|
Finnish Aviation Museum
The Finnish Aviation Museum ( fi, Suomen ilmailumuseo, sv, Finlands flygmuseum) is a museum specialising in aircraft, located near Helsinki Airport in Veromies, Vantaa, Finland. History The Aviation Museum Society ( fi, Ilmailumuseoyhdistys ry) was founded on 4 December 1969. Opened in 1972, the museum was initially located in the basement of the Helsinki Airport terminal but received its own facilities in 1981. The museum has constantly expanded and today has an office wing, research rooms, aviation library, archive, and an auditorium for 200 people. Currently the museum is owned by the Finnish Aviation Museum Foundation ( fi, Suomen Ilmailumuseosäätiö), founded in 1996. Exhibition The museum displays some 9,600 items, and the library has over 16,000 books and 160,000 aviation-related magazines. Furthermore, the museum has a large collection of flight instruction and service books. There are also some 78,000 photographs, negatives, and slides. The archive spans some 1,800 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviapolis
Aviapolis is a business, retail, entertainment, and housing marketing brand area in central Vantaa, Finland, covering roughly , including Finland's main airline hub and airport, Helsinki Airport. The term is officially used as the name of one of the major regions of Vantaa, encompassing the districts of Lentokenttä, Pakkala, Tammisto, Veromies, Viinikkala, and Ylästö. It is Vantaa's only major region not named after a city district. Business Currently Aviapolis is referred to as the most popular business site in Greater Helsinki, surpassing even the Helsinki City center. Businesses areas already located at Aviapolis include Technopolis Technology Park, Airport Plaza Business Park Oy, and the WTC Helsinki Airport. Transport Having Finland's largest airport, Helsinki Airport, the international connections of Aviapolis are broad, boasting the shortest flying distances from EU to many Asian destinations. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas DC-3
The Douglas DC-3 is a propeller-driven airliner manufactured by Douglas Aircraft Company, which had a lasting effect on the airline industry in the 1930s to 1940s and World War II. It was developed as a larger, improved 14-bed sleeper version of the Douglas DC-2. It is a low-wing metal monoplane with conventional landing gear, powered by two radial piston engines of . (Although most DC-3s flying today use Pratt & Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp engines, many DC-3s built for civil service originally had the Wright R-1820 Cyclone.) The DC-3 has a cruising speed of , a capacity of 21 to 32 passengers or 6,000 lbs (2,700 kg) of cargo, and a range of , and can operate from short runways. The DC-3 had many exceptional qualities compared to previous aircraft. It was fast, had a good range, was more reliable, and carried passengers in greater comfort. Before the war, it pioneered many air travel routes. It was able to cross the continental United States from New York to Los An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hansa-Brandenburg W
The Hansa-Brandenburg W was a reconnaissance floatplane produced in Germany in 1914 to equip the Imperial German Navy. Similar in general layout to the Hansa-Brandenburg B.I landplane, the W was a conventional three-bay biplane with unstaggered wings of equal span. The pilot and observer sat in tandem, open cockpits, and the undercarriage consisted of twin pontoons. The NW and GNW of 1915 were a revised versions powered by a more powerful engine. Variants * W - initial production version with Benz Bz.II engine (27 built) * NW - revised version with Mercedes D.III engine * GNW - revised version with Mercedes D.III engine Operators ; *Kaiserliche Marine ; *Ottoman Air Force The Aviation Squadrons of the Ottoman Empire were military aviation units of the Ottoman Army and Navy.Edward J. Erickson, ''Ordered To Die: A History of the Ottoman Army in the First World War'', "Appendix D The Ottoman Aviation Inspectorate an ... Specifications (NW) References * * {{Han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinonen HK-1
The Heinonen HK-1 Keltiäinen is a Finnish single-seat, single-engined sport aircraft of the 1950s. Only a single example was built, which was used by its designer to set a class distance record in 1957 that stood for 18 years before being beaten. Design and development Juhani Heinonen, an aeronautical engineer who had previously worked for the Valmet aircraft factory at Tampere, and then for Finnair, designed a single-seat, single engined aerobatic sport aircraft, the Heinonen HK-1. It was a low winged monoplane of all-wooden construction, powered by a Walter Mikron air-cooled inline engine rated at driving a two-bladed propeller. Split flaps were fitted to the wings, while the aircraft had a fixed tailwheel undercarriage, with a steerable tailwheel but no brakes. The pilot sat under a sliding perspex canopy.Best-Devereux ''Flight'' 17 January 1958, p. 85. A prototype was built at the glider school at Jämi, first flying in August 1954. Operational history The HK-1 was displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PIK-7
__NOTOC__ The ''Harakka'' ("European magpie") was a primary glider produced for pilot training in Finland in the 1940s. Its design was typical of this class of aircraft, a "keel" with a pilot's seat suspended beneath a high, strut-braced monoplane wing, and carrying a conventional empennage at the end of an open framework."Harakka I (H-12)" First flown in February 1945, the type was built from plans by Finnish gliding clubs and soon replaced earlier primary gliders such as the Grunau 9,"Grunau 9 ja PIK-7 Harakka, kerhon 1940-50-lukujen alkeiskoulukoneet" becoming a standard piece of equipment in the clubs.Hardy 1982, p.74 In 1946, Raimo Häkkinen and Juhani Heinonen from Polyteknikkojen Ilmailukerho redesigned the Harakka to strengthen it."PIK-sarjan lentokoneet" This improved version became known as the Harakka II or PIK-7."PIK-sarjan lentokoneet"Taylor 1989, p.726"Harakka II (H-57)" In 1948, a single example of a more radically redesigned version designated Harakka III flew." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grunau Baby
The Schneider Grunau Baby was a single-seat sailplane first built in Germany in 1931, with some 6,000 examples constructed in some 20 countries. It was relatively easy to build from plans, it flew well, and the aircraft was strong enough to handle mild aerobatics and the occasional hard landing. When the Baby first appeared, it was accepted wisdom that the pilot should feel as much unimpeded airflow as possible, to better sense rising and falling currents of air and temperature changes etc. It was designed by Edmund Schneider with the assistance of Wolf Hirth and Hugo Kromer as a smaller version of Schneider's ESG 31 of the previous year, incorporating an elliptical wing design based on work done by Akaflieg Darmstadt. It was named after Grunau, the town where Schneider's factory was located, now Jeżów Sudecki in Poland. The first 14 inner ribs were of the Göttingen 535 shape with the outer ribs gradually changing up to the last 22nd rib, having a bi-convex and symmetric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schneider Grunau 9
The ESG Grunau 9, later known as the ESG 29 and post-1933 as the DFS 108-10, was one of the first primary gliders, built in Germany from the late 1920s. It was widely sold. Design and development The Grunau 9 was a German single seat trainer glider, one of the first of a group that later became known as primary gliders. It was developed by Edmund Schneider from Alexander Lippisch's Djävlar Anamma (german: Hols der Teufel, en, to the Devil with it) via the Espenlaub primary. The Grunau 9 was produced in numbers and was sold widely. The core of the flat frame fuselage was formed with a horizontal beam about long, to which two other converging struts were attached, making overall a vertical A-frame. The downward sloping extremities of these beams carried a slightly deeper horizontal box structure below the cross beam, with the open pilot's seat and controls upon it. On some later aircraft there was an extra vertical member for the lower cross beam to the wing root to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
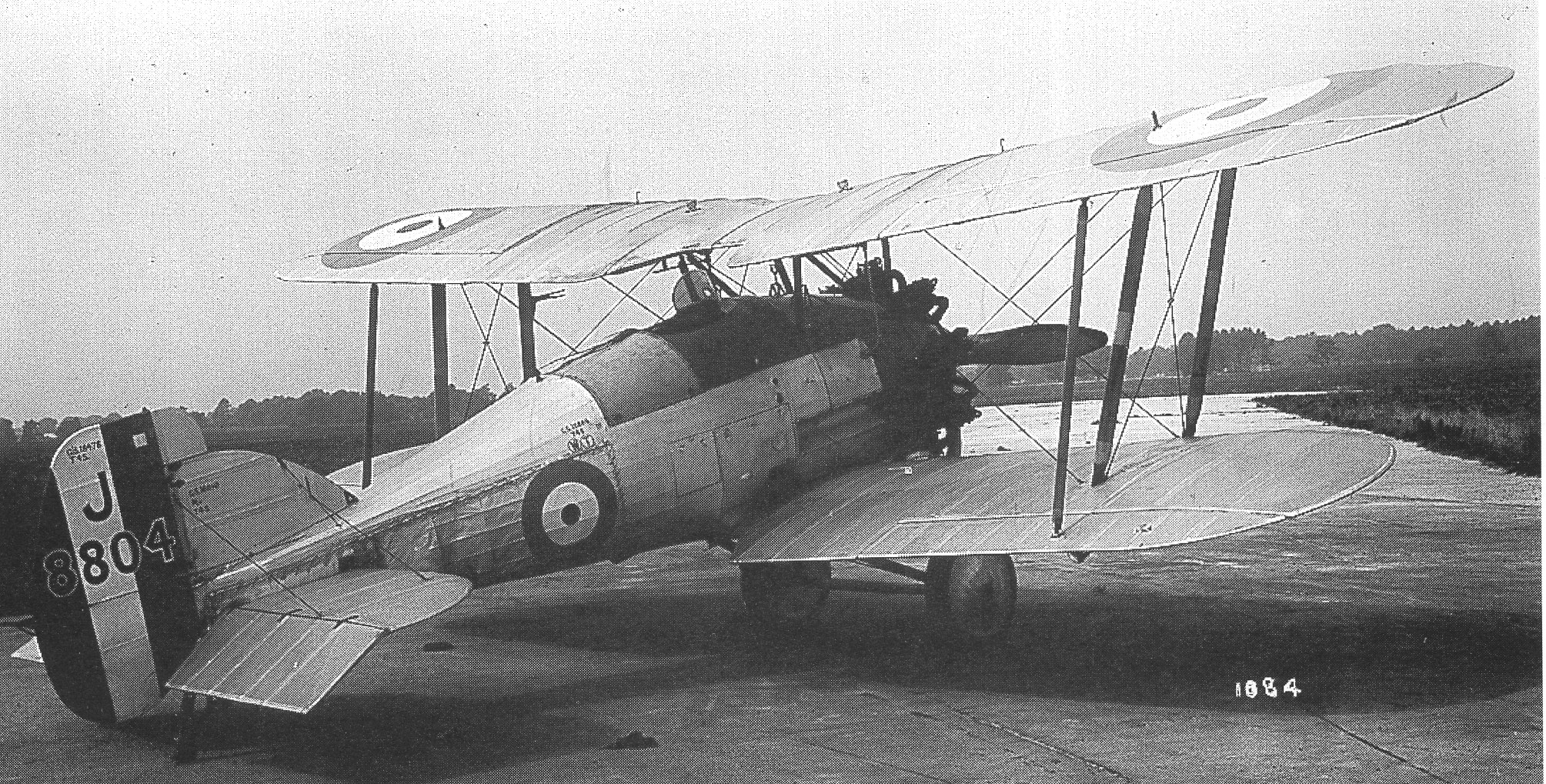
Gloster Gamecock
The Gloster Gamecock was a biplane fighter designed and produced by the British aircraft manufacturer Gloster. The Gamecock was a development of the earlier Grebe Mk III, an early interwar fighter procured by the Royal Air Force (RAF). Work on the type commenced in 1924 as a response to Air Ministry Specification 37/23. The principal difference between the two aircraft was the adoption of the Bristol Jupiter radial engine for the Gamecock. in the place of the somewhat unreliable Armstrong Siddeley Jaguar. Various other structural improvements were also made to the fuselage, the armament was also revised to include internally-mounted machine guns. On 22 February 1925, the prototype Gamecock performed its maiden flight. Evaluation flights at RAF Martlesham Heath resulted in considerable praise for the aircraft; few changes were made as a result. During September 1925, the Air Ministry placed an initial order for 30 production aircraft to fulfil Specification 18/25. Furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fouga Magister
Fouga (also known as Air Fouga) was a French manufacturing company established by Gaston Fouga at Béziers during 1920. Originally specialising in the repair of railway rolling stock, the firm eventually became most noted for the aircraft it produced from its woodworking facilities at Aire-sur-l'Adour. The most successful product to be created by Fouga was the CM.170 Magister, a postwar jet-powered military trainer aircraft derived from the firm's experiences with sailplanes. Many of its features, such as its slender tapering wings, reflecting the company's sailplane heritage. During May 1958, Fouga was acquired by rival French aircraft manufacturer Potez; the company's former facilities at Toulouse continue to produce aircraft as a part of the multinational Airbus Group. History During 1920, the company was established by Gaston Fouga; from the onset, it was based at the town of Béziers in the Occitanie region of Southern France. Initially, Fouga's operated centred arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folland Gnat Mk
{{surname ...
Folland is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Alison Folland (born 1978), American actress and filmmaker * Gerald Folland (born 1947), American mathematician * Henry Folland (1889–1954), British aviation engineer and aircraft designer * Leah Norah Folland (1874–1957), British educationalist, philanthropist and politician * Michael Fleming Folland (1949–1969), United States Army soldier * Neil Folland (born 1960), British cricketer * Nicholas Folland (born 1967), Australian artist and arts educator * Nick Folland (born 1963), British cricketer * Rob Folland (born 1979), British footballer See also *Folland Aircraft Folland Aircraft was a British aircraft manufacturing company which was active between 1937 and 1963. History British Marine Aircraft Limited was formed in February 1936 to produce Sikorsky S-42-A flying boats under licence in the UK. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focke-Wulf Fw 44 Stieglitz
The Focke-Wulf Fw 44 ''Stieglitz'' ("Goldfinch") is a 1930s German two-seat biplane. An early design by Kurt Tank, it was produced by the Focke-Wulf company as a pilot training and sports flying aircraft. It was also eventually built under license in several other countries. Design and development The Fw 44 was designed as a biplane with conventional layout and straight, untapered wings. Its two open cockpits were arranged in tandem, and both cockpits were equipped with flight controls and instruments. The Fw 44 had fixed tailwheel landing gear. It employed ailerons on both upper and lower wings. It did not use flaps. It was flown with a Siemens-Halske Sh 14 radial engine. The first prototype flew in 1932. After many tests and modifications to increase the plane's durability and aerodynamics, the final Fw 44 proved to have excellent airworthiness. A second version of the Fw 44 was the Fw 44B, which had an Argus As 8 four-cylinder inverted inline air-cooled engine of 90 kW ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fieseler Fi 156
The Fieseler Fi 156 ''Storch'' (, " stork") was a German liaison aircraft built by Fieseler before and during World War II. Production continued in other countries into the 1950s for the private market. It was notable for its excellent short field (STOL) performance and low stalling speed of 50 km/h (31 mph). French-built later variants often appear at air shows. Compared to most other liaison aircraft of the period, the ''Storch'' was quite large and heavy, with its wingspan exceeding 14 meters (nearly 47 feet) and its weight slightly over 1,300 kg (2,900 pounds) when fully loaded. It was significantly heavier, slower, and less agile than Allied liaison aircraft such as the American Piper L-4 or Stinson L-5, or the British Auster. Design and development Conception and production In 1935, the RLM ('' Reichsluftfahrtministerium'', Reich Aviation Ministry) invited several aviation companies to submit design proposals that would compete for the production contract for a new ''L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_5.jpg)