|
Fanamaket Language
Tangga is an Oceanic language The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages ... of New Ireland, spoken on Tanga and Feni islands and in Sena, Muliama and Varangansau villages in the Tanglamet area of Namatanai of New Ireland itself. These three locations are highly divergent; children from one understand little to nothing of the others, and adults consider them to be distinct languages, though they recognize their common history of their migration from Tanga and Feni to New Ireland. References Languages of New Ireland Province St George linkage {{MesoMelanesian-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Ireland (island)
New Ireland (Tok Pisin: ''Niu Ailan'') or Latangai, is a large island in Papua New Guinea, approximately in area with 120,000 people. It is named after the island of Ireland. It is the largest island of New Ireland Province, lying northeast of the island of New Britain. Both islands are part of the Bismarck Archipelago, named after Otto von Bismarck, and they are separated by Saint George's Channel. The administrative centre of the island and of New Ireland province is the town of Kavieng located at the northern end of the island. While the island was part of German New Guinea, it was named Neumecklenburg ("New Mecklenburg"). Geography The island is part of the Bismarck Archipelago and is often described as having the shape of a musket. New Ireland is surrounded by the Bismarck Sea in the southwest and by the Pacific Ocean in the northeast. For much of its in length, the island's width varies between less than to , yet the central mountainous spine is very steep an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo-Polynesian Languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesian and Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula. Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan serve as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. The languages spoken south-westward from central Micronesia until Easter Island are sometimes referred to as the Polynesian languages. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family show the strong influence of Sanskrit and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam. Two morphological characteristics of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori, Western Fijian and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Oceanic Languages
The Western Oceanic languages is a linkage of Oceanic languages, proposed and studied by . Classification The West Oceanic linkage is made up of three sub-linkages:. * North New Guinea linkage * Meso-Melanesian linkage * Papuan Tip linkage The center of dispersal was evidently near the Willaumez Peninsula The Willaumez Peninsula is located on the north coast of New Britain in the West New Britain Province. It was named after Jean-Baptiste Philibert Willaumez Jean-Baptiste Philibert Willaumez (7 August 1763 – 17 May 1845) was a French sailor, ... on the north coast of New Britain. Notes References * * {{Austronesian languages Oceanic languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meso-Melanesian Languages
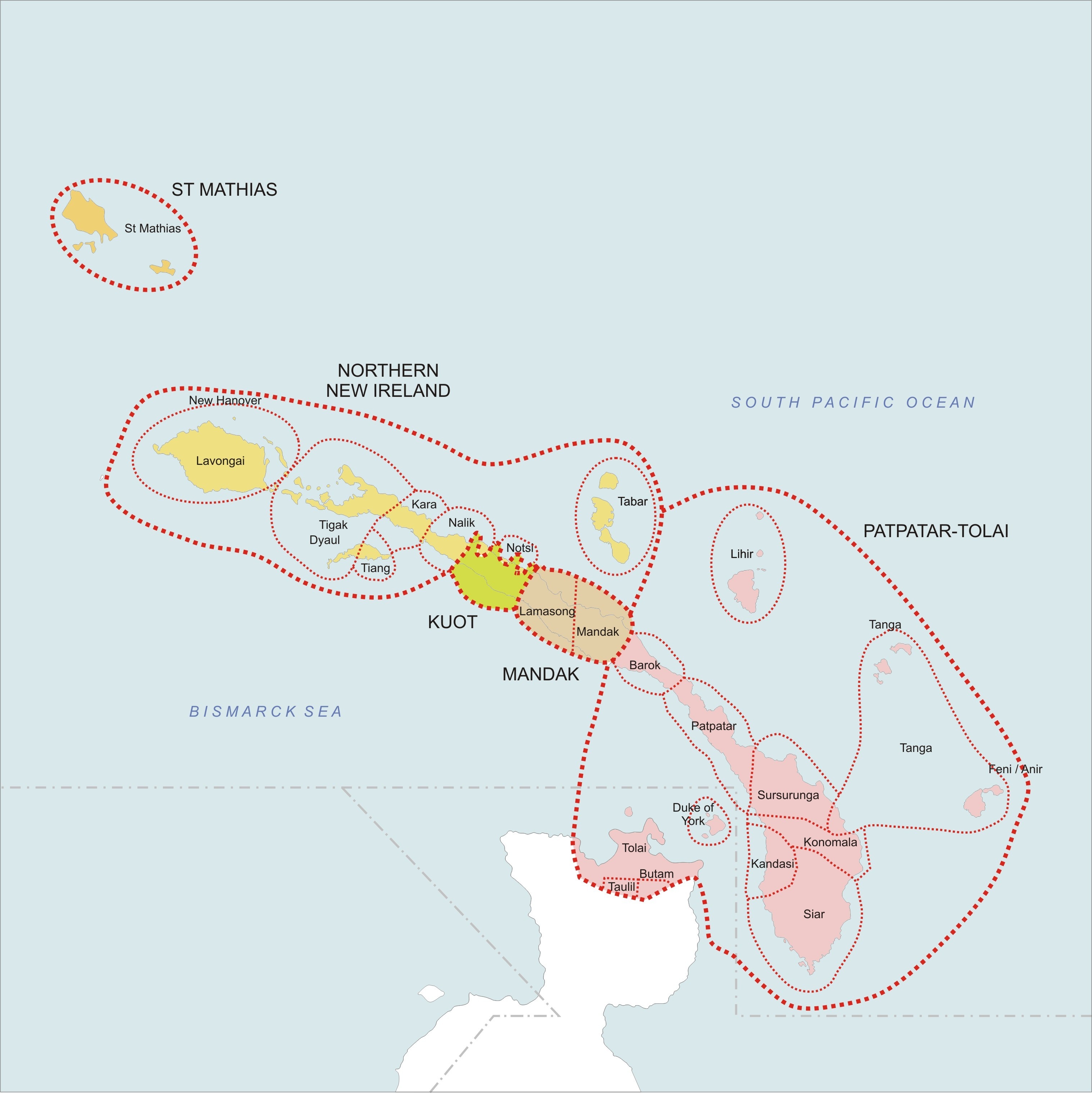
The Meso-Melanesian languages are a Linkage (linguistics), linkage of Oceanic languages spoken in the large Melanesian islands of New Ireland and the Solomon Islands east of New Guinea. Uneapa language, Bali is one of the most conservative languages. Composition The languages group as follows: *Willaumez Peninsula, Willaumez linkage: Bola language (Austronesian), Bola, Bulu language (Oceanic), Bulu, Meramera language, Meramera, Nakanai language, Nakanai *Bali–Vitu: Uneapa language, Bali (Uneapa), Vitu language, Vitu (Muduapa) [may be a single language] *New Ireland – Northwest Solomonic linkage **Tungag–Nalik family: Tigak language, Tigak, Tungag language, Tungag, Nalik language, Nalik, Laxudumau language, Laxudumau, Kara language (Papua New Guinea), Kara, Tiang language, Tiang **Tabar linkage: Mandara language, Madara (Tabar), Lihir language, Lihir, Notsi language, Notsi **Madak linkage: Barok language, Barok, Lavatbura-Lamusong language, Lavatbura-Lamusong, Madak langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Language
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori, Western Fijian and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanga Islands
The Tanga Islands are an island group in Papua New Guinea, located north-east of New Ireland and part of the Bismarck Archipelago. Tanga is made up of four main islands — Boang, Maledok, Lif and Tefa — and a number of smaller, uninhabited islands. Boang (ca. 27 km2) consists entirely of a raised, relatively flat-topped plateau of Pleistocene, coralline limestone, which rises up to 170 m above sea level (asl.) and has sheer cliffs around a large part of its perimeter. The islands are the remnants of a stratovolcano which collapsed to form a caldera A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is .... Lif (283 m), Tefa (155 m), and Malendok (472 m) islands are on the caldera rim, while Bitlik and Bitbok islands are lava domes constructed near the center of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feni Islands
The Feni Islands are an island group in Papua New Guinea, located east of New Ireland, at . It is a part of the Bismarck Archipelago. The largest island of the group is Ambitle, the other island is Babase Island Babase Island is an island of the Feni Islands in Papua New Guinea, located east of New Ireland. It consists of a stratovolcano and a lava dome, joined by an isthmus An isthmus (; ; ) is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas .... References External links Feni Islands on oceandots.com Islands of Papua New Guinea New Ireland Province {{NewIrelandProvince-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namatanai
Namatanai is a town on the island province of New Ireland in Papua New Guinea. It is the second largest settlement on the island and connected to the largest and provincial capital of Kavieng (264 km to the north-west) by the Boluminski Highway. In 2005, Namantanai was estimated to have a population of 1300 people. It is the seat of Namatanai Rural LLG. During German New Guinea German New Guinea (german: Deutsch-Neu-Guinea) consisted of the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups and was the first part of the German colonial empire. The mainland part of the territory, called , ..., Namatanai was an important station. Today the Namatanai Hotel sits on top of the old German Station house. On 28 January 1943, Japanese troops on the Goya Maru landed at Namatanai and searched the station but found no Australian troops and departed. On 15 June 1943, Chinese man, Leong Cheung, was publicly shot in town. Namatanai has a small airfield ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of New Ireland Province
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken language, spoken, sign language, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of Productivity (linguistics), productivity and Displacement (linguistics), displacement, and rely on Convention (norm), social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are speech, spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |