|
Funk Island Ecological Reserve
Funk Island is a small, barren, isolated, uninhabited island approximately northeast of Musgrave Harbour, Newfoundland and Labrador, Newfoundland, Canada. Geography The island is roughly trapezoidal in shape, with a maximum length of 0.8 km (½ mile) and a maximum width of 0.3 km (300 yards) and is nearly flat, rising 14 metres (45') out of the North Atlantic. The island is composed of feldspar, feldspathic granite and is traversed by two distinct fault lines which cross the island in a northwesterly direction, almost parallel to each other. The fault lines divide the island into three separate entities. The northeastern portion consists mainly of bare rock; the central portion has scattered vegetation; and the largest portion of the island, the southwestern, which occupies over half of the land surface, is covered with grasses, lichens and mosses. Landing on Funk Island is extremely difficult and dangerous, though in calm weather there are three points where a safe land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labrador Sea
The Labrador Sea (French: ''mer du Labrador'', Danish: ''Labradorhavet'') is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean between the Labrador Peninsula and Greenland. The sea is flanked by continental shelf, continental shelves to the southwest, northwest, and northeast. It connects to the north with Baffin Bay through the Davis Strait. It is a marginal sea of the Atlantic. The sea formed upon separation of the North American Plate and Greenland Plate that started about 60 million years ago and stopped about 40 million years ago. It contains one of the world's largest turbidity current channel systems, the Northwest Atlantic Mid-Ocean Channel (NAMOC), that runs for thousands of kilometers along the sea bottom toward the Atlantic Ocean. The Labrador Sea is a major source of the North Atlantic Deep Water, a cold water mass that flows at great depth along the western edge of the North Atlantic, spreading out to form the largest identifiable water mass in the World Ocean. History The Labrad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Auk
The great auk (''Pinguinus impennis'') is a species of flightless alcid that became extinct in the mid-19th century. It was the only modern species in the genus ''Pinguinus''. It is not closely related to the birds now known as penguins, which were discovered later by Europeans and so named by sailors because of their physical resemblance to the great auk. It bred on rocky, remote islands with easy access to the ocean and a plentiful food supply, a rarity in nature that provided only a few breeding sites for the great auks. When not breeding, they spent their time foraging in the waters of the North Atlantic, ranging as far south as northern Spain and along the coastlines of Canada, Greenland, Iceland, the Faroe Islands, Norway, Ireland, and Great Britain. The bird was tall and weighed about , making it the largest alcid to survive into the modern era, and the second-largest member of the alcid family overall (the prehistoric ''Miomancalla'' was larger). It had a black ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and to New Zealand and Australia in particular. He made detailed maps of Newfoundland prior to making three voyages to the Pacific, during which he achieved the first recorded European contact with the eastern coastline of Australia and the Hawaiian Islands, and the first recorded circumnavigation of New Zealand. Cook joined the British merchant navy as a teenager and joined the Royal Navy in 1755. He saw action in the Seven Years' War and subsequently surveyed and mapped much of the entrance to the St. Lawrence River during the siege of Quebec, which brought him to the attention of the Admiralty and the Royal Society. This acclaim came at a crucial moment for the direction of British overseas exploration, and it led to his commission in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Moll
Herman Moll (mid-17th century – 22 September 1732) was a London cartographer, engraver, and publisher. Origin and early life While Moll's exact place and date of birth are unknown, he was probably born in the mid-seventeenth century in Germany or the United Provinces. The earliest extant mention of Moll was made by the natural philosopher Robert Hooke, who recorded in 1678 that Moll was working in London as an engraver. Moll later specialized in engraving maps, and went on to produce maps and globes from his studies of the work of other cartographers. Cartographic work Early years in London Moll probably sold his first maps from a stall in various places in London. From 1688 he had his own shop in Wanley's Court in London's Blackfriars. Between 1691 and 1710 his business was located at the corner of Spring Gardens and Charing Cross, and he finally moved along the River Thames to the Strand where he remained until his death. In the 1690s, Moll worked mainly as an engra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartography
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively. The fundamental objectives of traditional cartography are to: * Set the map's agenda and select traits of the object to be mapped. This is the concern of map editing. Traits may be physical, such as roads or land masses, or may be abstract, such as toponyms or political boundaries. * Represent the terrain of the mapped object on flat media. This is the concern of map projections. * Eliminate characteristics of the mapped object that are not relevant to the map's purpose. This is the concern of generalization. * Reduce the complexity of the characteristics that will be mapped. This is also the concern of generalization. * Orchestrate the elements of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Italy is also considered part of Western Europe, and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. It has a territorial exclave in Switzerland, Campione. Italy covers an area of , with a population of over 60 million. It is the third-most populous member state of the European Union, the sixth-most populous country in Europe, and the tenth-largest country in the continent by land area. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome. Italy was the native place of many civilizations such as the Italic peoples and the Etruscans, while due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, the country has also historically been home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Mortier
Pieter Mortier, or Pierre Mortier as the publisher of books in French, was the name of three successive generations of booksellers and publishers in the Dutch Republic. Pieter Mortier I (1661–1711) The first Pieter Mortier (Leiden, 1661 – Amsterdam, 1711) was the son of a political refugee from France, and became a mapmaker and engraver. He travelled to Paris in 1681–1685, then returned to Amsterdam where he operated as a bookseller from 1685 until 1711. He won the privilege in 1690 of publishing maps and atlases by French publishers in Amsterdam for the Dutch market. He used this privilege to win a similar set of privileges for printing an "illustrated print bible" in 1700. Also known as "Mortier's Bible" (Dutch: ''Mortierbijbel'' or ''Prentbijbel Mortier''), this book's official name was ''Historie des Ouden en Nieuwen Testaments, verrykt met meer dan vierhonderd printverbeeldingen in koper gesneeden'' ("History of the Old and New Testaments: enriched with more than four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James MacLehose And Sons
James MacLehose and Sons was a bookseller, publisher, and printer in Glasgow in the 19th century. Started as independent businesses by James J. MacLehose and his brother, Robert MacLehose, the MacLehose family was active in the Glasgow book business in various ways through the 19th century. The business was associated with Glasgow University and published many University Press titles. A collection of books were deposited at Glasgow University and are now in shelfmark "MacLehose", and family and business records and manuscripts are in the special collections with call number "Sp Coll MS Gen 1594". The businesses operated variously under the names James MacLehose, Robert MacLehose, the MacLehose firm, James MacLehose and Sons, Robert MacLehose and Company, Robert MacLehose and Company, Limited, MacLehose, Jackson & Co., Jackson, Wylie & Co. (no relation to John Wiley & Sons John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American multinational publishing company fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 635,640. Straddling the border between historic Lanarkshire and Renfrewshire, the city now forms the Glasgow City Council area, one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and is governed by Glasgow City Council. It is situated on the River Clyde in the country's West Central Lowlands. Glasgow has the largest economy in Scotland and the third-highest GDP per capita of any city in the UK. Glasgow's major cultural institutions – the Burrell Collection, Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum, the Royal Conservatoire of Scotland, the Royal Scottish National Orchestra, Scottish Ballet and Scottish Opera – enjoy international reputations. The city was the European Capital of Culture in 1990 and is notable for its architecture, cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Hore
Richard Hore () was an English explorer who conducted an early voyage to the coast of what is now Newfoundland, where his passengers allegedly engaged in cannibalism in order to survive. His travels are attested in the writings of Richard Hakluyt, who documented the ill-fated expedition. Apart from his famous journey and its immediate aftermath, little is known about the life of Richard Hore. In Hakluyt's ''Principal Navigations'' One of the few contemporary accounts of Richard Hore's life is contained in ''The Principal Navigations, Voyages, Traffiques and Discoveries of the English Nation'', a late 16th century history by Richard Hakluyt. Master Hore, described as "a man of goodly stature and of great courage" who was "given to the studie of Cosmographie," succeeded in attracting a number of gentlemen interested in visiting the North American coast. According to Hakluyt, the expedition was to set out on two ships: the ''Trinity'', captained by Hore himself, and the ''Minion'', up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Hakluyt
Richard Hakluyt (; 1553 – 23 November 1616) was an English writer. He is known for promoting the English colonization of North America through his works, notably ''Divers Voyages Touching the Discoverie of America'' (1582) and ''The Principal Navigations, Voyages, Traffiques and Discoveries of the English Nation'' (1589–1600). Hakluyt was educated at Westminster School and Christ Church, Oxford. Between 1583 and 1588 he was chaplain and secretary to Sir Edward Stafford, English ambassador at the French court. An ordained priest, Hakluyt held important positions at Bristol Cathedral and Westminster Abbey and was personal chaplain to Robert Cecil, 1st Earl of Salisbury, principal Secretary of State to Elizabeth I and James I. He was the chief promoter of a petition to James I for letters patent to colonize Virginia, which were granted to the London Company and Plymouth Company (referred to collectively as the Virginia Company) in 1606. The Hakluyt Society, which pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
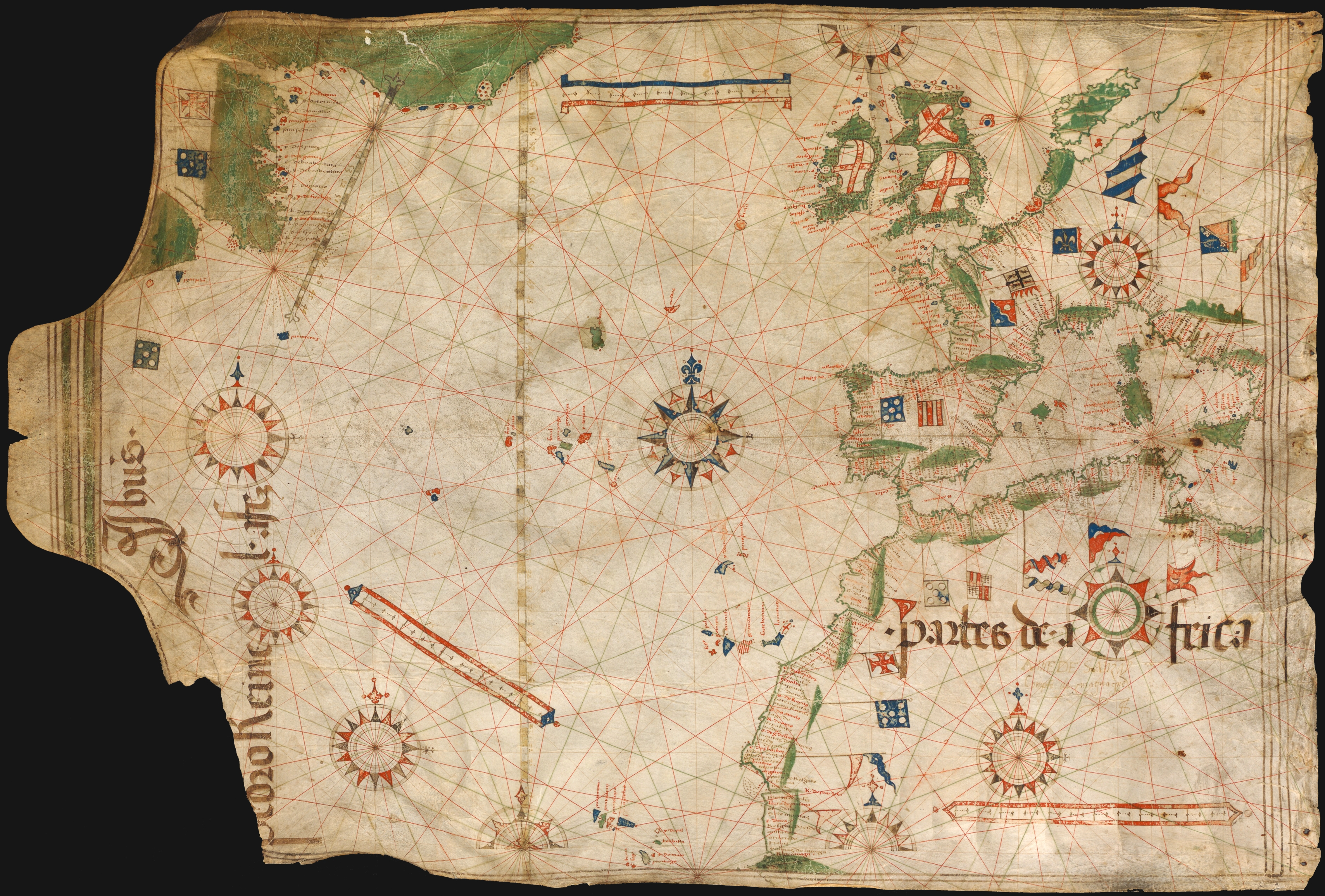
Pedro Reinel
Pedro Reinel (fl. 1485 – 1540) was a Portuguese cartographer. Between 1485 and 1519 Reinel served three Portuguese kings: João II, Manuel I and João III. He and his son, Jorge Reinel, were among the most renowned cartographers of their era, a period when European knowledge of geography and cartography were expanding rapidly. There is some evidence he was of African descent. Historian Rafael Moreira believes Reinel's father was an ivory carver brought from West Africa to serve in the royal workshops. Reinel was the author of one of the oldest signed Portolan charts, tentatively dated about 1485. This nautical chart depicts the western Mediterranean and the African coasts extending as far as the Congo River. It includes the recently completed first voyage of exploration made by Diogo Cão in 1482–1484. The African coast is drawn in two distinct sections: first is a conventional tracing of the Atlantic coast as far as Cabo Corço where the map runs out of space. The remainder of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)