|
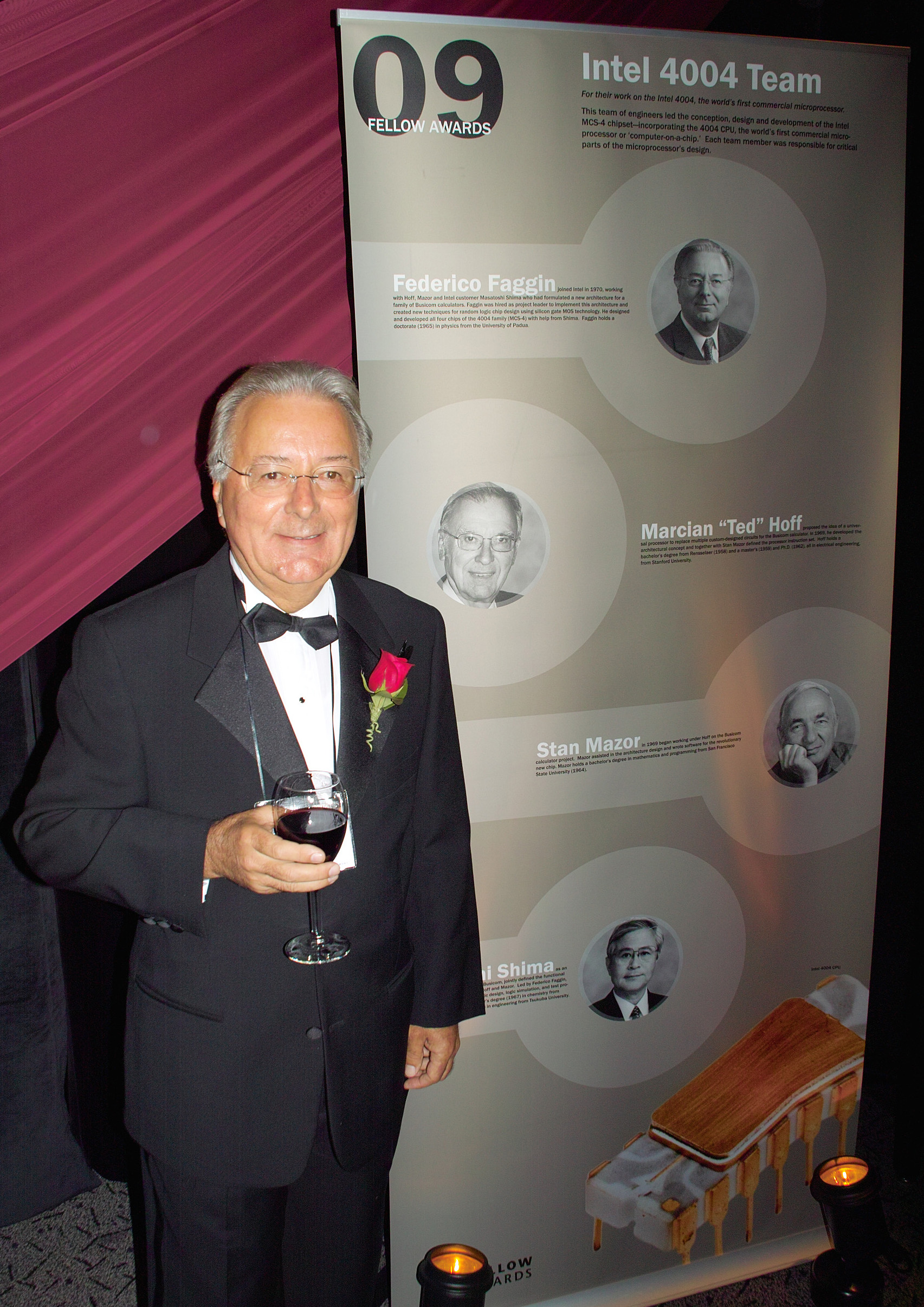
Federico Faggin
Federico Faggin (, ; born 1 December 1941) is an Italian physicist, engineer, inventor and entrepreneur. He is best known for designing the first commercial microprocessor, the Intel 4004. He led the 4004 (MCS-4) project and the design group during the first five years of Intel's microprocessor effort. Faggin also created, while working at Fairchild Semiconductor in 1968, the self-aligned MOS (metal–oxide–semiconductor) silicon-gate technology (SGT), which made possible MOS semiconductor memory chips, CCD image sensors, and the microprocessor. After the 4004, he led development of the Intel 8008 and 8080, using his SGT methodology for random logic chip design, which was essential to the creation of early Intel microprocessors. He was co-founder (with Ralph Ungermann) and CEO of Zilog, the first company solely dedicated to microprocessors, and led the development of the Zilog Z80 and Z8 processors. He was later the co-founder and CEO of Cygnet Technologies, and then Synapti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicenza
Vicenza ( , ; ) is a city in northeastern Italy. It is in the Veneto region at the northern base of the ''Monte Berico'', where it straddles the Bacchiglione River. Vicenza is approximately west of Venice and east of Milan. Vicenza is a thriving and cosmopolitan city, with a rich history and culture, and many museums, art galleries, piazzas, villas, churches and elegant Renaissance '' palazzi''. With the Palladian Villas of the Veneto in the surrounding area, and his renowned ''Teatro Olimpico'' (Olympic Theater), the "city of Palladio" has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1994. In December 2008, Vicenza had an estimated population of 115,927 and a metropolitan area of 270,000. Vicenza is the third-largest Italian industrial centre as measured by the value of its exports, and is one of the country's wealthiest cities, in large part due to its textile and steel industries, which employ tens of thousands. Additionally, about one fifth of the country's gold a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyoto Prize
The is Japan's highest private award for lifetime achievement in the arts and sciences. It is given not only to those that are top representatives of their own respective fields, but to "those who have contributed significantly to the scientific, cultural, and spiritual betterment of mankind". The Kyoto Prize was created in collaboration with the Nobel Foundation and is regarded by many as Japan's version of the Nobel Prize, representing one of the most prestigious awards available in fields that are not traditionally honored with a Nobel. The prizes are endowed with 100 million yen (roughly 800,000 USD) per category and have been awarded annually since 1985 by the Inamori Foundation, founded by Kazuo Inamori. The laureates are announced each June; the prize presentation ceremony and related events are held in Kyoto, Japan, each November. Categories and fields The Kyoto Prize consists of three different categories, each with 4 subfields. The subfields rotate every year to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zilog Z8
The Zilog Z8 is a microcontroller architecture, originally introduced in 1979, which today also includes the Z8 Encore!, eZ8 Encore!, eZ8 Encore! XP, and eZ8 Encore! MC families. Signifying features of the architecture are up to 4,096 fast on-chip registers which may be used as accumulators, pointers, or as ordinary random-access memory (RAM). A 16-bit address space for between 1 kibibyte (KB) and 64 KB of either programmable read-only memory (PROM, OTP), read-only memory (ROM), or flash memory, are used to store code and constants, and there is a second 16-bit address space which can be used for large applications. On chip peripherals include analog-to-digital converter (A/D), Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) bus and Inter-Integrated Circuit (I²C) channels, IrDA encoders/decoders etc. There are versions with from 8 up to 80 pins, housed in dual in-line package (PDIP), Quad Flat No-leads package (MicroLeadFrame, MLF), small outline integrated circuit (SOIC), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Ungermann
Ralph Kelley Ungermann (20 January 1942 – 2 June 2015) was an American engineer and entrepreneur. He is best known for founding Zilog with Federico Faggin and Ungermann-Bass with Charlie Bass. Due to his work in U-B, he was considered to be a founding father of the data communications industry. Early life and education Ralph was born in Provo, Utah on January 20, 1942. When he was 3 years old, his family moved to Santa Paula, California. At first, Ralph wanted to study law but he changed his idea to study engineering after witnessing the launch of Sputnik 1, first satellite ever to the space. He enrolled to University of California, Berkeley and received a Bachelor's degree. Then he received Master's degree in Computer architecture from University of California, Irvine. After college, Ralph started to work at Collins Radio, where he got fascinated with semiconductors and early LAN technology.https://archive.computerhistory.org/resources/access/text/2018/03/102738765-05-01 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Microprocessors
This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of Intel's processors from the pioneering 4-bit 4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product. Latest 13th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Raptor Lake") 12th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Alder Lake") Mobile (codenamed "Alder Lake") 11th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Rocket Lake") Mobile (codenamed "Tiger Lake") 10th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Comet Lake") Mobile (codenamed "Comet Lake", " Ice Lake", and " Amber Lake") 9th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Coffee Lake Refresh") 8th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Coffee Lake") Mobile (codenamed "Coffee Lake", " Amber Lake" and " Whiskey Lake") 7th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Kaby Lake" and "Skylake-X") Mobile (codenamed "Kaby Lake" and " Apollo Lake") All processors All processors are listed in chron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 8008
The Intel 8008 ("''eight-thousand-eight''" or "''eighty-oh-eight''") is an early byte-oriented microprocessor designed by Computer Terminal Corporation (CTC), implemented and manufactured by Intel, and introduced in April 1972. It is an 8-bit CPU with an external 14-bit address bus that could address 16 KB of memory. Originally known as the 1201, the chip was commissioned by Computer Terminal Corporation (CTC) to implement an instruction set of their design for their Datapoint 2200 programmable terminal. As the chip was delayed and did not meet CTC's performance goals, the 2200 ended up using CTC's own TTL-based CPU instead. An agreement permitted Intel to market the chip to other customers after Seiko expressed an interest in using it for a calculator. History CTC formed in San Antonio in 1968 under the direction of Austin O. "Gus" Roche and Phil Ray, both NASA engineers. Roche, in particular, was primarily interested in producing a desktop computer. However, given the immaturi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
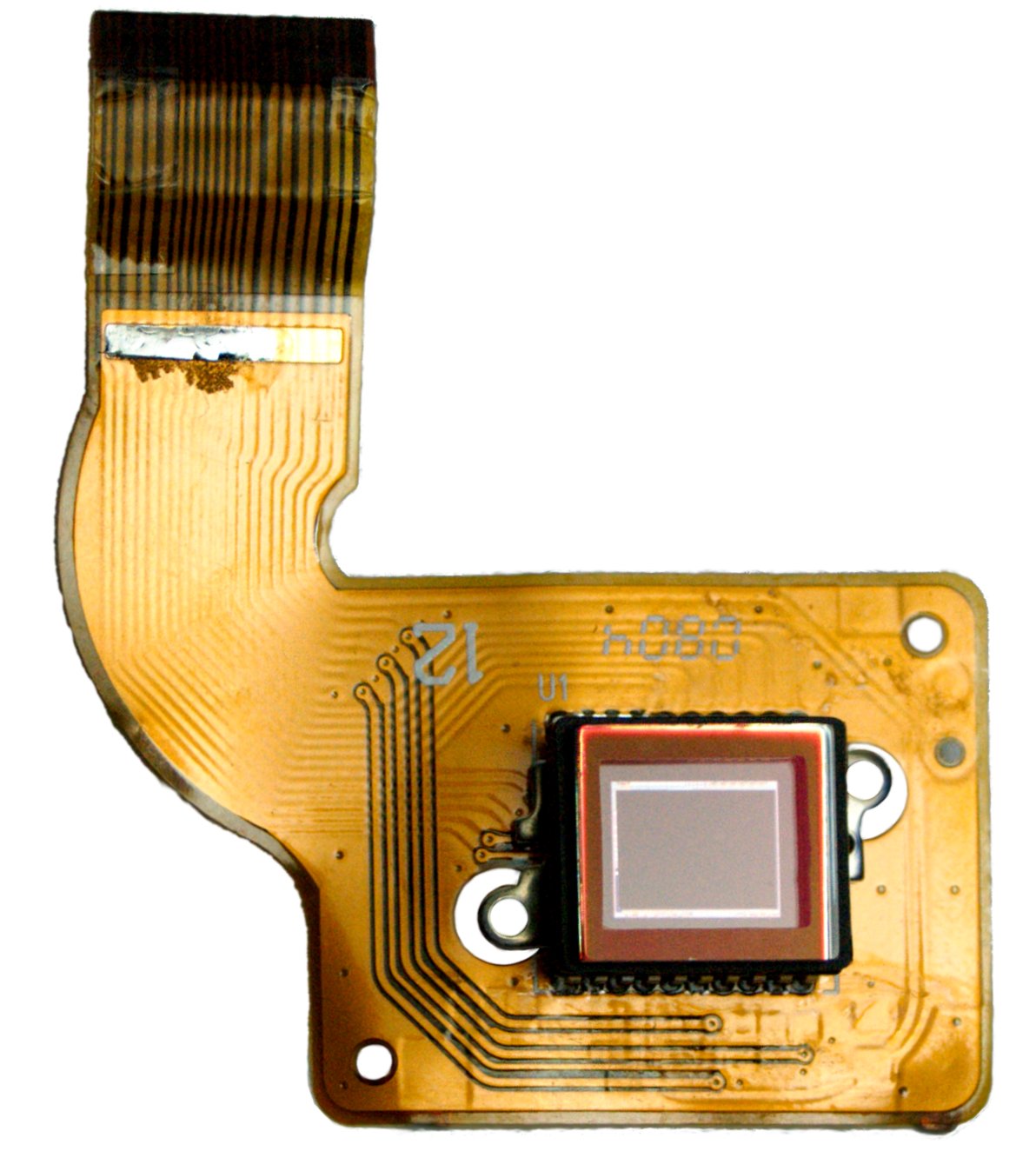
Image Sensors
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they pass through or reflect off objects) into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging. The two main types of electronic image sensors are the charge-coupled device (CCD) and the active-pixel sensor (CMOS sensor). Both CCD and CMOS sensors are based on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology, with CCDs based on MOS capacitors and CMOS sensors based on M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and professional digital cameras, act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Chip
Semiconductor memory is a digital electronics, digital electronic semiconductor device used for digital data storage, such as computer memory. It typically refers to devices in which data is stored within metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) memory cell (computing), memory cells on a silicon integrated circuit memory chip. There are numerous different types using different semiconductor technologies. The two main types of random-access memory (RAM) are static RAM (SRAM), which uses several transistors per memory cell, and dynamic RAM (DRAM), which uses a transistor and a MOS capacitor per cell. Non-volatile memory (such as EPROM, EEPROM and flash memory) uses floating-gate memory cells, which consist of a single Floating-gate MOSFET, floating-gate transistor per cell. Most types of semiconductor memory have the property of random access, which means that it takes the same amount of time to access any memory location, so data can be efficiently accessed in any random order. This co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal–oxide–semiconductor
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. A metal-insulator-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MISFET) is a term almost synonymous with MOSFET. Another synonym is IGFET for insulated-gate field-effect transistor. The basic principle of the field-effect transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925.Lilienfeld, Julius Edgar (1926-10-08) "Method and apparatus for controlling electric currents" upright=1.6, Two power MOSFETs in V_in_the_''off''_state,_and_can_conduct_a_continuous_current_of_30 surface-mount_packages._Operating_as_switches,_each_of_these_components_can_sus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-aligned Gate
In semiconductor electronics fabrication technology, a self-aligned gate is a transistor manufacturing approach whereby the gate electrode of a MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor) is used as a mask for the doping of the source and drain regions. This technique ensures that the gate is naturally and precisely aligned to the edges of the source and drain. The use of self-aligned gates in MOS transistors is one of the key innovations that led to the large increase in computing power in the 1970s. Self-aligned gates are still used in most modern integrated circuit processes. Introduction IC construction Integrated circuits (ICs, or "chips") are produced in a multi-step process that builds up multiple layers on the surface of a disk of silicon known as a "wafer". Each layer is patterned by coating the wafer in photoresist and then exposing it to ultraviolet light being shone through a stencil-like "mask". Depending on the process, the photoresist that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit. The integrated circuit is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock-driven, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system. The integration of a whole CPU onto a single or a few integrated circuits using Very-Large-Scale Integration (VLSI) greatly reduced the cost of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)