|
Feryal Özel
Feryal Özel (born May 27, 1975) is a Turkish-American astrophysicist born in Istanbul, Turkey, specializing in the physics of compact objects and high energy astrophysical phenomena. As of 2022, Özel is the Department Chair and a professor at the Georgia Institute of Technology School of Physics in Atlanta. She was previously a professor at the University of Arizona in Tucson, in the Astronomy Department and Steward Observatory. Özel graduated ''summa cum laude'' from Columbia University's Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science and received her PhD at Harvard University with Ramesh Narayan acting as Thesis advisor. She was a Hubble Fellow and member at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey. She was a Fellow at the Harvard-Radcliffe Institute and a visiting professor at the Miller Institute at UC Berkeley. Özel is widely recognized for her contributions to the field of neutron stars, black holes, and magnetars. She is a member and Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, cultural and historic hub. The city straddles the Bosporus strait, lying in both Europe and Asia, and has a population of over 15 million residents, comprising 19% of the population of Turkey. Istanbul is the list of European cities by population within city limits, most populous European city, and the world's List of largest cities, 15th-largest city. The city was founded as Byzantium ( grc-gre, Βυζάντιον, ) in the 7th century BCE by Ancient Greece, Greek settlers from Megara. In 330 CE, the Roman emperor Constantine the Great made it his imperial capital, renaming it first as New Rome ( grc-gre, Νέα Ῥώμη, ; la, Nova Roma) and then as Constantinople () after himself. The city grew in size and influence, eventually becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miller Institute
The Miller Institute for Basic Research in Science was established on the University of California, Berkeley, campus in 1955 after Adolph C. Miller and his wife, Mary Sprague Miller, made a donation to the university. It was their wish that the donation be used to establish an institute "dedicated to the encouragement of creative thought and conduct of pure science". The Miller Institute sponsors Miller Research Professors, Visiting Miller Professors and Miller Research Fellows. The first appointments of Miller Professors were made in January 1957. In 2008 the institute created the Miller Senior Fellow program. This program is aimed differently, but is still within the institute's general purpose of supporting excellence in science at Berkeley. The Senior Fellow advances that goal by providing selected faculty with significant discretionary research funds as recognition of distinction in scientific research. The first five-year award went to Professor Randy Schekman, illustratin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
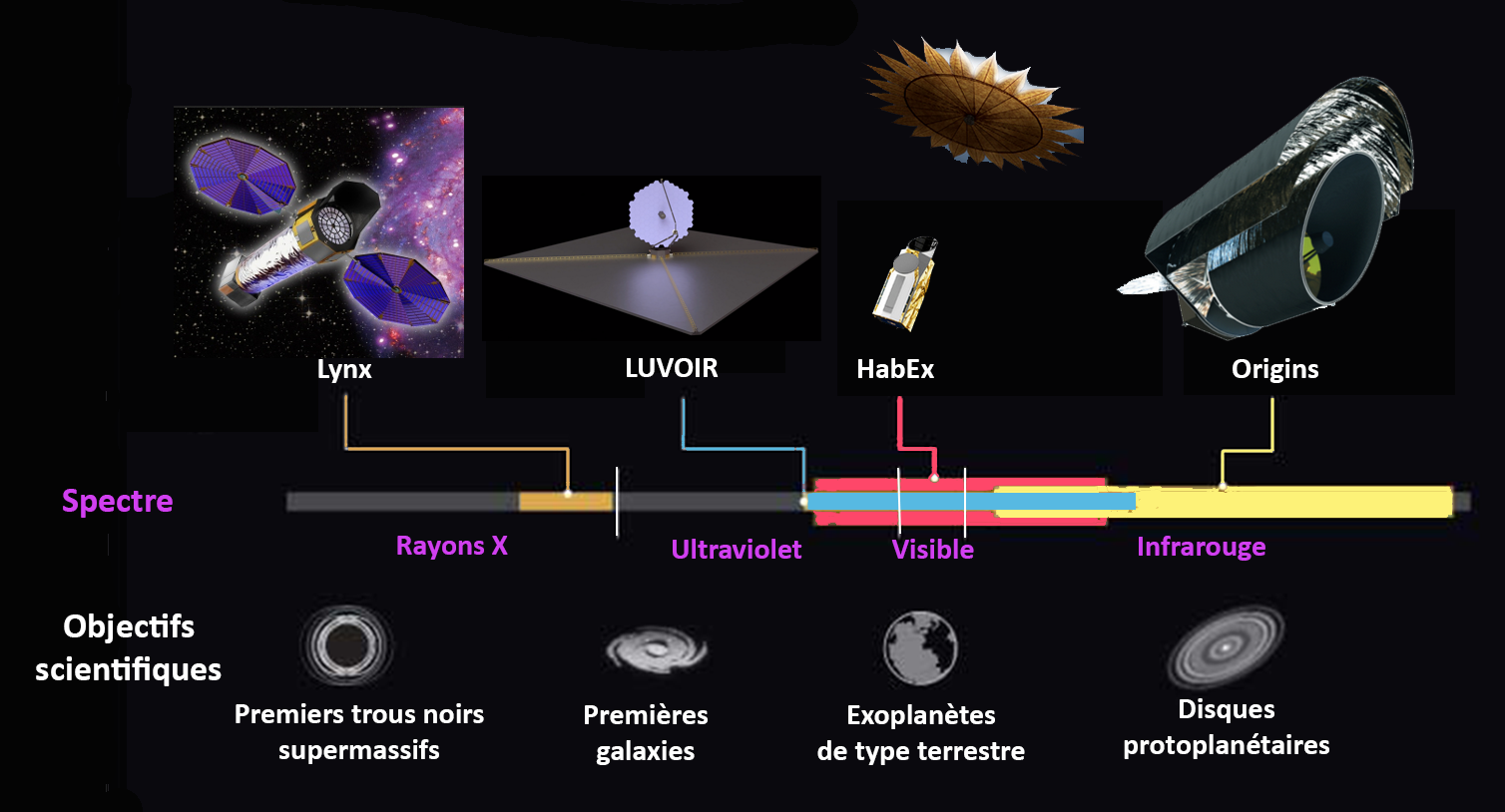
Lynx X-ray Observatory
The Lynx X-ray Observatory (''Lynx'') is a NASA-funded Large Mission Concept Study commissioned as part of the National Academy of Sciences 2020 Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey. The concept study phase is complete as of August 2019, and the ''Lynx'' final report has been submitted to the Decadal Survey for prioritization. If launched, ''Lynx'' would be the most powerful X-ray astronomy observatory constructed to date, enabling order-of-magnitude advances in capability over the current Chandra X-ray Observatory and XMM-Newton space telescopes. Background In 2016, following recommendations laid out in the so-called Astrophysics Roadmap of 2013, NASA established four space telescope concept studies for future Large strategic science missions. In addition to ''Lynx'' (originally called X-ray Surveyor in thRoadmap document'','' they are the Habitable Exoplanet Imaging Mission (HabEx), the Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor (LUVOIR), and the Origins Space Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexey Vikhlinin
Alexey Vikhlinin (born September 17, 1970) is a Russian-American astrophysicist notable for achievements in the astrophysics of high energy phenomenon, namely galaxy cluster cosmology and the design of space-based X-ray observatories. He is currently a senior astrophysicist at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, part of the Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian in Cambridge, Massachusetts. He was recently the Science and Technology Definition Team (STDT) Community Co-Chair (along with Feryal Özel) for the ''Lynx X-ray Observatory'', a NASA-funded Large Mission Concept Study under consideration by th2020 Decadal Survey on Astronomy and Astrophysics Biography Born in Ryazan, Russia on September 17, 1970, Vikhlinin was educated at the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, graduating in 1993 with a degree in Space Physics. He received his Doctor of Philosophy in Astronomy from the Russian Institute for Space Research in 1995, and a Doctor of Sciences fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History (U
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Universe (TV Series)
''The Universe'' is an American documentary film, documentary Television show, television series that features computer-generated imagery and computer graphics of astronomical objects in the universe plus interviews with experts who study in the fields of cosmology, astronomy, and astrophysics. The program is produced by Flight 33 Productions and Workaholic Productions. The series premiered on May 29, 2007, on History (U.S. TV network), The History Channel and four subsequent seasons were aired until 2010. Starting from October 25, 2011, new episodes began airing exclusively on H2 (TV network), H2. The series currently airs on Viceland and Story Television. Format The series covers topics concerning space exploration, the Solar System, and astronomical objects in the universe. It shows computer-generated imagery, CGI renderings of these aforementioned, video footage, photographs, and views from scientists, project managers, engineers, advocates, writers and other experts. The epi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Ideas (TV Series)
''Big Ideas'' was a Canadian television series produced and broadcast by TVOntario, on the air since 2001. The program showcases public intellectual culture. It was conceived and produced by Wodek Szemberg. The show presented public lectures by acclaimed university educators and other distinguished guests. The original host, Irshad Manji, was succeeded by Canadian actor/director/playwright Andrew Moodie on January 7, 2006. In September 2011, Piya Chattopadhyay took over as host. In 2007, ''Big Ideas'' held its Best Lecturer competition for the second time. Michael Persinger, from Laurentian University, received the award. Podcasts of the lectures are available through the ''Big Ideas'' website as well as from iTunes. ''Big Ideas'' is also the name of an unrelated PBS series that originally aired in 2003, as well as of a radio series on Australian Broadcasting Corporation's Radio National Radio National, known on-air as RN, is an Australia-wide public service broadcastin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Physical Society
The American Physical Society (APS) is a not-for-profit membership organization of professionals in physics and related disciplines, comprising nearly fifty divisions, sections, and other units. Its mission is the advancement and diffusion of knowledge of physics. The society publishes more than a dozen scientific journals, including the prestigious '' Physical Review'' and ''Physical Review Letters'', and organizes more than twenty science meetings each year. APS is a member society of the American Institute of Physics. Since January 2021 the organization has been led by chief executive officer Jonathan Bagger. History The American Physical Society was founded on May 20, 1899, when thirty-six physicists gathered at Columbia University for that purpose. They proclaimed the mission of the new Society to be "to advance and diffuse the knowledge of physics", and in one way or another the APS has been at that task ever since. In the early years, virtually the sole activity of the AP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Goeppert-Mayer Award
The Maria Goeppert-Mayer Award is an annual prize presented by the American Physical Society in recognition of an outstanding contribution to physics research by a woman. It recognizes and enhances outstanding achievements by women physicists in the early years of their careers. The prize has been awarded since 1986 and is named after Maria Goeppert-Mayer, Nobel laureate in 1963 with J. Hans D. Jensen and Eugene Wigner, Eugene Paul Wigner. Goeppert-Mayer and Jensen were awarded their prize "for their discovery of the nuclear shell model, nuclear shell structure". Goeppert-Mayer was the second woman to receive a Nobel prize in physics after Marie Curie. Recipients Source: * 1986: Judith Young (astronomer), Judith S. Young * 1987: Louise Dolan * 1988: Bonny L. Schumaker * 1989: Cherry A. Murray * 1990: Ellen D. Williams (chemist), Ellen Williams * 1991: Alice White (physicist), Alice E. White * 1992: Barbara Cooper (physicist), Barbara Hope Cooper * 1993: Ewine van Dishoeck * 1994 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier 87
Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, generally abbreviated to M87) is a supergiant elliptical galaxy with several trillion stars in the constellation Virgo. One of the largest and most massive galaxies in the local universe, it has a large population of globular clusters — about 15,000 compared with the 150–200 orbiting the Milky Way — and a jet of energetic plasma that originates at the core and extends at least , traveling at a relativistic speed. It is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky and a popular target for both amateur and professional astronomers. The French astronomer Charles Messier discovered M87 in 1781, and cataloged it as a nebula. M87 is about from Earth and is the second-brightest galaxy within the northern Virgo Cluster, having many satellite galaxies. Unlike a disk-shaped spiral galaxy, M87 has no distinctive dust lanes. Instead, it has an almost featureless, ellipsoidal shape typical of most giant elliptical gala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
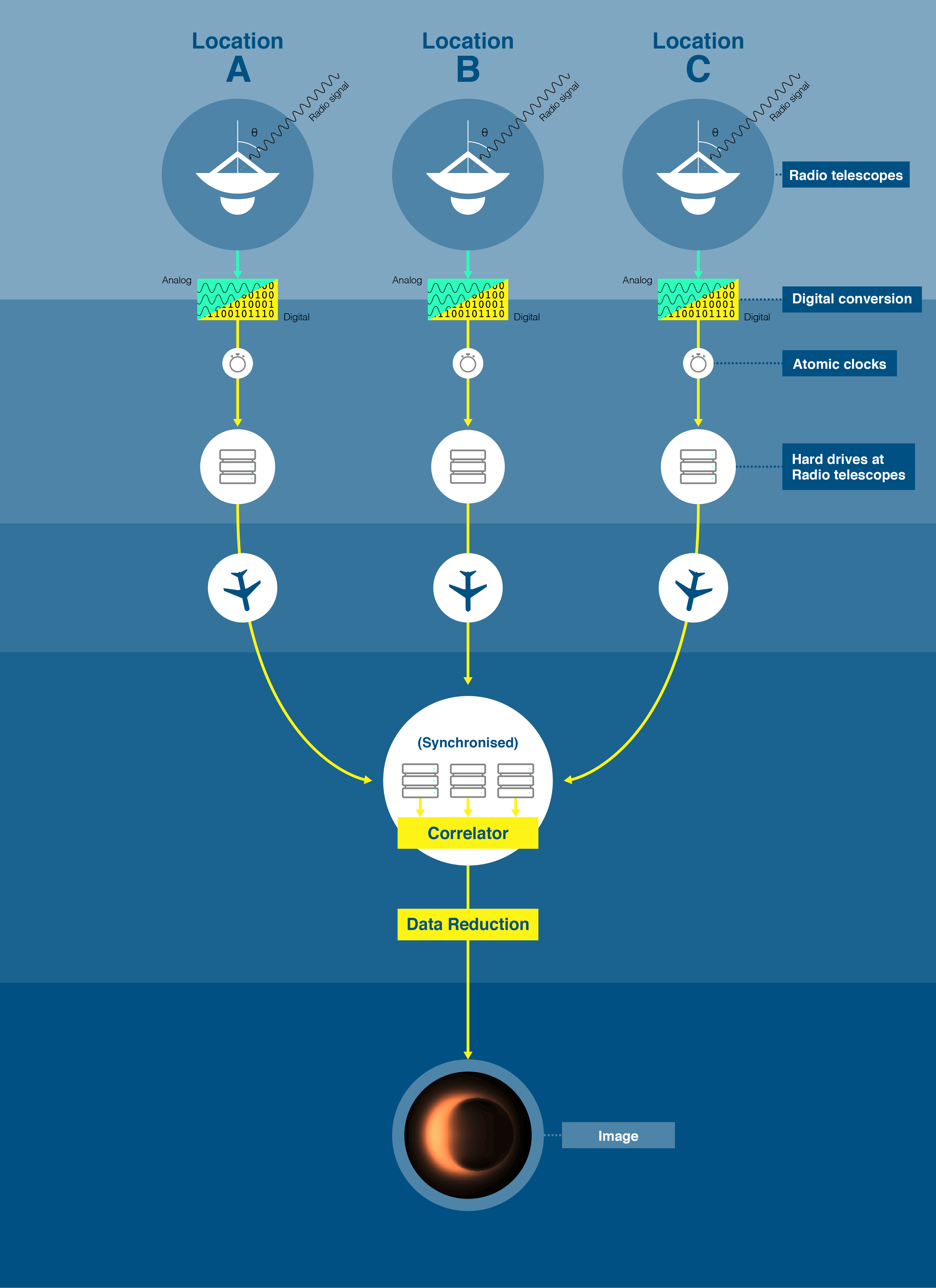
Event Horizon Telescope
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a large telescope array consisting of a global network of radio telescopes. The EHT project combines data from several very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) stations around Earth, which form a combined array with an angular resolution sufficient to observe objects the size of a supermassive black hole's event horizon. The project's observational targets include the two black holes with the largest angular diameter as observed from Earth: the black hole at the center of the supergiant elliptical galaxy Messier 87 (M87*, pronounced "M87-Star"), and Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*, pronounced "Sagittarius A-Star") at the center of the Milky Way. The Event Horizon Telescope project is an international collaboration that was launched in 2009 after a long period of theoretical and technical developments. On the theory side, work on the photon orbit and first simulations of what a black hole would look like progressed to predictions of VLBI imaging for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetar
A magnetar is a type of neutron star with an extremely powerful magnetic field (∼109 to 1011 T, ∼1013 to 1015 G). The magnetic-field decay powers the emission of high-energy electromagnetic radiation, particularly X-rays and gamma rays.Ward; Brownlee, p.286 The existence of magnetars was proposed in 1992 by Robert Duncan and . Their proposal sought to explain the properties of transient sources of gamma rays, now known as soft gamma repeaters (SGRs). Over the following decade, the magnetar hypothesis became widely accepted, and was extended to explain anomalous X-ray pulsars (AXPs). , 24 confirmed magnetars were known. It has been suggested that magnetars are the source of fast radio bursts (FRB), in particular as a result of findings in 2020 by scientists using the Australian Square Kilometre Array. Description Like other neutron stars, magnetars are around in diameter, and have a mass about 1.4 solar masses. They are formed by the collapse of a star with a mass 10– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)