|
Fire Ball
The Fire Ball is an amusement ride manufactured by Larson International. It replaced a series of Larson rides manufactured prior to its unveiling, the first being the Super Loops and the second being the Ring of Fire. Several variations of each exist (e.g. Space Raiders, Mega Loop). The rides run the same but the older models have a caged train, whereas the Fire Ball has an open face-off train. Also, some owners of the older Ring of Fire rides have had the caged train replaced with the new Fire Ball train. Design The Fire Ball is high, long, and wide. It has a capacity of 20 people, with 10 two-person seats. The ride can be transported on a tandem axle trailer measuring high, long, and wide. There is a large steel boxed-track loop attached to a concrete base or portable trailer with supporting outriggers and steel cables. In this boxed track is a multiple-piece pivoted end-rim (inertia ring) with wheel dogs attached settled within this boxed track. On one section of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Diablo Roller Coaster
EL, El or el may refer to: Religion * El (deity), a Semitic word for "God" People * EL (rapper) (born 1983), stage name of Elorm Adablah, a Ghanaian rapper and sound engineer * El DeBarge, music artist * El Franco Lee (1949–2016), American politician * Ephrat Livni (born 1972), American street artist Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit * El, short for Eleven, a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things'' * El, family name of Kal-El (Superman) and his father Jor-El in ''Superman'' *E.L. Faldt, character in the road comedy film ''Road Trip'' Literature * ''Él'', 1926 autobiographical novel by Mercedes Pinto * ''Él'' (visual novel), a 2000 Japanese adult visual novel Music * Él Records, an independent record label from the UK founded by Mike Alway * ''Él'' (Lucero album), a 1982 album by Lucero * "Él", Spanish song by Rubén Blades from ''Caminando'' (album) * "Él" (Luc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tandem
Tandem, or in tandem, is an arrangement in which a team of machines, animals or people are lined up one behind another, all facing in the same direction. The original use of the term in English was in ''tandem harness'', which is used for two or more draft horses, or other draft animals, harnessed in a single line one behind another, as opposed to a pair, harnessed side by side, or a team of several pairs. The tandem harness allows additional animals to provide pulling power for a vehicle designed for a single animal. The English word ''tandem'' derives from the Latin adverb , meaning ''at length'' or ''finally''. It is a word play, using the Latin phrase (referring to time, not position) for English "at length, lengthwise". Tandem bicycles are named for their tandem seating, a more common arrangement than side-by-side "sociable" seating. ''Tandem'' can also be used more generally to refer to any group of persons or objects working together, not necessarily in line. Automob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
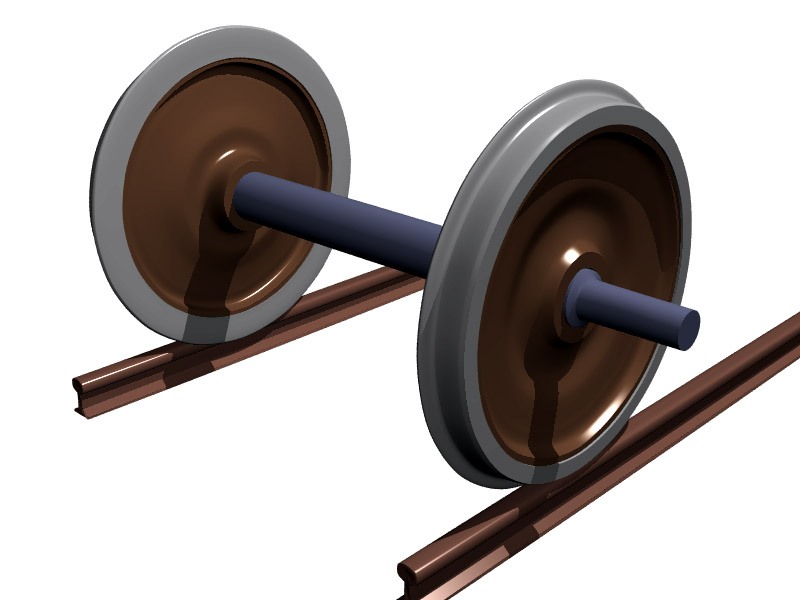
Axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle is supported. In the latter case, a bearing or bushing sits inside a central hole in the wheel to allow the wheel or gear to rotate around the axle. Sometimes, especially on bicycles, the latter type axle is referred to as a ''spindle''. Terminology On cars and trucks, several senses of the word ''axle'' occur in casual usage, referring to the shaft itself, its housing, or simply any transverse pair of wheels. Strictly speaking, a shaft which rotates with the wheel, being either bolted or splined in fixed relation to it, is called an ''axle'' or ''axle shaft''. However, in looser usage, an entire assembly including the surrounding axle housing (typically a casting) is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outrigger
An outrigger is a projecting structure on a boat, with specific meaning depending on types of vessel. Outriggers may also refer to legs on a wheeled vehicle that are folded out when it needs stabilization, for example on a crane that lifts heavy loads. Powered vessels and sailboats An outrigger describes any contraposing float rigging beyond the side (gunwale) of a boat to improve the vessel's stability. If a single outrigger is used it is usually but not always windward. The technology was originally developed by the Austronesian people. There are two main types of boats with outriggers: double outriggers (prevalent in maritime Southeast Asia) and single outriggers (prevalent in Madagascar, Melanesia, Micronesia and Polynesia). Multihull ships are also derived from outrigger boats. In an outrigger canoe and in sailboats such as the proa, an outrigger is a thin, long, solid, hull used to stabilise an inherently unstable main hull. The outrigger is positioned rigidly and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel Cable
Steel wire rope (right hand lang lay) Wire rope is several strands of metal wire twisted into a helix forming a composite ''rope'', in a pattern known as ''laid rope''. Larger diameter wire rope consists of multiple strands of such laid rope in a pattern known as ''cable laid''. In stricter senses, the term ''wire rope'' refers to a diameter larger than , with smaller gauges designated cable or cords. Initially wrought iron wires were used, but today steel is the main material used for wire ropes. Historically, wire rope evolved from wrought iron chains, which had a record of mechanical failure. While flaws in chain links or solid steel bars can lead to catastrophic failure, flaws in the wires making up a steel cable are less critical as the other wires easily take up the load. While friction between the individual wires and strands causes wear over the life of the rope, it also helps to compensate for minor failures in the short run. Wire ropes were developed starting with mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Train
In rail transport, a train (from Old French , from Latin , "to pull, to draw") is a series of connected vehicles that run along a railway track and Passenger train, transport people or Rail freight transport, freight. Trains are typically pulled or pushed by locomotives (often known simply as "engines"), though some are self-propelled, such as multiple units. Passengers and cargo are carried in railroad cars, also known as wagons. Trains are designed to a certain Track gauge, gauge, or distance between rails. Most trains operate on steel tracks with steel wheels, the low friction of which makes them more efficient than other forms of transport. Trains have their roots in wagonways, which used railway tracks and were Horsecar, powered by horses or Cable railway, pulled by cables. Following the invention of the steam locomotive in the United Kingdom in 1804, trains rapidly spread around the world, allowing freight and passengers to move over land faster and cheaper than ever pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If is an object's mass and is its velocity (also a vector quantity), then the object's momentum is : \mathbf = m \mathbf. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement of momentum is the kilogram metre per second (kg⋅m/s), which is equivalent to the newton-second. Newton's second law of motion states that the rate of change of a body's momentum is equal to the net force acting on it. Momentum depends on the frame of reference, but in any inertial frame it is a ''conserved'' quantity, meaning that if a closed system is not affected by external forces, its total linear momentum does not change. Momentum is also conserved in special relativity (with a modified formula) and, in a modified form, in electrodynamics, quantum mechanics, quan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquaplaning
Aquaplaning or hydroplaning by the tires of a road vehicle, aircraft or other wheeled vehicle occurs when a layer of water builds between the wheels of the vehicle and the road surface, leading to a loss of traction that prevents the vehicle from responding to control inputs. If it occurs to all wheels simultaneously, the vehicle becomes, in effect, an uncontrolled sled. Aquaplaning is a different phenomenon from when water on the surface of the roadway merely acts as a lubricant. Traction is diminished on wet pavement even when aquaplaning is not occurring. Causes Every vehicle function that changes direction or speed relies on friction between the tires and the road surface. The grooves of a rubber tire are designed to disperse water from beneath the tire, providing high friction even in wet conditions. Aquaplaning occurs when a tire encounters more water than it can dissipate. Water pressure in front of the wheel forces a wedge of water under the leading edge of the tire, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightning
Lightning is a naturally occurring electrostatic discharge during which two electric charge, electrically charged regions, both in the atmosphere or with one on the land, ground, temporarily neutralize themselves, causing the instantaneous release of an average of one Joule, gigajoule of energy. This discharge may produce a wide range of electromagnetic radiation, from heat created by the rapid movement of electrons, to brilliant flashes of visible light in the form of black-body radiation. Lightning causes thunder, a sound from the shock wave which develops as gases in the vicinity of the discharge experience a sudden increase in pressure. Lightning occurs commonly during thunderstorms as well as other types of energetic weather systems, but volcanic lightning can also occur during volcanic eruptions. The three main kinds of lightning are distinguished by where they occur: either inside a single Cumulonimbus cloud, thundercloud (intra-cloud), between two clouds (cloud-to-cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dead Man's Switch
A dead man's switch (see alternative names) is a switch that is designed to be activated or deactivated if the human operator becomes incapacitated, such as through death, loss of consciousness, or being bodily removed from control. Originally applied to switches on a vehicle or machine, it has since come to be used to describe other intangible uses, as in computer software. These switches are usually used as a form of fail-safe where they stop a machine with no operator from a potentially dangerous action or incapacitate a device as a result of accident, malfunction, or misuse. They are common in such applications in locomotives, aircraft refuelling, freight elevators, lawn mowers, tractors, personal watercraft, outboard motors, chainsaws, snowblowers, tread machines, snowmobiles, amusement rides, and many medical imaging devices. On some machines, these switches merely bring the machines back to a safe state, such as reducing the throttle to idle or applying brakes while leav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827). Definition One volt is defined as the electric potential between two points of a conducting wire when an electric current of one ampere dissipates one watt of power between those points. Equivalently, it is the potential difference between two points that will impart one joule of energy per coulomb of charge that passes through it. It can be expressed in terms of SI base units ( m, kg, second, s, and ampere, A) as : \text = \frac = \frac = \frac. It can also be expressed as amperes times ohms (current times resistance, Ohm's law), webers per second (magnetic flux per time), watts per ampere (power per current), or joules per coulomb (energy per charge), which is also equivalent to electronvolts per elementary charge: : \text = \tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampere
The ampere (, ; symbol: A), often shortened to amp,SI supports only the use of symbols and deprecates the use of abbreviations for units. is the unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). One ampere is equal to electrons worth of charge moving past a point in a second. It is named after French mathematician and physicist André-Marie Ampère (1775–1836), considered the father of electromagnetism along with Danish physicist Hans Christian Ørsted. As of the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, the ampere is defined by fixing the elementary charge to be exactly C ( coulomb), which means an ampere is an electrical current equivalent to elementary charges moving every seconds or elementary charges moving in a second. Prior to the redefinition the ampere was defined as the current that would need to be passed through 2 parallel wires 1 metre apart to produce a magnetic force of newtons per metre. The earlier CGS system had two definitio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


