|
Feedline
In a radio antenna, the feed line (feedline), or feeder, is the cable or other transmission line that connects the antenna with the radio transmitter or receiver. In a transmitting antenna, it feeds the radio frequency (RF) current from the transmitter to the antenna, where it is radiated as radio waves. In a receiving antenna it transfers the tiny RF voltage induced in the antenna by the radio wave to the receiver. In order to carry RF current efficiently, feed lines are made of specialized types of cable called transmission line. The most widely used types of feed line are coaxial cable, twin-lead, ladder line, and at microwave frequencies, waveguide. Particularly with a transmitting antenna, the feed line is a critical component that must be adjusted to work correctly with the antenna and transmitter. Each type of transmission line has a specific characteristic impedance. This must be matched to the impedance of the antenna and the transmitter, to transfer powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
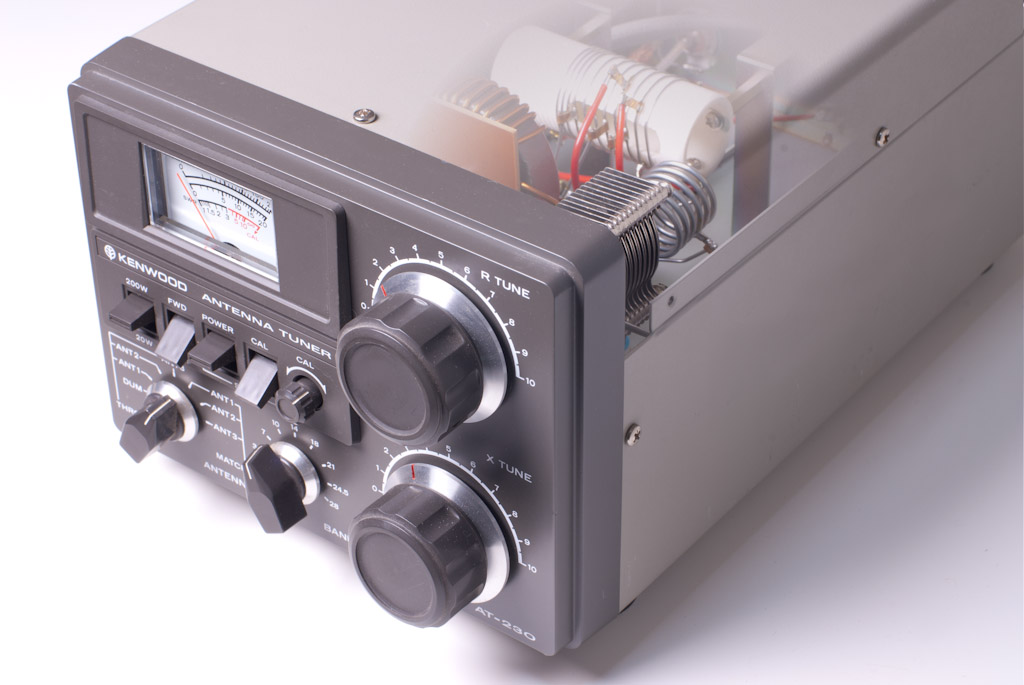
Antenna Tuner
An antenna tuner (and any of the names in the list below) is a device that is inserted between a radio transmitter and its antenna; when placed close by the antenna and properly adjusted (tuned) it optimizes power transfer by matching the impedance of the radio to the impedance of the end of the feedline connecting the antenna to the transmitter. Various alternate names are used for this device: antenna matching unit, impedance matching unit, matchbox, matching network, transmatch, antenna match, antenna tuning unit (ATU), antenna coupler, feedline coupler. English language technical jargon makes no distinction between the terms. Antenna tuners are particularly important for use with transmitters. Transmitters are typically designed to feed power into a reactance-free, resistive load of a specific value: Radio transmitters built after the 1950s are almost all designed for 50 Ω (Ohm) cabling. However the impedance of any antenna normally varies, depending on freque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin-lead
Twin-lead cable is a two-conductor flat cable used as a balanced transmission line to carry radio frequency (RF) signals. It is constructed of two stranded or solid copper or copper-clad steel wires, held a precise distance apart by a plastic (usually polyethylene) ribbon. The uniform spacing of the wires is the key to the cable's function as a transmission line; any abrupt changes in spacing would reflect some of the signal back toward the source. The plastic also covers and insulates the wires. It is available with several different values of characteristic impedance, the most common type is 300 ohm. Twin lead is mainly used as an antenna feedline at shortwave and VHF frequencies, to connect radio receivers and transmitters to their antennas. It can have significantly lower signal loss than miniature flexible coaxial cable, the main alternative type of feedline at these frequencies; for example, type RG-58 coaxial cable loses 6.6 dB per 100 m at 30 MHz, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladder Line
Twin-lead cable is a two-conductor flat cable used as a balanced transmission line to carry radio frequency (RF) signals. It is constructed of two stranded or solid copper or copper-clad steel wires, held a precise distance apart by a plastic (usually polyethylene) ribbon. The uniform spacing of the wires is the key to the cable's function as a transmission line; any abrupt changes in spacing would reflect some of the signal back toward the source. The plastic also covers and insulates the wires. It is available with several different values of characteristic impedance, the most common type is 300 ohm. Twin lead is mainly used as an antenna feedline at shortwave and VHF frequencies, to connect radio receivers and transmitters to their antennas. It can have significantly lower signal loss than miniature flexible coaxial cable, the main alternative type of feedline at these frequencies; for example, type RG-58 coaxial cable loses 6.6 dB per 100 m at 30 MHz, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna (radio)
In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver. In transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic wave In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visib ...s (radio waves). In Receiver (radio), reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be Amplifier, amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment. An antenna is an array of conductor (material), conductors (Driven element, elements), elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable, or coax (pronounced ) is a type of electrical cable consisting of an inner conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting shield, with the two separated by a dielectric ( insulating material); many coaxial cables also have a protective outer sheath or jacket. The term ''coaxial'' refers to the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing a geometric axis. Coaxial cable is a type of transmission line, used to carry high-frequency electrical signals with low losses. It is used in such applications as telephone trunk lines, broadband internet networking cables, high-speed computer data busses, cable television signals, and connecting radio transmitters and receivers to their antennas. It differs from other shielded cables because the dimensions of the cable and connectors are controlled to give a precise, constant conductor spacing, which is needed for it to function efficiently as a transmission line. Coaxial cable was used in the first (1858) and followin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Wave Ratio
In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the transmission line, and SWR is defined as the ratio of the partial standing wave's amplitude at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at a node (minimum) along the line. The SWR is usually thought of in terms of the maximum and minimum AC voltages along the transmission line, thus called the voltage standing wave ratio or VSWR (sometimes pronounced "vizwar" ). For example, the VSWR value 1.2:1 means that an AC voltage, due to standing waves along the transmission line, will have a peak value 1.2 times that of the minimum AC voltage along that line, if the line is at least one half wavelength long. The SWR can be also defined as the ratio of the maximum amplitude to minimum amplitude of the transmission line's currents, electric field strength ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SWR Meter
The standing wave ratio meter, SWR meter, ISWR meter (current "" SWR), or VSWR meter (voltage SWR) measures the standing wave ratio (SWR) in a transmission line. The meter indirectly measures the degree of mismatch between a transmission line and its load (usually an antenna). Electronics technicians use it to adjust radio transmitters and their antennas and feedlines to be impedance matched so they work together properly, and evaluate the effectiveness of other impedance matching efforts. Directional SWR meter A directional SWR meter measures the magnitude of the forward and reflected waves by sensing each one individually, with directional couplers. A calculation then produces the SWR. Referring to the above diagram, the transmitter (TX) and antenna (ANT) terminals connect via an internal transmission line. This main line is electromagnetically coupled to two smaller sense lines (directional couplers). These are terminated with resistors at one end and diode rectifiers at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveguide (electromagnetism)
In radio-frequency engineering and communications engineering, waveguide is a hollow metal pipe used to carry radio waves. This type of waveguide is used as a transmission line mostly at microwave frequencies, for such purposes as connecting microwave transmitters and receivers to their antennas, in equipment such as microwave ovens, radar sets, satellite communications, and microwave radio links. The electromagnetic waves in a (metal-pipe) waveguide may be imagined as travelling down the guide in a zig-zag path, being repeatedly reflected between opposite walls of the guide. For the particular case of rectangular waveguide, it is possible to base an exact analysis on this view. Propagation in a dielectric waveguide may be viewed in the same way, with the waves confined to the dielectric by total internal reflection at its surface. Some structures, such as non-radiative dielectric waveguides and the Goubau line, use both metal walls and dielectric surfaces to confine the wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes: * ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma radiation (γ) * ''particle radiation'', such as alpha radiation (α), beta radiation (β), proton radiation and neutron radiation (particles of non-zero rest energy) * '' acoustic radiation'', such as ultrasound, sound, and seismic waves (dependent on a physical transmission medium) * ''gravitational wave, gravitational radiation'', that takes the form of gravitational waves, or ripples in the curvature of spacetime Radiation is often categorized as either ''ionizing radiation, ionizing'' or ''non-ionizing radiation, non-ionizing'' depending on the energy of the radiated particles. Ionizing radiation carries more than 10 electron volt, eV, which is enough to ionize atoms and molecules and break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
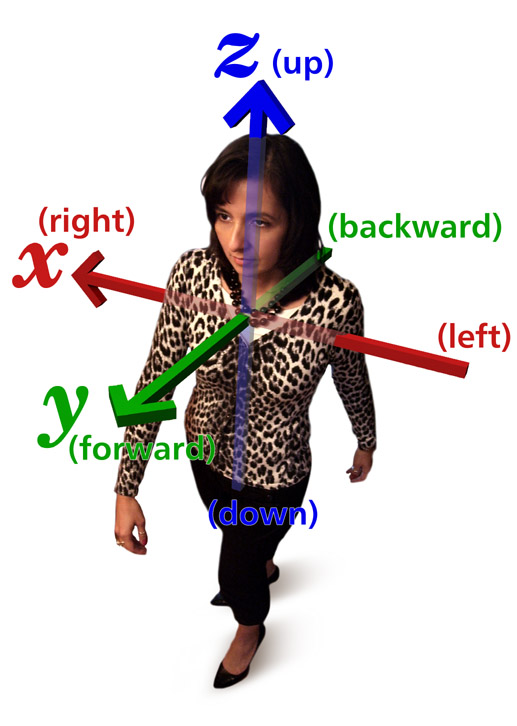
Direction (geometry, Geography)
Body relative directions (also known as egocentric coordinates) are geometrical orientations relative to a body such as a human person's. The most common ones are: left and right; forward(s) and backward(s); up and down. They form three pairs of orthogonal axes. Traditions and conventions Since definitions of left and right based on the geometry of the natural environment are unwieldy, in practice, the meaning of relative direction words is conveyed through tradition, acculturation, education, and direct reference. One common definition of up and down uses gravity and the planet Earth as a frame of reference. Since there is a very noticeable force of gravity acting between the Earth and any other nearby object, down is defined as that direction which an object moves in reference to the Earth when the object is allowed to fall freely. Up is then defined as the opposite direction of down. Another common definition uses a human body, standing upright, as a frame of reference. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnitude (mathematics)
In mathematics, the magnitude or size of a mathematical object is a property which determines whether the object is larger or smaller than other objects of the same kind. More formally, an object's magnitude is the displayed result of an order theory, ordering (or ranking)—of the class (mathematics), class of objects to which it belongs. In physics, magnitude can be defined as quantity or distance. History The Greeks distinguished between several types of magnitude, including: *Positive fractions *Line segments (ordered by length) *Geometric shape, Plane figures (ordered by area) *Solid geometry, Solids (ordered by volume) *Angle, Angles (ordered by angular magnitude) They proved that the first two could not be the same, or even isomorphic systems of magnitude. They did not consider negative number, negative magnitudes to be meaningful, and ''magnitude'' is still primarily used in contexts in which zero is either the smallest size or less than all possible sizes. Numbers Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Current
An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is measured as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface or into a control volume. The moving particles are called charge carriers, which may be one of several types of particles, depending on the conductor. In electric circuits the charge carriers are often electrons moving through a wire. In semiconductors they can be electrons or holes. In an electrolyte the charge carriers are ions, while in plasma, an ionized gas, they are ions and electrons. The SI unit of electric current is the ampere, or ''amp'', which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. The ampere (symbol: A) is an SI base unit. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter. Electric currents create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, generators, inductors, and transformers. In ordinary con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |