|
Fei Shi (Three Kingdoms)
Fei Shi ( 214–234, died after 234), courtesy name Gongju, was an official of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Life Fei Shi was from Nan'an County (南安縣), Qianwei Commandery (犍為郡), which is around present-day Leshan, Sichuan. He originally served under Liu Zhang, the Governor of Yi Province (covering present-day Sichuan and Chongqing), as the Prefect of Mianzhu County (綿竹縣). In 214, after the warlord Liu Bei seized control of Yi Province from Liu Zhang, Fei Shi came into the service of Liu Bei. Between 214 and 219, Fei Shi held a number of appointments in Liu Bei's administration, including Administrator (太守) of Zangke Commandery (牂牁郡). Around 219, after Liu Bei declared himself King of Hanzhong, he tasked Fei Shi with travelling to Jing Province to inform Guan Yu about his appointment as General of the Vanguard (前將軍). However, when Guan Yu learned that Huang Zhong would server as the General of the Rear (後將 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fei (surname)
Fei () is a traditional Chinese surname. It was 65th in the Hundred Family Surnames.K. S. Tom. 989(1989). Echoes from Old China: Life, Legends and Lore of the Middle Kingdom. University of Hawaii Press. . This surname has three main sources. Two of them are from the State of Lu during the Spring and Autumn period (722–481 BC), part of present-day Shandong province. A senior official of the state of Lu was granted a city named Fei, while the son of a certain duke was granted a county named Fei. Both of these place names were adopted by descendants as surnames. A third source of the name is Fei Zhong, a high minister of the Yin Dynasty (1401–1122 BC).http://www.ancestry.com/facts/Fei-civil-war.ashx Notable people * Fei Hsiao-Tung, professor of sociology and anthropology * Fei Junlong, commander of the second Chinese space flight * Fei Wuji, corrupt minister of the State of Chu during the Spring and Autumn period * Fei Xiang (transcription of the English name “Philips� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
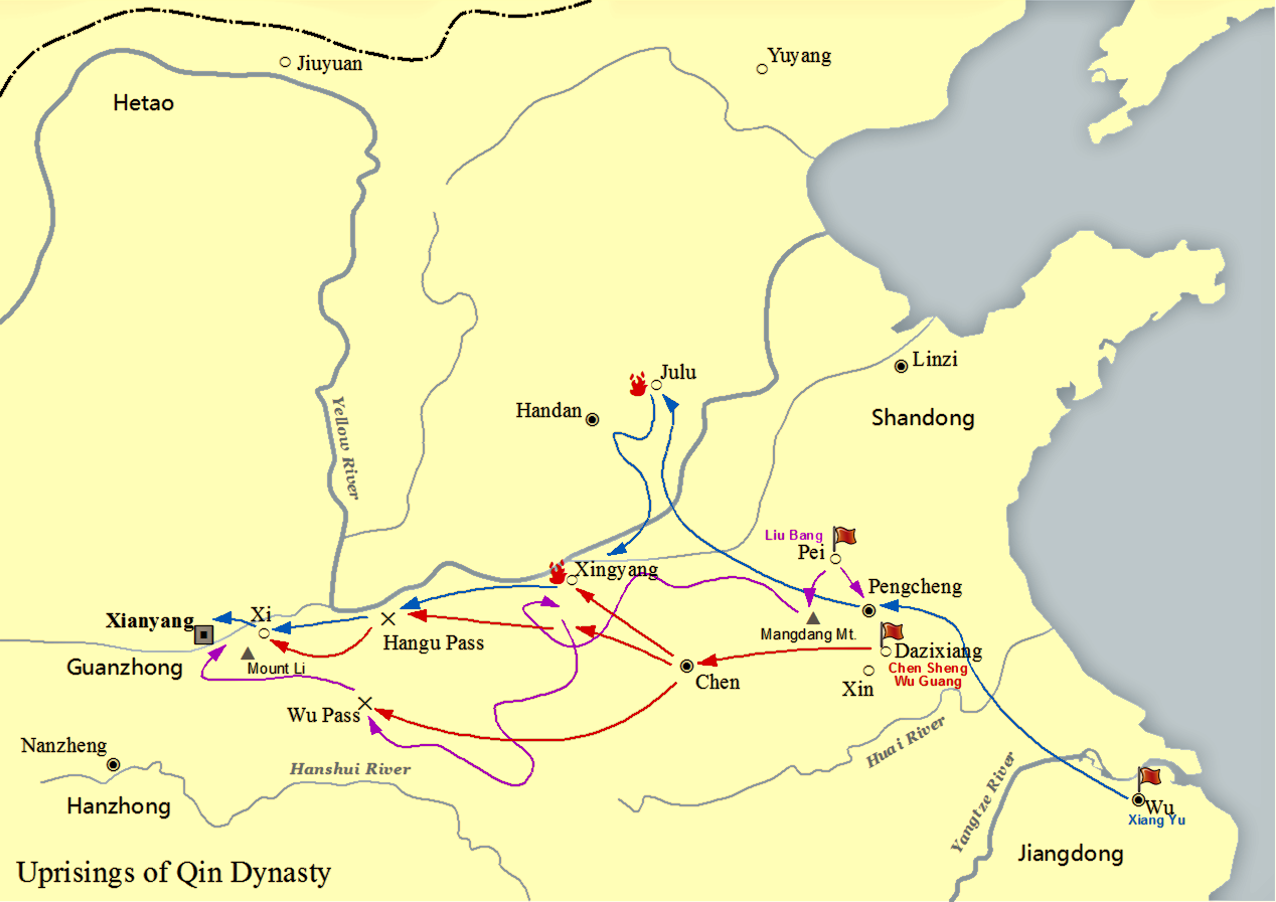
Chu–Han Contention
The Chu–Han Contention ( zh, , lk=on) or Chu–Han War () was an interregnum period in ancient China between the fallen Qin dynasty and the subsequent Han dynasty. After the third and last Qin ruler, Ziying, unconditionally surrendered to rebel forces in 206 BCE, the former Qin Empire was divided by rebel leader Xiang Yu into the Eighteen Kingdoms, which were ruled by various rebel leaders and surrendered Qin generals. A civil war soon broke out, most prominently between two major contending powers – Xiang Yu's Western Chu and Liu Bang's Han. Some of the other kingdoms also waged war among themselves but these were largely insignificant compared to the main conflict between Chu and Han. The war ended in 202 BCE with a total Han victory at the Battle of Gaixia, where Xiang Yu fled to Wujiang and committed suicide after a violent last stand. Liu Bang subsequently proclaimed himself Emperor and established the Han dynasty as the ruling dynasty of China. Background In 22 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Guangwu Of Han
Emperor Guangwu of Han (; 15 January 5 BC – 29 March AD 57), born Liu Xiu (), courtesy name Wenshu (), was a Chinese monarch. He served as an emperor of the Han dynasty by restoring the dynasty in AD 25, thus founding the Eastern Han (Later Han) dynasty. He ruled over parts of China at first, and through suppression and conquest of regional warlords, the whole of China proper was consolidated by the time of his death in AD 57. During his reign, Taoism was made the official religion of China, and the Chinese folk religion began to decline. Liu Xiu was one of the many descendants of the Han imperial family. Following the usurpation of the Han throne by Wang Mang and the ensuing civil war during the disintegration of Wang's short-lived Xin dynasty, he emerged as one of several descendants of the fallen dynasty claiming the imperial throne. After assembling forces and proclaiming himself emperor in the face of competitors, he was able to defeat his rivals, destroy the peasant ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gengshi Emperor
The Gengshi Emperor (; died AD 25), born Liu Xuan (), was an emperor of the Han dynasty restored after the fall of Wang Mang's Xin dynasty brought on by the Lülin. He was also known by his courtesy name Shenggong () and as the King or Prince of Huaiyang (), a posthumous title bestowed upon him by Emperor Guangwu of the Eastern Han. The Gengshi Emperor was viewed as a weak and incompetent ruler, who briefly ruled over an empire willing to let him rule over them, but was unable to keep that empire together. He was eventually deposed by the Chimei ("Red Eyebrows") and strangled a few months after his defeat. Traditional historians treat his emperor status ambiguously—and sometimes he would be referred to as an emperor (with reference to his era name—thus, the Gengshi Emperor) and sometimes he would be referred to by his posthumous title, Prince of Huaiyang. The later title implied that he was only a pretender and the Eastern Han was the legitimate restoration of the earlier Han. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Hui Of Jin
Duke Hui of Jin (died 637BC), born Yiwu, was the duke of Jin (.650–637BC) during the Spring and Autumn Period of China's Zhou dynasty. Life Early life Yiwu was one of the nine sons of Duke Xian. His mother was Xiao Rongzi. He was the younger sibling of Shensheng and Chong'er (later Duke Wen) and the older sibling of Xiqi. As part of her scheme to secure the succession to her son, the concubine Li Ji removed Xiqi's older siblings from the capital on the pretext of pacifying their territories. Prince Yiwu was sent to defend Erqu in what is now Ji County, Shanxi. After the death of Duke Xian in the ninth lunar month during 651BC, Li Ji placed the 15-year-old Xiqi on the throne and made Xun Xi chancellor to help him with administration. In the tenth lunar month of 651BC, before Duke Xian had even been properly buried, a Jin minister named Li Ke killed Xiqi. The chancellor Xun Xi then placed Zhuozi, the youngest son of Duke Xian, on the throne even though he was still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xi Zuochi
Xi Zuochi (after 316 – 384), courtesy name Yanwei, was a Jin dynasty historian native to Xiangyang, Hubei. He is principally remembered for being the first historian to regard the Wei dynasty as an illegitimate successor to the Han dynasty. Life Born into a powerful family of local magnates, Xi Zuochi was ambitious and studious from a young age. Beginning his career as a clerk, Xi Zuochi came to the attention of Inspector of Jing Province Huan Wen through the repeated recommendations of Yuan Qiao (), magistrate of Jiangxia Commandery. Huan Wen greatly esteemed Xi Zuochi, promoting him three times during the course of a single year, such that Xi Zuochi held the position of Superintendent of Records in the central administration of Jing Province while he was still a young man, possibly not yet thirty years old. Huan Wen would occasionally employ Xi Zuochi as an administrative aide whilst on campaign, and he excelled in all his duties whether in camp or in the office.''Book of Ji ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiang Yu
Xiang Yu (, –202 BC), born Xiang Ji (), was the Hegemon-King (Chinese: 霸王, ''Bà Wáng'') of Western Chu during the Chu–Han Contention period (206–202 BC) of China. A noble of the Chu state, Xiang Yu rebelled against the Qin dynasty and became a prominent warlord. He was granted the title of "Duke of Lu" () by King Huai II of the restoring Chu state in 208 BC. The following year, he led the Chu forces to victory at the Battle of Julu against the Qin armies led by Zhang Han. After the fall of Qin, Xiang Yu was enthroned as the "Hegemon-King of Western Chu" () and ruled a vast area covering modern-day central and eastern China, with Pengcheng as his capital. He engaged Liu Bang, the founding emperor of the Han dynasty, in a long struggle for power, known as the Chu–Han Contention, which concluded with his eventual defeat at the Battle of Gaixia and his suicide. Xiang Yu is depicted in the Wu Shuang Pu (, Table of Peerless Heroes) by Jin Guliang. Names and titles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Gaozu Of Han
Emperor Gaozu of Han (256 – 1 June 195 BC), born Liu Bang () with courtesy name Ji (季), was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning in 202–195 BC. His temple name was "Taizu" while his posthumous name was Emperor Gao, or Gaodi; "Gaozu of Han", derived from the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', is the common way of referring to this sovereign even though he was not accorded the temple name "Gaozu", which literally means "High Founder". Liu Bang was one of the few dynasty founders in Chinese history who was born into a peasant family. Prior to coming to power, Liu Bang initially served for the Qin dynasty as a minor law enforcement officer in his home town Pei County, within the conquered state of Chu. With the First Emperor's death and the Qin Empire's subsequent political chaos, Liu Bang renounced his civil service position and became an anti-Qin rebel leader. He won the race against fellow rebel leader Xiang Yu to invade the Qin heartlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the ChuHan contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) and the Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the "Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as "Han characters". The emperor was at the pinnacle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Wei
Wei ( Hanzi: 魏; pinyin: ''Wèi'' < : *''ŋjweiC'' < : *''ŋuiC'') (220–266), known as Cao Wei or Former Wei in historiography, was one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the period (220–280). With its capital initially located at , and thereafter |
Han Xin
Han Xin (; 231/230–196 BC) was a Chinese military general and politician who served Liu Bang during the Chu–Han Contention and contributed greatly to the founding of the Han dynasty. Han Xin was named as one of the "Three Heroes of the early Han dynasty" ( zh, script=Hant, 漢初三傑), along with Zhang Liang and Xiao He. Han Xin is best remembered as a brilliant military leader for the strategies and tactics he employed in warfare, some of which became the origins of certain Chinese idioms, he was undefeated in battle and for his accomplishments he was considered the "God of War". In recognition of Han Xin's contributions, Liu Bang conferred the titles of " King of Qi" on him in 203 BC and "King of Chu" in the following year. However, Liu Bang feared Han Xin's growing influence and gradually reduced his authority, demoting him to "Marquis of Huaiyin" in late 202 BC. In 196 BC, Han Xin was accused of participating in a rebellion and lured into a trap and executed on Empre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Ping (Han Dynasty)
Chen Ping (陈平 d. 178 BC) was a Chinese politician who served as a chancellor in the early Western Han dynasty. He was an advisor to Liu Bang (Emperor Gao), the founding emperor of the Han dynasty. He played an important role in helping Liu Bang overcome his rival, Xiang Yu, in the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC). Early life Chen Ping was from Huyou Town (), Yangwu (陽武 present-day Lankao County, Henan). He was born in a peasant family, and his parents died when he was still young so he lived with his elder brother. His elder brother worked as a farmer on the 30 '' mu'' of land that their family owned while Chen Ping spent his time reading. As a child, Chen Ping had an ambition to serve his country. Chen Ping remained single until his 30s, when he met Zhang Fu (), a wealthy man. Zhang Fu had a granddaughter who married five times, but all her husbands died not long after they married her, so other men did not want to marry her. One day, Zhang Fu followed Chen Ping to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)