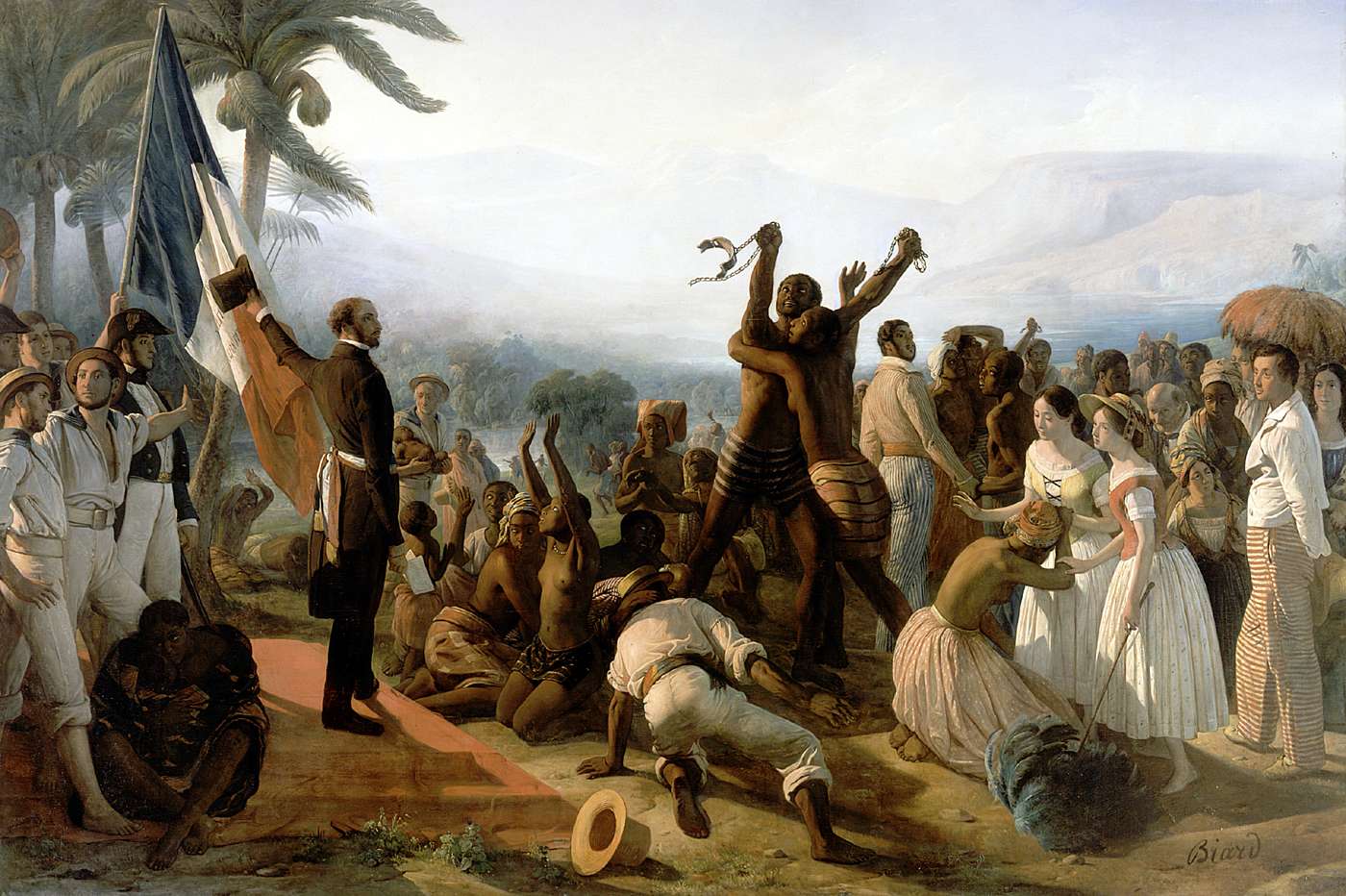|
Fessenheim
Fessenheim (; gsw-FR, Fassene) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It is known for: * its hydroelectric power plant on the Grand Canal d'Alsace (built 1953–1956, inaugurated 1957); * the Fessenheim Nuclear Power Plant next to the Grand Canal d'Alsace, formerly the oldest in service in France since 1977 until it shut down in 2020; * a road and pedestrian bridge over the Rhine (210 m long, 7 m wide) to Hartheim in Germany since 2006; * the Victor Schœlcher museum, honoring the 19th Century Abolitionist Victor Schœlcher - born in Fessenheim. See also * Communes of the Haut-Rhin département The following is a list of the 366 communes of the French department of Haut-Rhin. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020): [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fessenheim Nuclear Power Plant
The Fessenheim Nuclear Power Plant is located in the Fessenheim commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France, north east of the Mulhouse urban area, within of the border with Germany, and approximately from Switzerland. Unit 1 was closed in February 2020 and unit 2 on 29 June 2020. Description The Fessenheim plant has two pressurized water reactors, which each generated 920 MWe. Construction at Fessenheim began in 1970 and the plant was commissioned in 1977. Autorité de sûreté nucléaire, accessed 2009-05-17 It is built alongside the Grand Canal d'Alsace, a canal channelling the Upper Rhine river, from which it drew of cooling water annually. The plant employed around 700 staff and 200 contractors, and indirectly supports a further 600 to 2,000 people during maintenance operations. The plant contributed around 16,000,000 euro in tax to the various local authorities, including providing the commune of Fessenheim with 70% of its revenue. In Octobe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fessenheim-le-Bas
Fessenheim-le-Bas (; german: Niederfessenheim) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It has been built near an old Roman road leading from Strasbourg to Saverne. Notable people * Aloyse Kobès (born at Fessenheim on 14 April 1820; died at Dakar on 11 October 1872) was the first missionary bishop from Alsace. Since 1972 a French school at Dakar has borne his name. Transport link The town is served by Bus Route 205 of the Compagnie des Transports Strasbourgeois (CTS) inter-urban service. See also * Fessenheim * Communes of the Bas-Rhin department * Kochersberg The Kochersberg () is a natural region of the French département of Bas-Rhin in Alsace and is a part of the hills found along the eastern side of the Vosges mountains. It gave its name to the Communauté de communes du Kochersberg, a cooperation ... References Communes of Bas-Rhin Bas-Rhin communes articles needing translation from French Wikipedia {{BasRhin-g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond Couvègnes
Raymond Couvègnes (1893–1985) was a French sculptor and medallist. Biography Raymond Couvègnes was born in Ermont on 27 February 1893 and died in Paris on 15 December 1985. His father was Emile Couvègnes, a director of the "Compagnie des chemin de fer du Nord" and a military historian. He showed an early talent for design and attended the École d'arts appliqués Bernard Palissy before enrolling at the École nationale supérieure des Beaux-Arts. He studied under Injalbert and in 1927 won the Prix de Rome for sculpture. His early works involved sculptural work which arose in the reconstruction of churches and town halls in Northern France where so much damaged had been sustained in the 1914–1918 war. Examples of such work involved Montdidier town hall and churches in Roye, Arvillers, Moreuil, Le Bosquel and Athies. For the most part he worked using moulded concrete (béton moulé). In his next phase his works were executed in limestone or stone including in Paris a bust o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Canal D'Alsace
The Grand Canal of Alsace (, ) is a canal in eastern France, channeling the Upper Rhine river. It is 50 kilometers (about 30 miles) long between Kembs and Vogelgrun, and provides access to the region from the Rhine River, Basel in Switzerland, and the North Sea for barges of up to about 5000 metric tons. The Grand Canal permits the navigation of more than 30,000 boats a year between Basel and Strasbourg. Construction of the canal began in 1932 and was completed in 1959. The canal diverts much of the water from the original bed of the fast-flowing Rhine in this area, which is almost entirely unnavigable by boats. The Grand Canal produces hydroelectric power at Kembs, Ottmarsheim, Fessenheim and Vogelgrun, supplying electricity to one of the most heavily industrialized regions in France and even to Germany. Furthermore, the canal provides enough water throughout the year to a nuclear power plant at Fessenheim, eliminating the need for water towers. See also * Fessenheim N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Schœlcher
Victor Schœlcher (; 22 July 1804 – 25 December 1893) was a French abolitionist, writer, politician and journalist, best known for his leading role in the abolition of slavery in France in 1848, during the Second Republic. Early life Schœlcher was born in Paris on 22 July 1804. His father, Marc Schœlcher (1766–1832), from Fessenheim in Alsace, was the owner of a porcelain factory. His mother, Victoire Jacob (1767–1839), from Meaux in Seine-et-Marne, was a laundry maid in Paris at the time of their marriage. He was baptized in Saint-Laurent Church on 9 September 1804. He enrolled in the Lycée Louis-le-Grand in 1818, but left one year later and began working at the family's porcelain factory in the rue du Faubourg Saint-Denis. In his teenage years Schœlcher became an opponent of the Bourbon monarchy while frequenting the literary and political salons of Paris. In 1820, at the age of 16, he joined Freemasonry, being initiated into the Parisian lodge ''Les Amis de la V� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of The Haut-Rhin Département
The following is a list of the 366 communes of the French department of Haut-Rhin. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):BANATIC Périmètre des EPCI à fiscalité propre. Accessed 3 July 2020. *CA *CA *CA * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsatian Language
Alsatian ( gsw-FR, Elsässisch, links=no or "Alsatian German"; Lorraine Franconian: ''Elsässerdeitsch''; french: Alsacien; german: Elsässisch or ) is the group of Alemannic German dialects spoken in most of Alsace, a formerly disputed region in eastern France that has passed between French and German control five times since 1681. Language family Alsatian is closely related to other nearby Alemannic dialects, such as Swiss German, Swabian, and Markgräflerisch as well as Kaiserstühlerisch. It is often confused with Lorraine Franconian, a more distantly related Franconian dialect spoken in the northwest corner of Alsace and in neighbouring Lorraine. Like other dialects and languages, Alsatian has also been influenced by outside sources. Words of Yiddish origin can be found in Alsatian, and modern conversational Alsatian includes adaptations of French words and English words, especially concerning new technologies. Many speakers of Alsatian could, if necessary, write ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haut-Rhin
Haut-Rhin (, ; Alsatian: ''Owerelsàss'' or '; german: Oberelsass, ) is a department in the Grand Est region of France, bordering both Germany and Switzerland. It is named after the river Rhine. Its name means ''Upper Rhine''. Haut-Rhin is the smaller and less populated of the two departments of the former administrative Alsace region, the other being the Bas-Rhin (Lower Rhine). Especially after the 1871 cession of the southern territory known since 1922 as Territoire de Belfort, although it is still densely populated compared to the rest of metropolitan France. It had a population of 767,086 in 2019.Populations légales 2019: 68 Haut-Rhin INSEE On 1 January 2021, the departments of |
Departments Of France
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (french: département, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivities"), between the administrative regions and the communes. Ninety-six departments are in metropolitan France, and five are overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 332 arrondissements, and these are divided into cantons. The last two levels of government have no autonomy; they are the basis of local organisation of police, fire departments and, sometimes, administration of elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council ( ing. lur.. From 1800 to April 2015, these were called general councils ( ing. lur.. Each council has a president. Their main areas of responsibility include the management of a number of social and welfare allowances, of junior high school () buildings and technical staff, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Est
Grand Est (; gsw-FR, Grossa Oschta; Moselle Franconian/ lb, Grouss Osten; Rhine Franconian: ''Groß Oschte''; german: Großer Osten ; en, "Great East") is an administrative region in Northeastern France. It superseded three former administrative regions, Alsace, Champagne-Ardenne and Lorraine, on 1 January 2016 under the provisional name of Alsace-Champagne-Ardenne-Lorraine (; ACAL or, less commonly, ALCA), as a result of territorial reform which had been passed by the French Parliament in 2014. The region sits astride three water basins (Seine, Meuse and Rhine), spanning an area of , the fifth largest in France; it includes two mountain ranges (Vosges and Ardennes). It shares borders with Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany and Switzerland. As of 2017, it had a population of 5,549,586 inhabitants. The prefecture and largest city, by far, is Strasbourg. The East of France has a rich and diverse culture, being situated at a crossroads between the Latin and Germanic worlds. This hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |