|
Fermi Acceleration
Fermi acceleration, sometimes referred to as ''diffusive shock acceleration'' (a subclass of Fermi accelerationOn the Origin of the Cosmic Radiation, E. Fermi, Physical Review 75, pp. 1169-1174, 1949), is the acceleration that charged particles undergo when being repeatedly reflected, usually by a magnetic mirror (see also Centrifugal mechanism of acceleration). It receives its name from physicist Enrico Fermi who first proposed the mechanism. This is thought to be the primary mechanism by which particles gain non-thermal energies in astrophysical shock waves. It plays a very important role in many astrophysical models, mainly of shocks including solar flares and supernova remnants. There are two types of Fermi acceleration: first-order Fermi acceleration (in shocks) and second-order Fermi acceleration (in the environment of moving magnetized gas clouds). In both cases the environment has to be collisionless in order for the mechanism to be effective. This is because Fermi accelera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting original research in relevant fields. Despite the name, the journal is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second volume, after the Astronomical Society of London became the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS). Until 1960 it carried the monthly notices of the RAS, at which time these were transferred to the newly established ''Quarterly Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (1960–1996) and then to its successor journal ''Astronomy & Geophysics'' (since 1997). Until 1965, MNRAS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
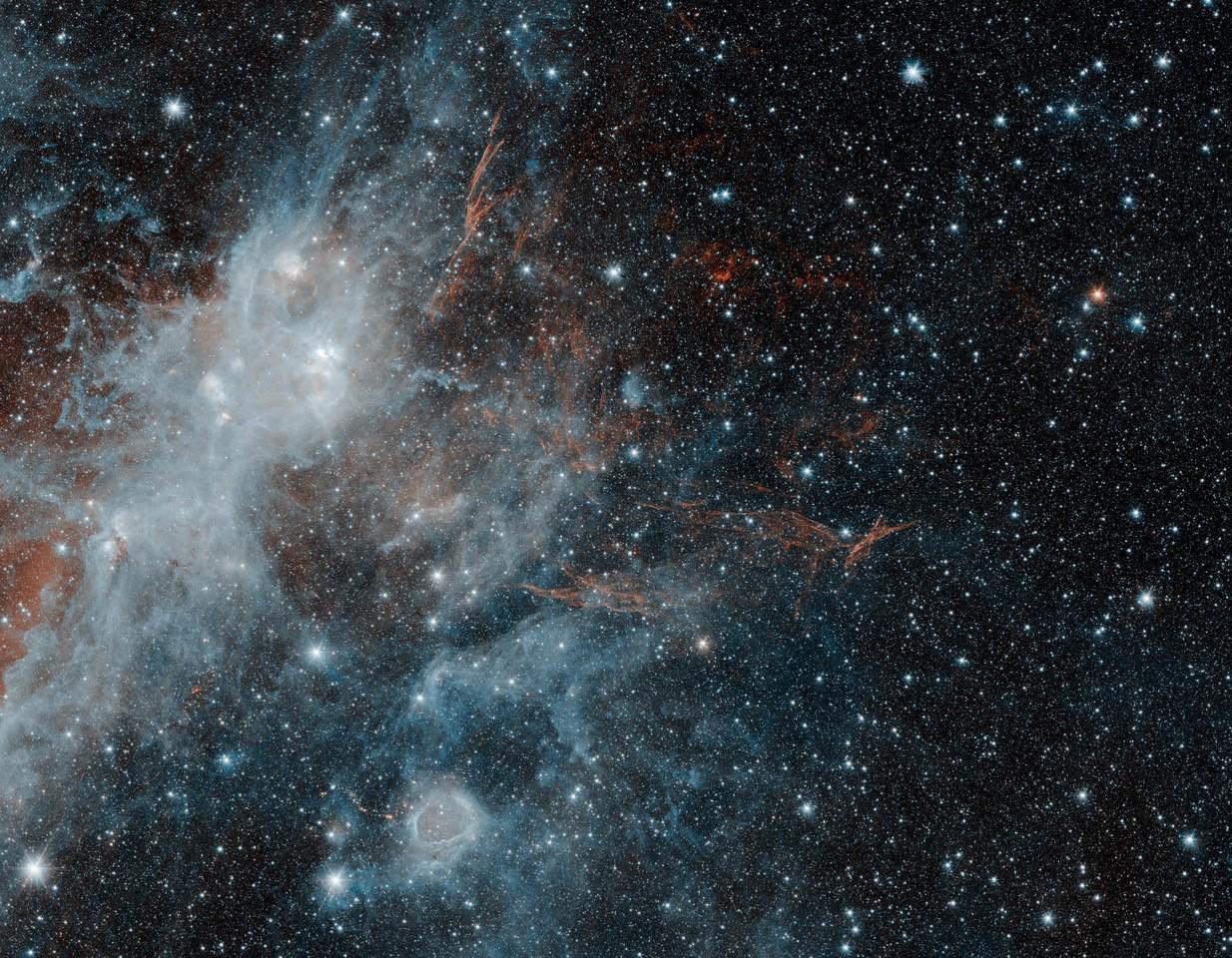
Supernova Remnant
A supernova remnant (SNR) is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar material it sweeps up and shocks along the way. There are two common routes to a supernova: either a massive star may run out of fuel, ceasing to generate fusion energy in its core, and collapsing inward under the force of its own gravity to form a neutron star or a black hole; or a white dwarf star may accrete material from a companion star until it reaches a critical mass and undergoes a thermonuclear explosion. In either case, the resulting supernova explosion expels much or all of the stellar material with velocities as much as 10% the speed of light (or approximately 30,000 km/s). These speeds are highly supersonic, so a strong shock wave forms ahead of the ejecta. That heats the upstream plasma up to temperatures well above mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamics (mechanics)
Dynamics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the study of forces and their effects on motion. Isaac Newton was the first to formulate the fundamental physical laws that govern dynamics in classical non-relativistic physics, especially his second law of motion. Principles Generally speaking, researchers involved in dynamics study how a physical system might develop or alter over time and study the causes of those changes. In addition, Newton established the fundamental physical laws which govern dynamics in physics. By studying his system of mechanics, dynamics can be understood. In particular, dynamics is mostly related to Newton's second law of motion. However, all three laws of motion are taken into account because these are interrelated in any given observation or experiment. Linear and rotational dynamics The study of dynamics falls under two categories: linear and rotational. Linear dynamics pertains to objects moving in a line and involves such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Quantities
A physical quantity is a physical property of a material or system that can be quantified by measurement. A physical quantity can be expressed as a ''value'', which is the algebraic multiplication of a ' Numerical value ' and a ' Unit '. For example, the physical quantity of mass can be quantified as '32.3 kg ', where '32.3' is the numerical value and 'kg' is the Unit. A physical quantity possesses at least two characteristics in common. # Numerical magnitude. # Units Symbols and nomenclature International recommendations for the use of symbols for quantities are set out in ISO/IEC 80000, the IUPAP red book and the Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry, IUPAC green book. For example, the recommended symbol for the physical quantity ''mass'' is ''m'', and the recommended symbol for the quantity ''electric charge'' is ''Q''. Subscripts and indices Subscripts are used for two reasons, to simply attach a name to the quantity or associate it with another quanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Power
Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion, nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors. Research into fusion reactors began in the 1940s, but as of 2022, only one design, an Inertial confinement fusion, inertial confinement laser-driven fusion machine at the US National Ignition Facility, has conclusively produced a positive fusion energy gain factor, i.e. more power output than input. Fusion processes require fuel and a confined environment with sufficient temperature, pressure, and confinement time to create a plasma (physics), plasma in which fusion can occur. The combination of these figures that results in a power-producing system is known as the Lawson criterion. In stars, the most common fuel is hydrogen, and gravity provides ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Glow
The Fermi glow consists of ultraviolet-glowing particles, mostly hydrogen, originating from the Solar System's bow shock, created when light from stars and the Sun enter the region between the heliopause and the interstellar mediumA Glowing Discovery at the Forefront of Our Plunge Through Space ". . 15 March 2000. and undergo , bouncing around the transition area several times, gaining energy via collisions with atoms of the interstellar medium. The first evidence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi–Ulam Model
The Fermi–Ulam model (FUM) is a dynamical system that was introduced by Poland, Polish mathematician Stanislaw Ulam in 1961. FUM is a variant of Enrico Fermi's primary work on acceleration of cosmic rays, namely Fermi acceleration. The system consists of a particle that elastic collision, collides elastically between a fixed wall and a moving one, each of infinite mass. The walls represent the magnetic mirrors with which the cosmic rays, cosmic particles collide. A. J. Lichtenberg and M. A. Lieberman provided a simplified version of FUM (SFUM) that derives from the Poincaré map, Poincaré surface of section x=const. and writes : u_=, u_n+U_\mathrm(\varphi_n), : \varphi_=\varphi_n+\frac \pmod k, where u_n is the velocity of the particle after the n-th collision with the fixed wall, \varphi_n is the corresponding phase of the moving wall, U_\mathrm is the velocity law of the moving wall and M is the stochasticity parameter of the system. If the velocity law of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ... in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Flare
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other solar phenomena. The occurrence of solar flares varies with the 11-year solar cycle. Solar flares are thought to occur when stored magnetic energy in the Sun's atmosphere accelerates charged particles in the surrounding plasma. This results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum. High-energy electromagnetic radiation from solar flares is absorbed by the daylight side of Earth's upper atmosphere, in particular the ionosphere, and does not reach the surface. This absorption can temporarily increase the ionization of the ionosphere which may interfere with short-wave radio communication. The prediction of solar flares is an active area of research. Flares also occur on other stars, where the term ''stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the ''net'' force acting on that object. The magnitude of an object's acceleration, as described by Newton's Second Law, is the combined effect of two causes: * the net balance of all external forces acting onto that object — magnitude is directly proportional to this net resulting force; * that object's mass, depending on the materials out of which it is made — magnitude is inversely proportional to the object's mass. The SI unit for acceleration is metre per second squared (, \mathrm). For example, when a vehicle starts from a standstill (zero velocity, in an inertial frame of reference) and travels in a straight line at increasing speeds, it is accelerating in the direction of travel. If the vehicle turns, an acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Wave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a medium but is characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in pressure, temperature, and density of the medium. For the purpose of comparison, in supersonic flows, additional increased expansion may be achieved through an expansion fan, also known as a Prandtl–Meyer expansion fan. The accompanying expansion wave may approach and eventually collide and recombine with the shock wave, creating a process of destructive interference. The sonic boom associated with the passage of a supersonic aircraft is a type of sound wave produced by constructive interference. Unlike solitons (another kind of nonlinear wave), the energy and speed of a shock wave alone dissipates relatively quickly with distance. When a shock wave passes through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi (; 29 September 1901 – 28 November 1954) was an Italian (later naturalized American) physicist and the creator of the world's first nuclear reactor, the Chicago Pile-1. He has been called the "architect of the nuclear age" and the "architect of the atomic bomb". He was one of very few physicists to excel in both theoretical physics and experimental physics. Fermi was awarded the 1938 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on induced radioactivity by neutron bombardment and for the discovery of transuranium elements. With his colleagues, Fermi filed several patents related to the use of nuclear power, all of which were taken over by the US government. He made significant contributions to the development of statistical mechanics, Quantum mechanics, quantum theory, and nuclear physics, nuclear and particle physics. Fermi's first major contribution involved the field of statistical mechanics. After Wolfgang Pauli formulated his Pauli exclusion principle, exclusion pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |