|
Föhn Cloud
A Föhn (Foehn) cloud is any cloud associated with a Föhn (Foehn), usually an Orographic lift, orographic cloud, a mountain wave cloud, or a lenticular cloud. Föhn is a regional term referring to winds in the Alps. See also * Cloud types * Föhn wind * Nor'west arch * Pileus (meteorology), Pileus References *Defant, F., 1951: Compendium of Meteorology, 667–669. External links American Meteorological Society Accessory clouds Föhn effect {{Cloud-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Palma - El Paso - Cumbre Nueva+Foehn (Mirador Llano Del Jable) 01 Ies
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second largest city in the United States. La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * La (musical note), or A, the sixth note * "L.A.", a song by Elliott Smith on Figure 8 (album), ''Figure 8'' (album) * L.A. (EP), ''L.A.'' (EP), by Teddy Thompson * ''L.A. (Light Album)'', a Beach Boys album * L.A. (Neil Young song), "L.A." (Neil Young song), 1973 * The La's, an English rock band * L.A. Reid, a prominent music producer * Yung L.A., a rapper * Lady A, an American country music trio * L.A. (Amy Macdonald song), "L.A." (Amy Macdonald song), 2007 * "La", a song by Australian-Israeli singer-songwriter Old Man River (musician), Old Man River Other media * l(a, a poem by E. E. Cummings * La (Tarzan), fictional queen of the lost city of Opar (Tarzan) * ''Lá'', later known as Lá Nua, an Irish language newspaper * La7, an Italian television channel * LucasArts, an American video game developer and publisher * Liber A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratocumulus Undulatus (22112021)
A stratocumulus cloud, occasionally called a cumulostratus, belongs to a genus-type of clouds characterized by large dark, rounded masses, usually in groups, lines, or waves, the individual elements being larger than those in altocumulus, and the whole being at a lower height, usually below . Weak convective currents create shallow cloud layers because of drier, stable air above preventing continued vertical development. Historically, in English, this type of cloud has been referred to as a twain cloud for being a combination of two types of clouds. Description Occurrence Vast areas of subtropical and polar oceans are covered with massive sheets of stratocumulus. These may organize into distinctive patterns which are currently under active study. In subtropics, they cover the edges of the horse latitude climatological highs, and reduce the amount of solar energy absorbed in the ocean. When these drift over land the summer heat or winter cold is reduced. 'Dull weather' is a common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Lenticular Clouds
Multiple may refer to: Economics *Multiple finance, a method used to analyze stock prices *Multiples of the price-to-earnings ratio *Chain stores, are also referred to as 'Multiples' *Box office multiple, the ratio of a film's total gross to that of its opening weekend Sociology *Multiples (sociology), a theory in sociology of science by Robert K. Merton, see Science *Multiple (mathematics), multiples of numbers *List of multiple discoveries, instances of scientists, working independently of each other, reaching similar findings *Multiple birth, because having twins is sometimes called having "multiples" *Multiple sclerosis, an inflammatory disease *Parlance for people with multiple identities, sometimes called "multiples"; often theorized as having dissociative identity disorder Printing *Printmaking, where ''multiple'' is often used as a term for a print, especially in the US * Artist's multiple, series of identical prints, collages or objects by an artist, subverting the ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
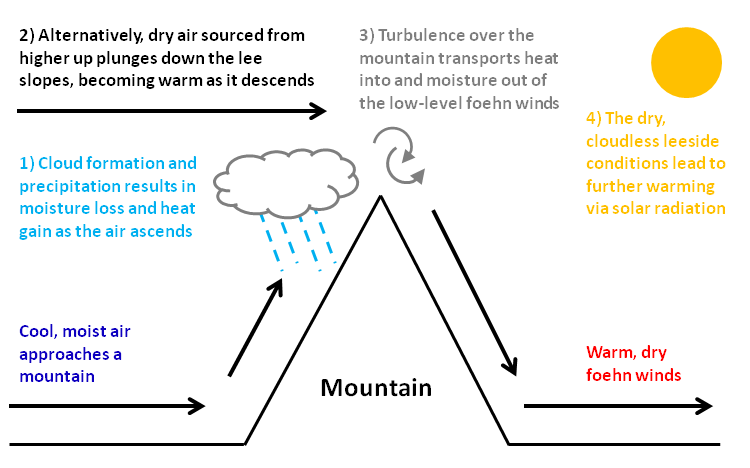
Föhn
A Foehn or Föhn (, , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm, downslope wind that occurs in the leeward, lee (downwind side) of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes (see orographic lift). As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes. Foehn winds can raise temperatures by as much as 14 °C (25 °F) in just a matter of hours. Switzerland, southern Germany and Austria have a warmer climate due to the Foehn, as moist winds off the Mediterranean Sea blow over the Alps. Etymology The name ''Foehn'' (german: Föhn, ) arose in the Alps, Alpine region. Originating from Latin ''(ventus) favonius'', a mild west wind of which Anemoi, Favonius was the Roman personification and probably transmitted by rm, favuogn or just ''fuogn'', the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orographic Lift
Orographic lift occurs when an air mass is forced from a low elevation to a higher elevation as it moves over rising terrain. As the air mass gains altitude it quickly cools down adiabatically, which can raise the relative humidity to 100% and create clouds and, under the right conditions, precipitation. Orographic lifting can have a number of effects, including precipitation, rain shadowing, leeward winds, and associated clouds. Precipitation Precipitation induced by orographic lift occurs in many places throughout the world. Examples include: * The Mogollon Rim in central Arizona * The western slope of the Sierra Nevada range in California * The mountains near Baja California North – specifically La Bocana to Laguna Hanson. * The windward slopes of Khasi and Jayantia Hills (see Mawsynram) in the state of Meghalaya in India. * The Western Highlands of Yemen, which receive by far the most rain in Arabia. * The Western Ghats that run along India's western coast. * The Grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Cloud
A wave cloud is a cloud form created by atmospheric internal waves. Formation The atmospheric internal waves that form wave clouds are created as stable air flows over a raised land feature such as a mountain range, and can form either directly above or in the lee of the feature. As an air mass travels through the wave, it undergoes repeated uplift and descent. If there is enough moisture in the atmosphere, clouds will form at the cooled crests of these waves. In the descending part of the wave, those clouds will evaporate due to adiabatic heating, leading to the characteristic clouded and clear bands. The cloud base on the leeward side is higher than on the windward side, because precipitation on the windward side removes water from the air.Wallace, John M., Hobbs, Peter V. Atmospheric Science, and Introductory Survey. San Diego, CA: Academic Press, 1977. It is possible that simple convection from mountain summits can also form wave clouds. This occurs as the convection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenticular Cloud
Lenticular clouds (Latin: ''Lenticularis'' lentil-shaped, from ''lenticula'' lentil) are stationary clouds that form mostly in the troposphere, typically in parallel alignment to the wind direction. They are often comparable in appearance to a lens or saucer. Nacreous clouds that form in the lower stratosphere sometimes have lenticular shapes. There are three main types of lenticular clouds: altocumulus standing lenticular (ACSL), stratocumulus standing lenticular (SCSL), and cirrocumulus standing lenticular (CCSL), varying in altitude above the ground. Because of their unique appearance, they have been suggested as an explanation for some unidentified flying object (UFO) sightings. Formation and appearance As air travels along the surface of the Earth, obstructions are often encountered, including natural features, such as mountains or hills, and artificial structures, such as buildings and other constructions, which disrupt the flow of air into "eddies", or areas of turb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Types
The list of cloud types groups all genera as ''high'' (cirro-, cirrus), ''middle'' (alto-), ''multi-level'' (nimbo-, cumulo-, cumulus), and ''low'' (strato-, stratus). These groupings are determined by the altitude level or levels in the troposphere at which each of the various cloud types is normally found. Small cumulus are commonly grouped with the low clouds because they do not show significant vertical extent. Of the multi-level genus-types, those with the greatest convective activity are often grouped separately as ''towering vertical''. The genus types all have Latin names. The genera are also grouped into five physical forms. These are, in approximate ascending order of instability or convective activity: ''stratiform'' sheets; ''cirriform'' wisps and patches; ''stratocumuliform'' patches, rolls, and ripples; ''cumuliform'' heaps, and ''cumulonimbiform'' towers that often have complex structures. Most genera are divided into ''species'' with Latin names, some of which are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Föhn Wind
A Foehn or Föhn (, , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm, downslope wind that occurs in the leeward, lee (downwind side) of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes (see orographic lift). As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes. Foehn winds can raise temperatures by as much as 14 °C (25 °F) in just a matter of hours. Switzerland, southern Germany and Austria have a warmer climate due to the Foehn, as moist winds off the Mediterranean Sea blow over the Alps. Etymology The name ''Foehn'' (german: Föhn, ) arose in the Alps, Alpine region. Originating from Latin ''(ventus) favonius'', a mild west wind of which Anemoi, Favonius was the Roman personification and probably transmitted by rm, favuogn or just ''fuogn'', the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nor'west Arch
The Nor'west arch is a weather pattern peculiar to the east coast of New Zealand's South Island. For this reason, it is also often referred to as the Canterbury arch, although it is visible in both Otago and Marlborough as well as in the Canterbury Region. It is shown in an apparent arch of high white cloud in an otherwise clear blue sky over the Southern Alps, and is accompanied by a strong hot northwesterly or northerly wind simply known as The Nor'wester. Closer to the Canterbury coast, some distance from the mountains of the Southern Alps, it appears as a clear area of blue above the mountains, with white cloud streaming to the east from it. The phenomenon is similar to the Chinook arch seen in the Pacific regions of the United States and Canada. Formation The Nor'west arch is a föhn cloud. The northwesterly wind drives warm moist air from over the Tasman Sea, and it is pushed up by the presence of the Southern Alps, causing it to cool rapidly. The area to the east of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pileus (meteorology)
A pileus (; Latin for "cap"), also called scarf cloud or cap cloud, is a small, horizontal, lenticular cloud appearing above a cumulus or cumulonimbus cloud. Pileus clouds are often short-lived, with the main cloud beneath them rising through convection to absorb them. They are formed by strong updraft at lower altitudes, acting upon moist air above, causing the air to cool to its dew point. As such, they are usually indicators of severe weather, and a pileus found atop a cumulus cloud often foreshadows transformation into a cumulonimbus cloud, as it indicates a strong updraft within the cloud. Pilei can also form above mountains, ash clouds, and pyrocumulus clouds from erupting volcanoes. Pilei form above some mushroom clouds of high- yield nuclear detonations. Appearance Sometimes several pileus clouds are observed above each other. The bright iridescent colors seen in pileus are sunlight diffracted in water vapor. Iridescent colors are strongest when the diffracting drop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Clouds
Accessory may refer to: * Accessory (legal term), a person who assists a criminal In anatomy * Accessory bone * Accessory muscle * Accessory nucleus, in anatomy, a cranial nerve nucleus * Accessory nerve In arts and entertainment * Accessory (band), with members Dirk Steyer and Ivo Lottig * Video game accessory, a piece of hardware used in conjunction with a video game console for playing video games * ''Accessories'' (album), a compilation album from Dutch alternative rock band The Gathering * Accessory, a type of rulebook in ''Dungeons & Dragons'' and other role-playing games Other uses * Fashion accessory, an item used to complement a fashion or style * Accessory suite, a secondary dwelling on a parcel of land * Rental accessories and attachments, accessories used in the rental industry * Cable accessories for connecting and terminating cables * Accessory fruit, in which some of the flesh is derived from tissues other than the flower ovary See also * * * Access (disamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |