|
Fasta Pasta
FASTA is a DNA and protein sequence alignment software package first described by David J. Lipman and William R. Pearson in 1985. Its legacy is the FASTA format which is now ubiquitous in bioinformatics. History The original FASTA program was designed for protein sequence similarity searching. Because of the exponentially expanding genetic information and the limited speed and memory of computers in the 1980s heuristic methods were introduced aligning a query sequence to entire data-bases. FASTA, published in 1987, added the ability to do DNA:DNA searches, translated protein:DNA searches, and also provided a more sophisticated shuffling program for evaluating statistical significance. There are several programs in this package that allow the alignment of protein sequences and DNA sequences. Nowadays, increased computer performance makes it possible to perform searches for local alignment detection in a database using the Smith–Waterman algorithm. FASTA is pronounced "fas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Pearson (scientist)
William Raymond Pearson is professor of biochemistry and molecular Genetics in the School of Medicine at the University of Virginia. Pearson is best known for the development of the FASTA format. Education Pearson graduated with a BS in chemistry from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. He received his PhD in 1977 from Caltech. Career and research After his PhD, Pearson did a postdoctoral fellowship at Johns Hopkins University. Pearson's research interests are in computational biology. He was awarded Fellowship of the International Society for Computational Biology The International Society for Computational Biology (ISCB) is a scholarly society for researchers in computational biology and bioinformatics. The society was founded in 1997 to provide a stable financial home for the Intelligent Systems for Mole ... (ISCB) in 2018 for outstanding contributions to the fields of computational biology and bioinformatics. References Living people American bioinform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Virginia
The University of Virginia (UVA) is a Public university#United States, public research university in Charlottesville, Virginia. Founded in 1819 by Thomas Jefferson, the university is ranked among the top academic institutions in the United States, with College admissions in the United States, highly selective admission. Set within the The Lawn, Academical Village, a World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site, the university is referred to as a "Public Ivy" for offering an academic experience similar to that of an Ivy League university. It is known in part for certain rare characteristics among public universities such as #1800s, its historic foundations, #Honor system, student-run academic honor code, honor code, and Secret societies at the University of Virginia, secret societies. The original governing Board of Visitors included three List of presidents of the United States, U.S. presidents: Thomas Jefferson, Jefferson, James Madison, and James Monroe. The latter as si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
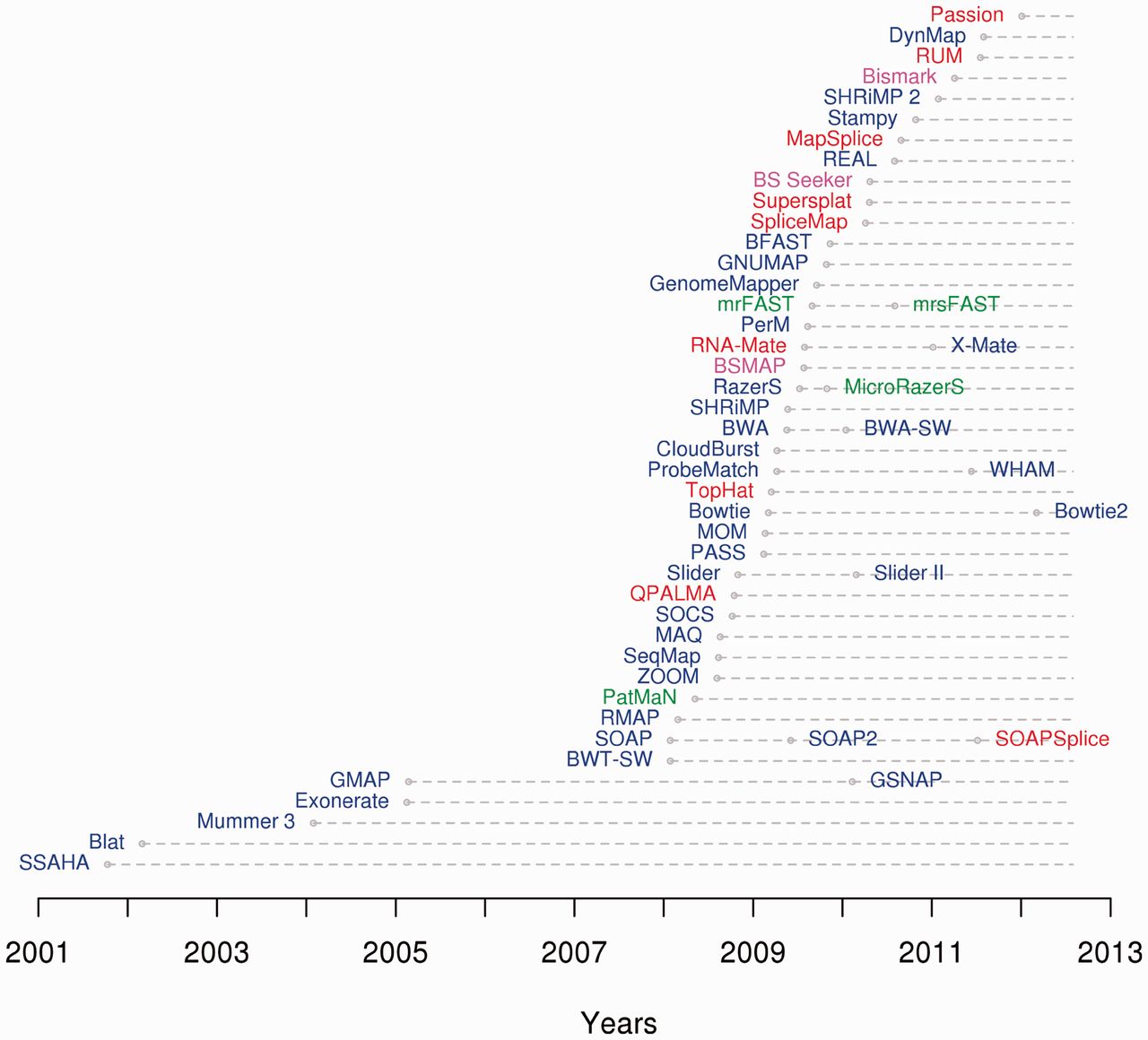
Sequence Alignment Software
This list of sequence alignment software is a compilation of software tools and web portals used in pairwise sequence alignment and multiple sequence alignment. See structural alignment software for structural alignment of proteins. Database search only *Sequence type: protein or nucleotide Pairwise alignment *Sequence type: protein or nucleotide **Alignment type: local or global Multiple sequence alignment *Sequence type: protein or nucleotide. **Alignment type: local or global Genomics analysis *Sequence type: protein or nucleotide Motif finding *Sequence type: protein or nucleotide Benchmarking Alignment viewers, editors Please see List of alignment visualization software. Short-read sequence alignment See also * List of open source bioinformatics software References {{Reflist Sequence Sequence alignment software This list of sequence alignment software is a compilation of software tools and web portals used in pairwise sequence alignment and multiple seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histogram
A histogram is an approximate representation of the distribution of numerical data. The term was first introduced by Karl Pearson. To construct a histogram, the first step is to " bin" (or "bucket") the range of values—that is, divide the entire range of values into a series of intervals—and then count how many values fall into each interval. The bins are usually specified as consecutive, non-overlapping intervals of a variable. The bins (intervals) must be adjacent and are often (but not required to be) of equal size. If the bins are of equal size, a bar is drawn over the bin with height proportional to the frequency—the number of cases in each bin. A histogram may also be normalized to display "relative" frequencies showing the proportion of cases that fall into each of several categories, with the sum of the heights equaling 1. However, bins need not be of equal width; in that case, the erected rectangle is defined to have its ''area'' proportional to the frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD, and is most commonly represented in mathematical texts and equations by the lower case Greek letter σ (sigma), for the population standard deviation, or the Latin letter '' s'', for the sample standard deviation. The standard deviation of a random variable, sample, statistical population, data set, or probability distribution is the square root of its variance. It is algebraically simpler, though in practice less robust, than the average absolute deviation. A useful property of the standard deviation is that, unlike the variance, it is expressed in the same unit as the data. The standard deviation of a popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Similarity Measure
In statistics and related fields, a similarity measure or similarity function or similarity metric is a real-valued function that quantifies the similarity between two objects. Although no single definition of a similarity exists, usually such measures are in some sense the inverse of distance metrics: they take on large values for similar objects and either zero or a negative value for very dissimilar objects. Though, in more broad terms, a similarity function may also satisfy metric axioms. Cosine similarity is a commonly used similarity measure for real-valued vectors, used in (among other fields) information retrieval to score the similarity of documents in the vector space model. In machine learning, common kernel functions such as the RBF kernel can be viewed as similarity functions. Use in clustering In spectral clustering, a similarity, or affinity, measure is used to transform data to overcome difficulties related to lack of convexity in the shape of the data distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substitution Matrix
In bioinformatics and evolutionary biology, a substitution matrix describes the frequency at which a character in a nucleotide sequence or a protein sequence changes to other character states over evolutionary time. The information is often in the form of log odds of finding two specific character states aligned and depends on the assumed number of evolutionary changes or sequence dissimilarity between compared sequences. It is an application of a stochastic matrix. Substitution matrices are usually seen in the context of amino acid or DNA sequence alignments, where they are used to calculate similarity scores between the aligned sequences. Background In the process of evolution, from one generation to the next the amino acid sequences of an organism's proteins are gradually altered through the action of DNA mutations. For example, the sequence ALEIRYLRD could mutate into the sequence ALEINYLRD in one step, and possibly AQEINYQRD over a longer period of evolutionary t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligonucleotide
Oligonucleotides are short DNA or RNA molecules, oligomers, that have a wide range of applications in genetic testing, research, and forensics. Commonly made in the laboratory by solid-phase chemical synthesis, these small bits of nucleic acids can be manufactured as single-stranded molecules with any user-specified sequence, and so are vital for artificial gene synthesis, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA sequencing, molecular cloning and as molecular probes. In nature, oligonucleotides are usually found as small RNA molecules that function in the regulation of gene expression (e.g. microRNA), or are degradation intermediates derived from the breakdown of larger nucleic acid molecules. Oligonucleotides are characterized by the sequence of nucleotide residues that make up the entire molecule. The length of the oligonucleotide is usually denoted by " -mer" (from Greek ''meros'', "part"). For example, an oligonucleotide of six nucleotides (nt) is a hexamer, while one of 25 nt wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K-mer
In bioinformatics, ''k''-mers are substrings of length k contained within a biological sequence. Primarily used within the context of computational genomics and sequence analysis, in which ''k''-mers are composed of nucleotides (''i.e''. A, T, G, and C), ''k''-mers are capitalized upon to assemble DNA sequences, improve heterologous gene expression, identify species in metagenomic samples, and create attenuated vaccines. Usually, the term ''k''-mer refers to all of a sequence's subsequences of length k, such that the sequence AGAT would have four monomers (A, G, A, and T), three 2-mers (AG, GA, AT), two 3-mers (AGA and GAT) and one 4-mer (AGAT). More generally, a sequence of length L will have L - k + 1 ''k''-mers and n^ total possible ''k''-mers, where n is number of possible monomers (e.g. four in the case of DNA). Introduction ''k''-mers are simply length k subsequences. For example, all the possible ''k''-mers of a DNA sequence are shown below: A method of visualizi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heuristic
A heuristic (; ), or heuristic technique, is any approach to problem solving or self-discovery that employs a practical method that is not guaranteed to be optimal, perfect, or rational, but is nevertheless sufficient for reaching an immediate, short-term goal or approximation. Where finding an optimal solution is impossible or impractical, heuristic methods can be used to speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution. Heuristics can be mental shortcuts that ease the cognitive load of making a decision. Examples that employ heuristics include using trial and error, a rule of thumb or an educated guess. Heuristics are the strategies derived from previous experiences with similar problems. These strategies depend on using readily accessible, though loosely applicable, information to control problem solving in human beings, machines and abstract issues. When an individual applies a heuristic in practice, it generally performs as expected. However it can alternatively cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-Coffee
T-Coffee (Tree-based Consistency Objective Function for Alignment Evaluation) is a multiple sequence alignment software using a progressive approach. It generates a library of pairwise alignments to guide the multiple sequence alignment. It can also combine multiple sequences alignments obtained previously and in the latest versions can use structural information from PDB files (3D-Coffee). It has advanced features to evaluate the quality of the alignments and some capacity for identifying occurrence of motifs (Mocca). It produces alignment in the aln format (Clustal) by default, but can also produce PIR, MSF, and FASTA format. The most common input formats are supported (FASTA, PIR). Algorithm T-Coffee algorithm consist of two main features, the first by utilizing heterogeneous data sources it is able to provide simple and flexible means of generating multiple alignments. T-coffee can compute multiple alignments using a library that was generated using a mixture of local and glo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |