|
Fiona Watt
Fiona Watt, (born 28 March 1956) is a British scientist who is internationally known for her contributions to the field of stem cell biology. In the 1980s, when the field was in its infancy, she highlighted key characteristics of stem cells and their environment that laid the foundation for much present day research. She is currently director of the Centre for Stem Cells & Regenerative Medicine at King's College London, and Executive Chair of the Medical Research Council (United Kingdom) (MRC), the first woman to lead the MRC since its foundation in 1913. On 13 July 2021 she was appointed as the new Director of the European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO). Early life and education Watt was born on 28 March 1956 in Edinburgh, Scotland. Her father was a dental surgeon who combined his clinical work with an active research programme. Her family were members of the Church of Scotland. Her younger sister, Wendy, died in 1982. Fiona Watt knew she wanted to be a scientist fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cell Biology
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50–150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. '' In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm – at the gastrulation stage. However, when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA methods or by artificially synthesising the DNA. A construct is usually created and used to insert this DNA into the host organism. The first recombinant DNA molecule was made by Paul Berg in 1972 by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with the lambda virus. As well as inserting genes, the process can be used to remove, or " knock out", genes. The new DNA can be inserted randomly, or targeted to a specific part of the genome. An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be genetically modified (G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELife
''eLife'' is a not-for-profit, peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journal for the biomedical and life sciences. It was established at the end of 2012 by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Max Planck Society, and Wellcome Trust, following a workshop held in 2010 at the Janelia Farm Research Campus. Together, these organizations provided the initial funding to support the business and publishing operations. In 2016, the organizations committed US$26 million to continue publication of the journal. The current editor-in-chief is Michael Eisen (University of California, Berkeley). Editorial decisions are made largely by senior editors and members of the board of reviewing editors, all of whom are active scientists working in fields ranging from human genetics and neuroscience to biophysics, epidemiology, and ecology. Business model ''eLife'' is a non-profit organisation, but for long-term sustainability of the service, the journal asks for an article processing charge of US$3,0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Cell Science
The ''Journal of Cell Science'' (formerly the ''Quarterly Journal of Microscopical Science'') is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in the field of cell biology. The journal is published by The Company of Biologists. The journal is partnered with Publons, is part of the Review Commons initiative and has two-way integration with bioRxiv. ''Journal of Cell Science'' is a hybrid journal and publishes 24 issues a year. Content over 6 months old is free to read. History Foundation and early years The journal was established in 1853 as the ''Quarterly Journal of Microscopical Science'' (''Q. J. Microsc. Sci.'', ). The founding editors were Edwin Lankester and George Busk.''Quarterly Journal of Microscopical Science'' 1(1), front matter (accessed 18 April 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Society For Stem Cell Research
The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) is an independent 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization based in Skokie, Illinois, United States. The organization's mission is to promote excellence in stem cell science and applications to human health. History The International Society for Stem Cell Research was formed in 2002 (incorporated on March 30, 2001) to foster the exchange of information on stem cell research. Leonard Zon, professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, served as the organization's first president. In June 2003, the International Society for Stem Cell Research held its first convention. More than 600 scientists attended, many of whom expressed frustration over restrictions that President George W. Bush's administration had placed on the field of stem-cell research, slowing the pace of research. Scientists who were leaders in their fields were prohibited from using funding from the National Institutes of Health to conduct certain experiments tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiona Watt (16032380933)
Fiona Watt, (born 28 March 1956) is a British scientist who is internationally known for her contributions to the field of stem cell biology. In the 1980s, when the field was in its infancy, she highlighted key characteristics of stem cells and their environment that laid the foundation for much present day research. She is currently director of the Centre for Stem Cells & Regenerative Medicine at King's College London, and Executive Chair of the Medical Research Council (United Kingdom) (MRC), the first woman to lead the MRC since its foundation in 1913. On 13 July 2021 she was appointed as the new Director of the European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO). Early life and education Watt was born on 28 March 1956 in Edinburgh, Scotland. Her father was a dental surgeon who combined his clinical work with an active research programme. Her family were members of the Church of Scotland. Her younger sister, Wendy, died in 1982. Fiona Watt knew she wanted to be a scientist fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of DNA repair#DNA damage, damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (DNA repair#Translesion synthesis, translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from Insertion (genetics), insertion or Deletion (genetics), deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Cell Sequencing
Single-cell sequencing examines the sequence information from individual cells with optimized next-generation sequencing technologies, providing a higher resolution of cellular differences and a better understanding of the function of an individual cell in the context of its microenvironment. For example, in cancer, sequencing the DNA of individual cells can give information about mutations carried by small populations of cells. In development, sequencing the RNAs expressed by individual cells can give insight into the existence and behavior of different cell types. In microbial systems, a population of the same species can appear genetically clonal. Still, single-cell sequencing of RNA or epigenetic modifications can reveal cell-to-cell variability that may help populations rapidly adapt to survive in changing environments. Background A typical human cell consists of about 2 x 3.3 billion base pairs of DNA and 600 million mRNA bases. Usually, a mix of millions of cells is used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Fate Determination
Within the field of developmental biology, one goal is to understand how a particular cell develops into a final cell type, known as fate determination. Within an embryo, several processes play out at the cellular and tissue level to create an organism. These processes include cell proliferation, differentiation, cellular movement and programmed cell death. Each cell in an embryo receives molecular signals from neighboring cells in the form of proteins, RNAs and even surface interactions. Almost all animals undergo a similar sequence of events during very early development, a conserved process known as embryogenesis. During embryogenesis, cells exist in three germ layers, and undergo gastrulation. While embryogenesis has been studied for more than a century, it was only recently (the past 25 years or so) that scientists discovered that a basic set of the same proteins and mRNAs are involved in embryogenesis. Evolutionary conservation is one of the reasons that model systems such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
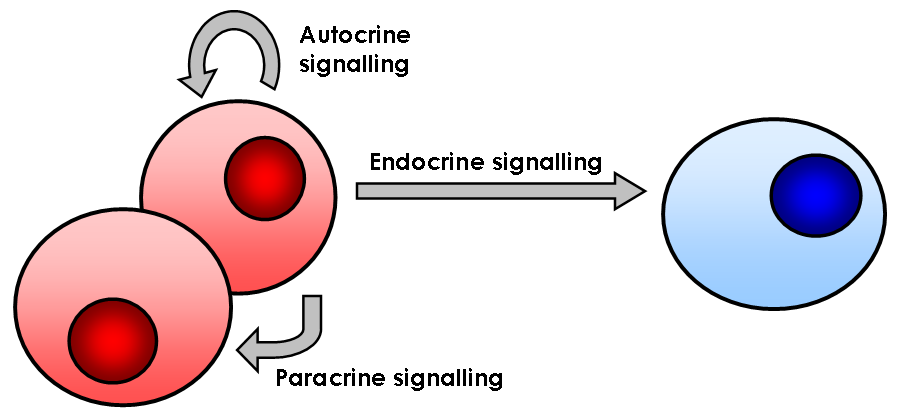
Cell Signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals (e.g., small molecules, peptides, or gas). Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage. Receptors play a key role in cell signaling as they are able to detect chemical signals or physical stimuli. Receptors are generally proteins located on the cell surface or within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are the high- affinity cell surface receptors for many polypeptide growth factors, cytokines, and hormones. Of the 90 unique tyrosine kinase genes identified in the human genome, 58 encode receptor tyrosine kinase proteins. Receptor tyrosine kinases have been shown not only to be key regulators of normal cellular processes but also to have a critical role in the development and progression of many types of cancer. Mutations in receptor tyrosine kinases lead to activation of a series of signalling cascades which have numerous effects on protein expression. Receptor tyrosine kinases are part of the larger family of protein tyrosine kinases, encompassing the receptor tyrosine kinase proteins which contain a transmembrane domain, as well as the non-receptor tyrosine kinases which do not possess transmembrane domains. History The first RTKs to be discovered were EGF and NGF in the 1960s, but the classification of receptor tyrosine kinases was no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)