|
FMC7
B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 or CD20 is expressed on the surface of all B-cells beginning at the pro-B phase (CD45R+, CD117+) and progressively increasing in concentration until maturity. In humans CD20 is encoded by the ''MS4A1'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the membrane-spanning 4A gene family. Members of this nascent protein family are characterized by common structural features and similar intron/exon splice boundaries and display unique expression patterns among hematopoietic cells and nonlymphoid tissues. This gene encodes a B-lymphocyte surface molecule that plays a role in the development and differentiation of B-cells into plasma cells. This family member is localized to 11q12, among a cluster of family members. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants that encode the same protein. Function The protein has no known natural ligand and its function is to enable optimal B-cell immune response, specifically against T-independent antigens. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Early on, there are typically no symptoms. Later, non-painful lymph node swelling, feeling tired, fever, night sweats, or weight loss for no clear reason may occur. Enlargement of the spleen and low red blood cells (anemia) may also occur. It typically worsens gradually over years. Risk factors include having a family history of the disease, with 10% of those who develop CLL having a family history of the disease. Exposure to Agent Orange, certain insecticides, sun exposure, exposure to hepatitis C virus, and common infections are also considered risk factors. CLL results in the buildup of B cell lymphocytes in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, and blood. These cells do not function well and crowd out healthy blood cells. CLL is divided into two main types: those with a mutated IGHV gene and those without. Diagnosis is typically based on blood te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hairy Cell Leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia is an uncommon hematological malignancy characterized by an accumulation of abnormal B lymphocytes. It is usually classified as a subtype of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Hairy cell leukemia makes up about 2% of all leukemias, with fewer than 2,000 new cases diagnosed annually in North America and Western Europe combined. Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) was originally described as histiocytic leukemia, malignant reticulosis, or lymphoid myelofibrosis in publications dating back to the 1920s. The disease was formally named leukemic reticuloendotheliosis, and its characterization was significantly advanced by Bertha Bouroncle and colleagues at the Ohio State University College of Medicine in 1958. Its common name, which was coined in 1966, is derived from the "hairy" appearance of the malignant B cells under a microscope. Signs and symptoms In HCL, the "hairy cells" (malignant B lymphocytes) accumulate in the bone marrow, interfering with the production of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
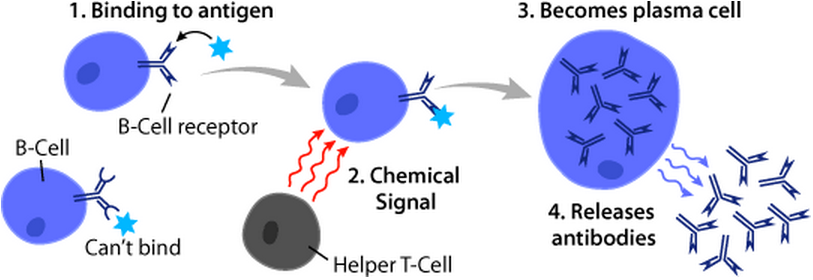
B-cells
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphomas
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, drenching sweats, unintended weight loss, itching, and constantly feeling tired. The enlarged lymph nodes are usually painless. The sweats are most common at night. Many subtypes of lymphomas are known. The two main categories of lymphomas are the non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) (90% of cases) and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) (10%). The World Health Organization (WHO) includes two other categories as types of lymphoma – multiple myeloma and immunoproliferative diseases. Lymphomas and leukemias are a part of the broader group of tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Risk factors for Hodgkin lymphoma include infection with Epstein–Barr virus and a history of the disease in the family. Risk factors for common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocrelizumab
Ocrelizumab, sold under the brand name Ocrevus, is a medication used for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS). It is a humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. It targets CD20 marker on B lymphocytes and hence is an immunosuppressive drug. Ocrelizumab binds to an epitope that overlaps with the epitope to which rituximab binds. It was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in March 2017, and the first FDA approved drug for the primary progressive form of MS; it was discovered and developed and is marketed by Hoffmann–La Roche's subsidiary Genentech under the trade name Ocrevus. With the approval, the FDA also required the company to conduct several Phase IV clinical trials to better understand whether the drug is safe and effective in young people, cancer risks, and effects on pregnant women and children they might bear. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical uses In the US, ocrelizumab is indicated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rituximab
Rituximab, sold under the brand name Rituxan among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer. It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (in non-geriatric patients), rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, pemphigus vulgaris, myasthenia gravis and Epstein–Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcers. It is given by slow injection into a vein. Biosimilars of Rituxan include Blitzima, Riabni, Ritemvia, Rituenza (F.K.A. Tuxella), Rixathon, Ruxience, and Truxima. Common side effects which often occur within two hours of the medication being given include rash, itchiness, low blood pressure, and shortness of breath. Infections are also common. Severe side effects include reactivation of hepatitis B in those previously infected, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and death. It is unclear if use during pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonal Antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell Lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies can have monovalent affinity, binding only to the same epitope (the part of an antigen that is recognized by the antibody). In contrast, polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes and are usually made by several different antibody-secreting plasma cell lineages. Bispecific monoclonal antibodies can also be engineered, by increasing the therapeutic targets of one monoclonal antibody to two epitopes. It is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to virtually any suitable substance; they can then serve to detect or purify it. This capability has become an investigative tool in biochemistry, molecular biology, and medicine. Monoclonal antibodies are being used on a clinical level for both the diagnosis and therapy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymoma
A thymoma is a tumor originating from the epithelial cells of the thymus that is considered a rare malignancy. Thymomas are frequently associated with neuromuscular disorders such as myasthenia gravis; thymoma is found in 20% of patients with myasthenia gravis. Once diagnosed, thymomas may be removed surgically. In the rare case of a malignant tumor, chemotherapy may be used. Signs and symptoms A third of all people with a thymoma have symptoms caused by compression of the surrounding organs by an expansive mass. These problems may take the form of superior vena cava syndrome, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), cough, or chest pain. One-third of patients have their tumors discovered because they have an associated autoimmune disorder. As mentioned earlier, the most common of those conditions is myasthenia gravis (MG); 10–15% of patients with MG have a thymoma and, conversely, 30–45% of patients with thymomas have MG. Additional associated autoimmune conditions include thymom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone pain, anemia, kidney dysfunction, and infections may occur. Complications may include amyloidosis. The cause of multiple myeloma is unknown. Risk factors include obesity, radiation exposure, family history, and certain chemicals. There is an increased risk of multiple myeloma in certain occupations. This is due to the occupational exposure to aromatic hydrocarbon solvents having a role in causation of multiple myeloma. Multiple myeloma may develop from monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance that progresses to smoldering myeloma. The abnormal plasma cells produce abnormal antibodies, which can cause kidney problems and overly thick blood. The plasma cells can also form a mass in the bone marrow or soft tissue. When one tumor is prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hodgkins Disease
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition was named after the English physician Thomas Hodgkin, who first described it in 1832. Symptoms may include fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Often, nonpainful enlarged lymph nodes occur in the neck, under the arm, or in the groin. Those affected may feel tired or be itchy. The two major types of Hodgkin lymphoma are classic Hodgkin lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. About half of cases of Hodgkin lymphoma are due to Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and these are generally the classic form. Other risk factors include a family history of the condition and having HIV/AIDS. Diagnosis is conducted by confirming the presence of cancer and identifying RS cells in lymph node biopsies. The virus-positive cases are classifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_mixed_cellulary_type.jpg)
