rule from the 17th century area of control to the far larger territories constituting the Dutch East Indies seventy years later. The KNIL was involved in many campaigns against indigenous groups in the area including the Padri War (1821–1845), the Java War (1825–1830), cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aceh
Aceh ( ), officially the Aceh Province ( ace, Nanggroë Acèh; id, Provinsi Aceh) is the westernmost province of Indonesia. It is located on the northernmost of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capital and largest city. Granted a special autonomous status, Aceh is a religiously conservative territory and the only Indonesian province practicing the Sharia law officially. There are ten indigenous ethnic groups in this region, the largest being the Acehnese people, accounting for approximately 80% to 90% of the region's population. Aceh is where the spread of Islam in Indonesia began, and was a key factor of the spread of Islam in Southeast Asia. Islam reached Aceh (Kingdoms of Fansur and Lamuri) around 1250 AD. In the early 17th century the Sultanate of Aceh was the most wealthy, powerful and cultivated state in the Malacca Straits region. Aceh has a history of political independence and resistance to control by outsiders, including the former Dutch colonists an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
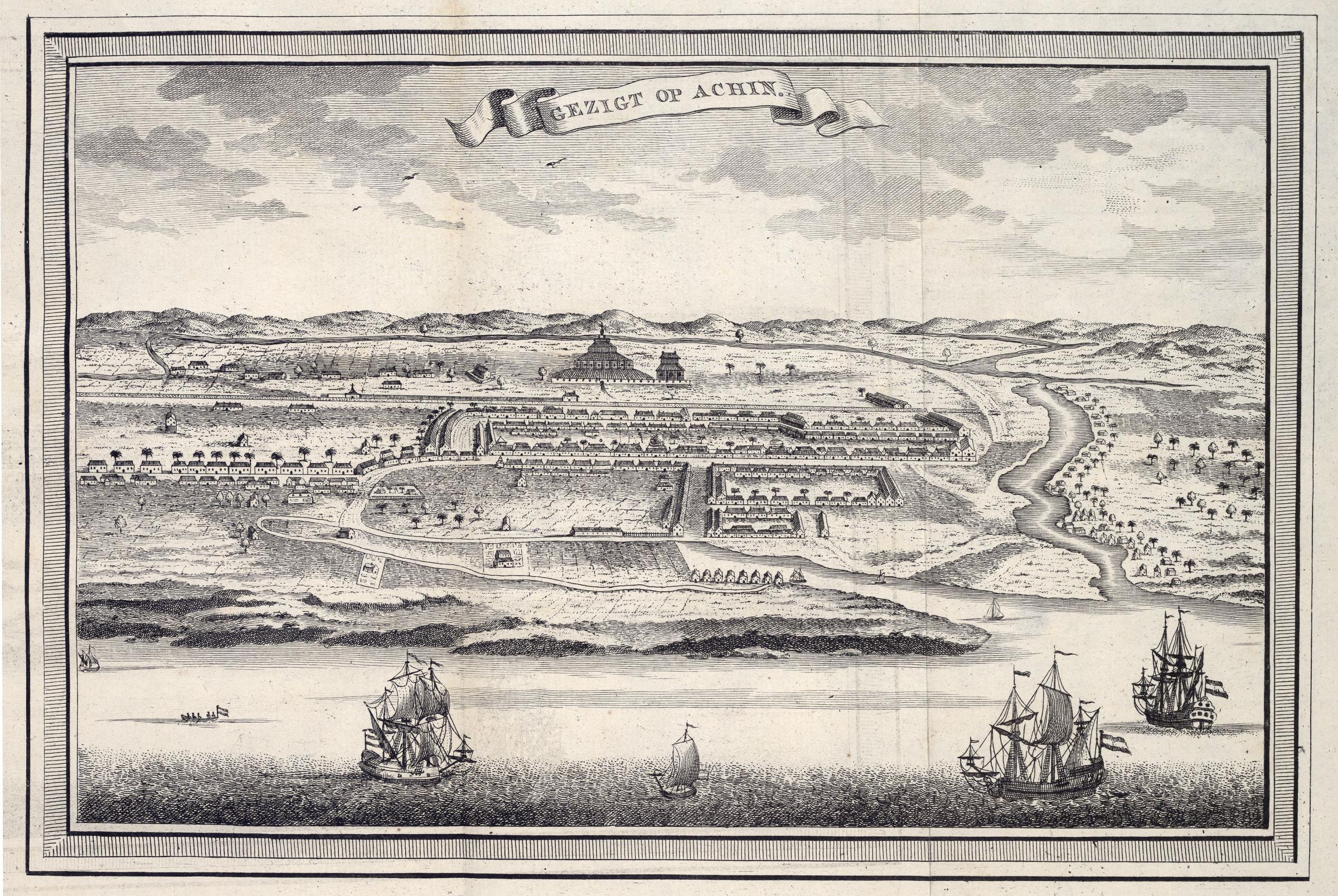
Banda Aceh
Banda Aceh ( Acehnese: ''Banda Acèh'', Jawoë: كوتا بند اچيه) is the capital and largest city in the province of Aceh, Indonesia. It is located on the island of Sumatra and has an elevation of . The city covers an area of and had a population of 223,446 people at the 2010 Census,Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011. rising to 252,899 at the 2020 Census. The official estimate as at mid 2021 was 255,029.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2022. Banda Aceh is located on the northwestern tip of Indonesia at the mouth of the Aceh River. Banda Aceh itself is a semi-enclave within Aceh Besar Regency, as Banda Aceh is surrounded by Aceh Besar to the south, east, and west, while it borders with the Strait of Malacca to the north. The city was originally established as Bandar Aceh Darussalam Kandang and served as a capital and hub for the Sultanate of Aceh upon its foundation in the late 15th century. Later its name was changed to ''Bandar Aceh Darussalam'', and then it bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Aceh Expedition
The Dutch dispatched a second expedition in Aceh in late 1873 during the Aceh War following the failed First Aceh Expedition of the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army to Aceh. At that time this expedition was one of the largest Dutch ever launched in the Indonesian archipelago, the expedition consisted of 8,500 troops, 4,500 servants and coolies, and a reserve of 1,500 troops was later added. Both the Dutch and Acehnese suffered from disease (mostly cholera) during this time. 1,400 colonial soldiers died between November 1873 and April 1874. After the Acehnese abandoned their capital, Banda Aceh, the Dutch moved into the capital in January 1874 thinking the Acehnese had surrendered and they had had won the war. They announced that the Aceh Sultanate was dissolved and that Aceh was annexed. Foreign powers thus refrained from interference, however, Acehnese resistance remained. Sultan Mahmud Syah and his followers withdrew to the hills and jungles territory of Aceh, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Indonesia
The history of Indonesia has been shaped by geographic position, its natural resources, a series of human migrations and contacts, wars of conquest, the spread of Islam from the island of Sumatra in the 7th century AD and the establishment of Islamic kingdoms, as well as by trade Bowls, Jars, Jugs and so on, economics and politics. Indonesia is an archipelagic country of 17,000 to 18,000 islands (8,844 named and 922 permanently inhabited) stretching along the equator in South East Asia. The country's strategic sea-lane position fostered inter-island and international trade; trade has since fundamentally shaped Indonesian history. The area of Indonesia is populated by peoples of various migrations, creating a diversity of cultures, ethnicities, and languages. The archipelago's landforms and climate significantly influenced agriculture and trade, and the formation of states. The boundaries of the state of Indonesia match the 20th-century borders of the Dutch East Indies. Fos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1873
Conflict may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films *Conflict (1921 film), ''Conflict'' (1921 film), an American silent film directed by Stuart Paton * Conflict (1936 film), ''Conflict'' (1936 film), an American boxing film starring John Wayne * Conflict (1937 film), ''Conflict'' (1937 film), a Swedish drama film directed by Per-Axel Branner * Conflict (1938 film), ''Conflict'' (1938 film), a French drama film directed by Léonide Moguy * Conflict (1945 film), ''Conflict'' (1945 film), an American suspense film starring Humphrey Bogart * Catholics (film), ''Catholics: A Fable'' (1973 film), or ''The Conflict'', a film starring Martin Sheen * Judith (1966 film), ''Judith'' (1966 film) or ''Conflict'', a film starring Sophia Loren * Samar (1999 film), ''Samar'' (1999 film) or ''Conflict'', a 1999 Indian film by Shyam Benegal Games * Conflict (series), ''Conflict'' (series), a 2002–2008 series of war games for the PS2, Xbox, and PC * Conflict (video game), ''Conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |