|
Ficus Ruminalis
The ''Ficus Ruminalis'' was a wild fig tree that had religious and mythological significance in ancient Rome. It stood near the small cave known as the Lupercal at the foot of the Palatine Hill and was the spot where according to tradition the floating makeshift cradle of Romulus and Remus landed on the banks of the Tiber. There they were nurtured by the she-wolf and discovered by Faustulus. The tree was sacred to Rumina, one of the birth and childhood deities, who protected breastfeeding in humans and animals. St. Augustine mentions a Jupiter Ruminus. Name The wild fig tree was thought to be the male, wild counterpart of the cultivated fig, which was female. In some Roman sources, the wild fig is ''caprificus'', literally "goat fig". The fruit of the fig tree is pendulous, and the tree exudes a milky sap if cut. ''Rumina'' and ''Ruminalis'' ("of Rumina") were connected by some Romans to ''rumis'' or ''ruma'', "teat, breast," but some modern linguists think it is more like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altar Mars Venus Massimo
An altar is a Table (furniture), table or platform for the presentation of religion, religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, Church (building), churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paganism, Christianity, Buddhism, Hinduism, Judaism, modern paganism, and in certain Islam, Islamic communities around Caucasus, Caucasia and Anatolia, Asia Minor. Many historical-medieval faiths also made use of them, including the Religion in ancient Rome, Roman, Religion in ancient Greece, Greek, and Norse paganism, Norse religions. Etymology The modern English language, English word ''wikt:altar#English, altar'' was derived from Middle English ''wikt:alter#Latin, altar'', from Old English ''wikt:alter, alter'', taken from Latin ''wikt:altare#Latin, altare'' ("altar"), probably related to ''wikt:adolere#Etymology 2, adolere'' ("burn"); thus "burning place", influenced by ''wikt:altus#Latin, altus'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextus Pompeius Festus
Sextus Pompeius Festus, usually known simply as Festus, was a Roman grammarian who probably flourished in the later 2nd century AD, perhaps at Narbo (Narbonne) in Gaul. Work He made a 20-volume epitome of Verrius Flaccus's voluminous and encyclopedic treatise ''De verborum significatione''. Flaccus had been a celebrated grammarian who flourished in the reign of Augustus. Festus gives the etymology as well as the meaning of many words, and his work throws considerable light on the language, mythology and antiquities of ancient Rome. He made a few alterations, and inserted some critical remarks of his own. He also omitted such ancient Latin words as had long been obsolete; these he apparently discussed in a separate work now lost, entitled ''Priscorum verborum cum exemplis''. Even incomplete, Festus' lexicon reflects at second hand the enormous intellectual effort that had been made in the Augustan Age to put together information on the traditions of the Roman world, which was alrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustan Literature (ancient Rome)
Augustan literature refers to the pieces of Latin literature that were written during the reign of Caesar Augustus (27 BC–AD 14), the first Roman emperor. In literary histories of the first part of the 20th century and earlier, Augustan literature was regarded along with that of the Late Republic as constituting the Golden Age of Latin literature, a period of stylistic classicism.Fergus Millar, "Ovid and the Domus Augusta: Rome Seen from Tomoi," ''Journal of Roman Studies'' 83 (1993), p. 6. Most of the literature periodized as "Augustan" was in fact written by men—Vergil, Horace, Propertius, Livy—whose careers were established during the triumviral years, before Octavian assumed the title ''Augustus''. Strictly speaking, Ovid is the poet whose work is most thoroughly embedded in the Augustan regime. Impact and style Augustan literature produced the most widely read, influential, and enduring of Rome's poets. The Republican poets Catullus and Lucretius are their immed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dionysius Of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus ( grc, Διονύσιος Ἀλεξάνδρου Ἁλικαρνασσεύς, ; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary style was ''atticistic'' – imitating Classical Attic Greek in its prime. Dionysius' opinion of the necessity of a promotion of paideia within education, from true knowledge of classical sources, endured for centuries in a form integral to the identity of the Greek elite. Life He was a Halicarnassian. At some time after the end of the civil wars he moved to Rome, and spent twenty-two years studying Latin and literature and preparing materials for his history. During this period, he gave lessons in rhetoric, and enjoyed the society of many distinguished men. The date of his death is unknown. In the 19th century, it was commonly supposed that he was the ancestor of Aelius Dionysius of Halicarnassus. Works His major work, entitled ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curule Aedile
''Aedile'' ( ; la, aedīlis , from , "temple edifice") was an elected office of the Roman Republic. Based in Rome, the aediles were responsible for maintenance of public buildings () and regulation of public festivals. They also had powers to enforce public order and duties to ensure the city of Rome was well supplied and its civil infrastructure well maintained, akin to modern local government. There were two pairs of aediles: the first were the "plebeian aediles" (Latin ''aediles plebis'') and possession of this office was limited to plebeians; the other two were "curule aediles" (Latin ''aediles curules''), open to both plebeians and patricians, in alternating years. An ''aedilis curulis'' was classified as a '' magister curulis''. The office of the aedilis was generally held by young men intending to follow the ''cursus honorum'' to high political office, traditionally after their quaestorship but before their praetorship. It was not a compulsory part of the cursus, and hence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
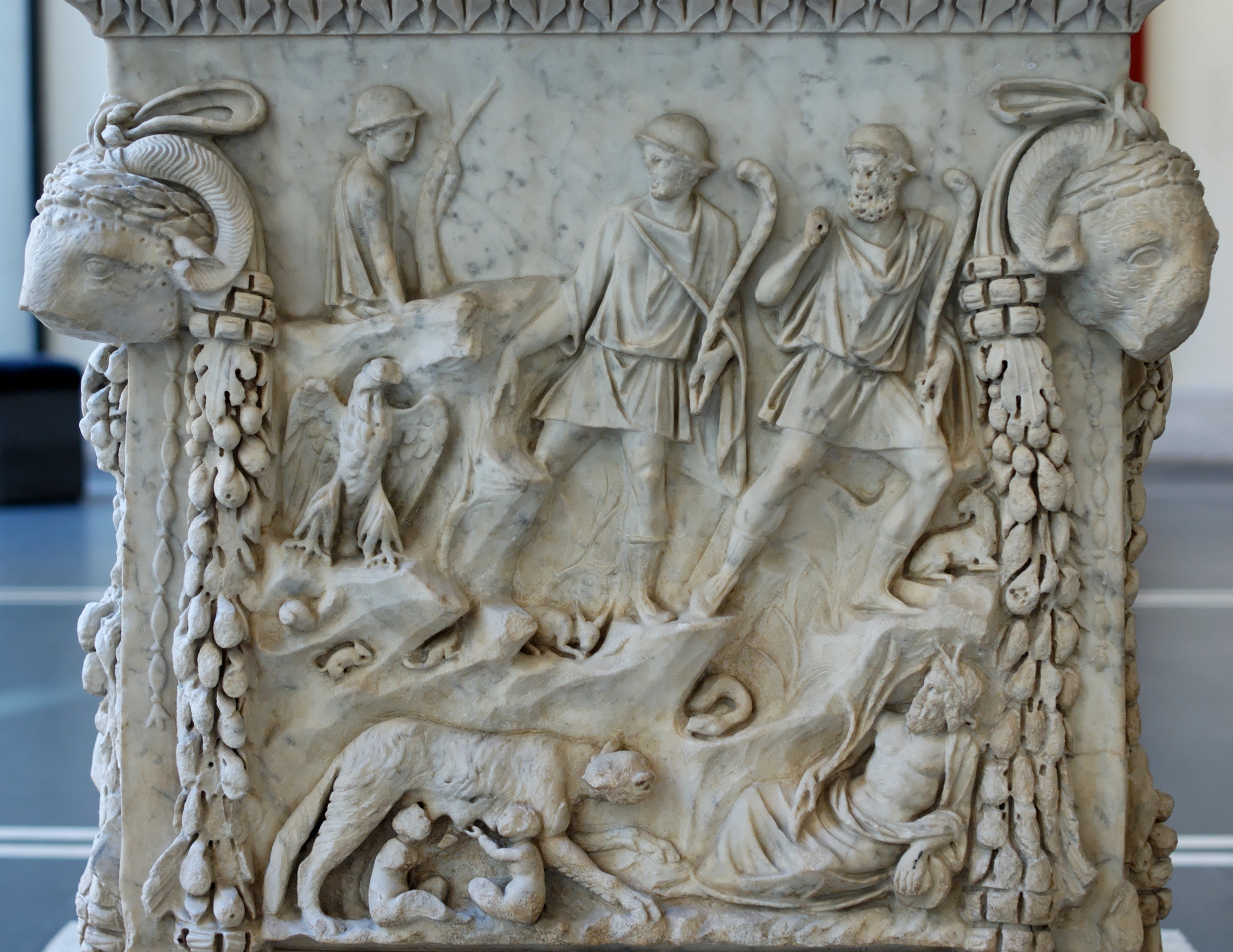
Founding Of Rome
The tale of the founding of Rome is recounted in traditional stories handed down by the ancient Romans themselves as the earliest history of their city in terms of legend and myth. The most familiar of these myths, and perhaps the most famous of all Roman myths, is the story of Romulus and Remus, twins who were suckled by a she-wolf as infants. Another account, set earlier in time, claims that the Roman people are descended from Trojan War hero Aeneas, who escaped to Italy after the war, and whose son, Iulus, was the ancestor of the family of Julius Caesar. The archaeological evidence of human occupation of the area of modern-day Rome dates from about 14,000 years ago. Founding myths and sources Aeneas The national epic of mythical Rome, the ''Aeneid'' of Virgil, tells the story of how Trojan prince Aeneas came to Italy. The ''Aeneid'' was written under Augustus, who claimed ancestry through Julius Caesar to Aeneas and his mother Venus. According to the ''Aeneid'', the surv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acca Larentia
Acca Larentia or Acca Larentina was a mythical woman, later goddess of fertility, in Roman mythology whose festival, the Larentalia, was celebrated on December 23. Myths Foster mother In one mythological tradition (that of Licinius Macer, et al.), she was the wife of the shepherd Faustulus. And after Romulus and Remus were thrown into the Tiber river, Faustulus brought them back to his home, where Acca Larentia would raise the children. She had twelve sons, and on the death of one of them Romulus took his place. and with the remaining eleven founded the college of the Arval brothers (Fratres Arvales). She is therefore identified with the Dea Dia of that collegium. The flamen Quirinalis acted in the role of Romulus (deified as Quirinus) to perform funerary rites for his foster mother. Benefactor of Rome Another tradition holds that Larentia was a beautiful girl of notorious reputation, roughly the same age as Romulus and Remus, during the reign of Ancus Marci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
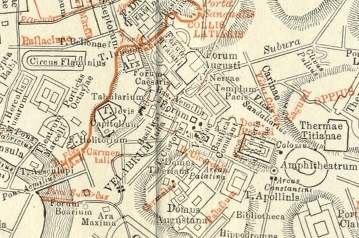
Velabrum
The Velabrum () is the low valley in the city of Rome that connects the Forum with the Forum Boarium, and the Capitoline Hill with the western slope of the Palatine Hill. The name Velabrum may translate to "place of mud." It was believed that before the construction of the Cloaca Maxima, which probably follows the course of an ancient stream, the area was a swamp, though this claim has been disproven by core samples taken from Velabrum in 1994. Ancient authorities state that in this marshy area the roots of a fig tree ''(Ficus Ruminalis)'' caught and stopped the basket carrying Romulus and Remus as it floated along on the Tiber current. The place therefore has a high symbolic significance. It was also used as a marketplace and a center of commerce. Even after the Cloaca was built, the area was still prone to flooding from the Tiber, until the ground level was raised after the Neronian fire. It is the site of the Arch of Janus, the Arcus Argentariorum and the church San Giorgio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Bernard Cook
Arthur Bernard Cook (22 October 1868 in Hampstead – 26 April 1952 in Cambridge) was a British archeologist and classical scholar, best known for his three-part work, ''Zeus: A Study in Ancient Religion''. Early life and education Arthur Bernard Cook was born in Hampstead, London on 22 October 1868. He was the son of William Henry Cook MD (1825-1882) and Harriet Bickersteth (1830-1918) His mother's family were leading ecclesiastical scholars of the time, including Edward Bickersteth (Dean of Lichfield) (1814-1892), Edward Bickersteth (bishop of Exeter) (1825-1906) and Edward Bickersteth (bishop of South Tokyo). (1850-1897) Cook was educated at St. Paul's School, where he won several academic prizes. He received an MA from the Trinity College, Cambridge. The Chancellor's Gold Medal is a distinguished annual award at Cambridge University for poetry, paralleling Oxford University's Newdigate prize. Cook's poem ''Windsor Castle'' won the Chancellor's Gold Medal for poetry at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Civitate Dei
''On the City of God Against the Pagans'' ( la, De civitate Dei contra paganos), often called ''The City of God'', is a book of Christian philosophy written in Latin by Augustine of Hippo in the early 5th century AD. The book was in response to allegations that Christianity brought about the decline of Rome and is considered one of Augustine's most important works, standing alongside '' The Confessions'', '' The Enchiridion'', '' On Christian Doctrine'', and ''On the Trinity''. As a work of one of the most influential Church Fathers, ''The City of God'' is a cornerstone of Western thought, expounding on many questions of theology, such as the suffering of the righteous, the existence of evil, the conflict between free will and divine omniscience, and the doctrine of original sin. Background The sack of Rome by the Visigoths in 410 left Romans in a deep state of shock, and many Romans saw it as punishment for abandoning traditional Roman religion in favor of Christianity. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
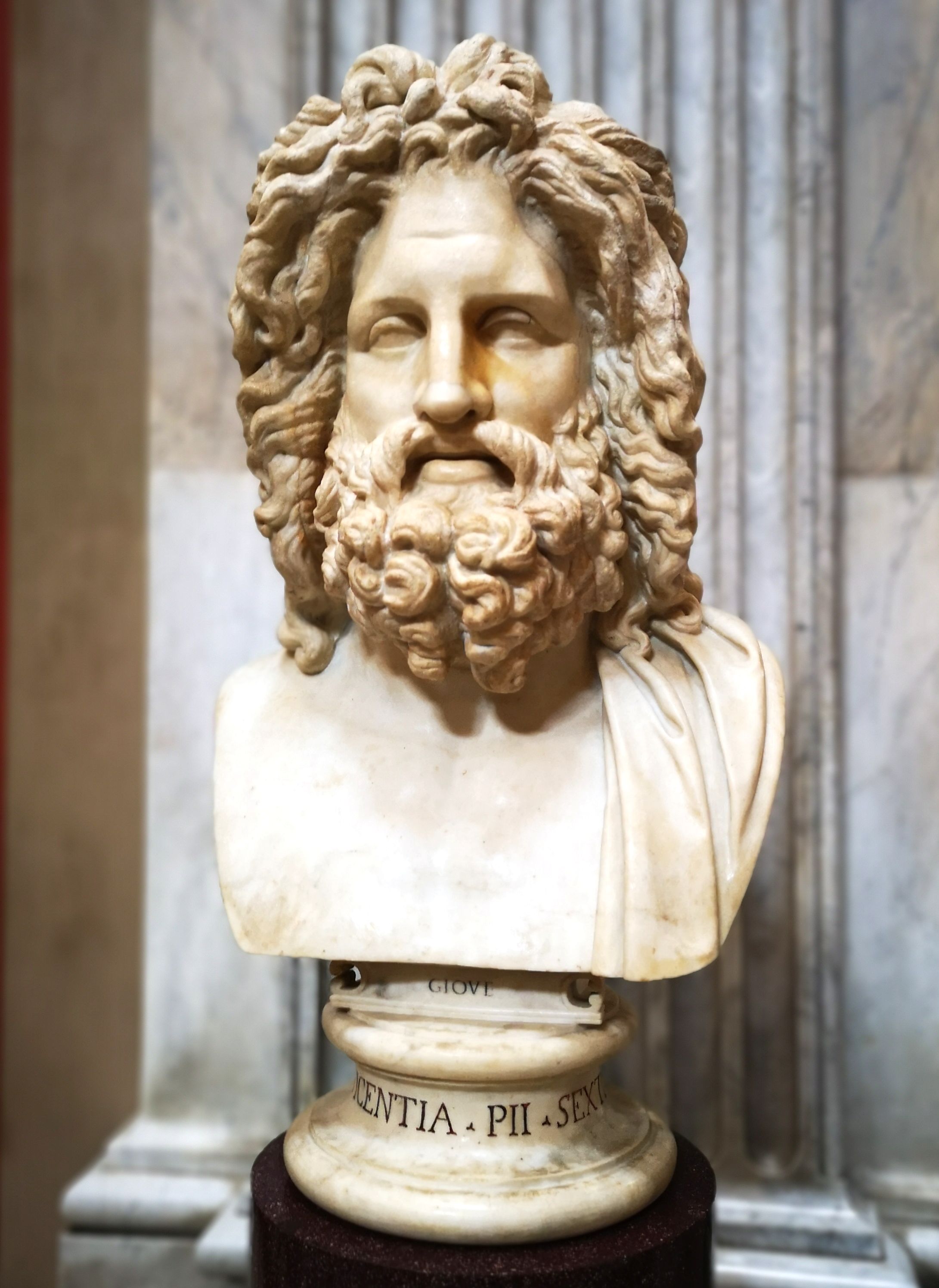
Jupiter (mythology)
Jupiter ( la, Iūpiter or , from Proto-Italic language, Proto-Italic "day, sky" + "father", thus "sky father" Greek: Zeus, Δίας or Zeus, Ζεύς), also known as Jove (genitive case, gen. ''Iovis'' ), is the sky god, god of the sky and god of thunder, thunder, and Pantheon (gods), king of the gods in ancient Roman religion and Roman mythology, mythology. Jupiter was the chief deity of Roman state religion throughout the Roman Republic, Republican and Roman Empire, Imperial eras, until Constantine the Great and Christianity, Christianity became the dominant religion of the Empire. In Roman mythology, he negotiates with Numa Pompilius, the second king of Rome, to establish principles of Roman religion such as offering, or sacrifice. Jupiter is usually thought to have originated as a sky god. His identifying implement is the thunderbolt and his primary sacred animal is the eagle, which held precedence over other birds in the taking of auspices and became one of the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustine Of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Africa. His writings influenced the development of Western philosophy and Western Christianity, and he is viewed as one of the most important Church Fathers of the Latin Church in the Patristic Period. His many important works include ''The City of God'', '' On Christian Doctrine'', and '' Confessions''. According to his contemporary, Jerome, Augustine "established anew the ancient Faith". In his youth he was drawn to the eclectic Manichaean faith, and later to the Hellenistic philosophy of Neoplatonism. After his conversion to Christianity and baptism in 386, Augustine developed his own approach to philosophy and theology, accommodating a variety of methods and perspectives. Believing the grace of Christ was indispensable to human freed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_1475.jpg)

