|
Fuhlrott
Prof. Dr. Johann Carl Fuhlrott (31 December 1803, Leinefelde, Germany – 17 October 1877, Wuppertal) was an early German paleoanthropologist. He is famous for recognizing the significance of the bones of Neanderthal 1, a Neanderthal specimen discovered by German laborers who were digging for limestone in Neander valley (''Neanderthal'' in German) in August 1856. Originally disregarded, Fuhlrott, to his eternal credit, had the insight to recognize them for what they were: the remains of a previously unknown type of human. Biography His parents were the innkeeper Johannes Philipp Fuhlrott and his wife Maria Magdalena, née Nussbaum. His parents had died by the time he was ten and he was raised by his uncle, the Catholic priest Carl Bernhard Fuhlrott, in Seulingen. In 1835 he married Josepha Amalia Kellner (1812–1850), with whom he had six children. After studying mathematics and natural sciences at the University of Bonn, Fuhlrott became a teacher at the Gymnasium in Elberfeld ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
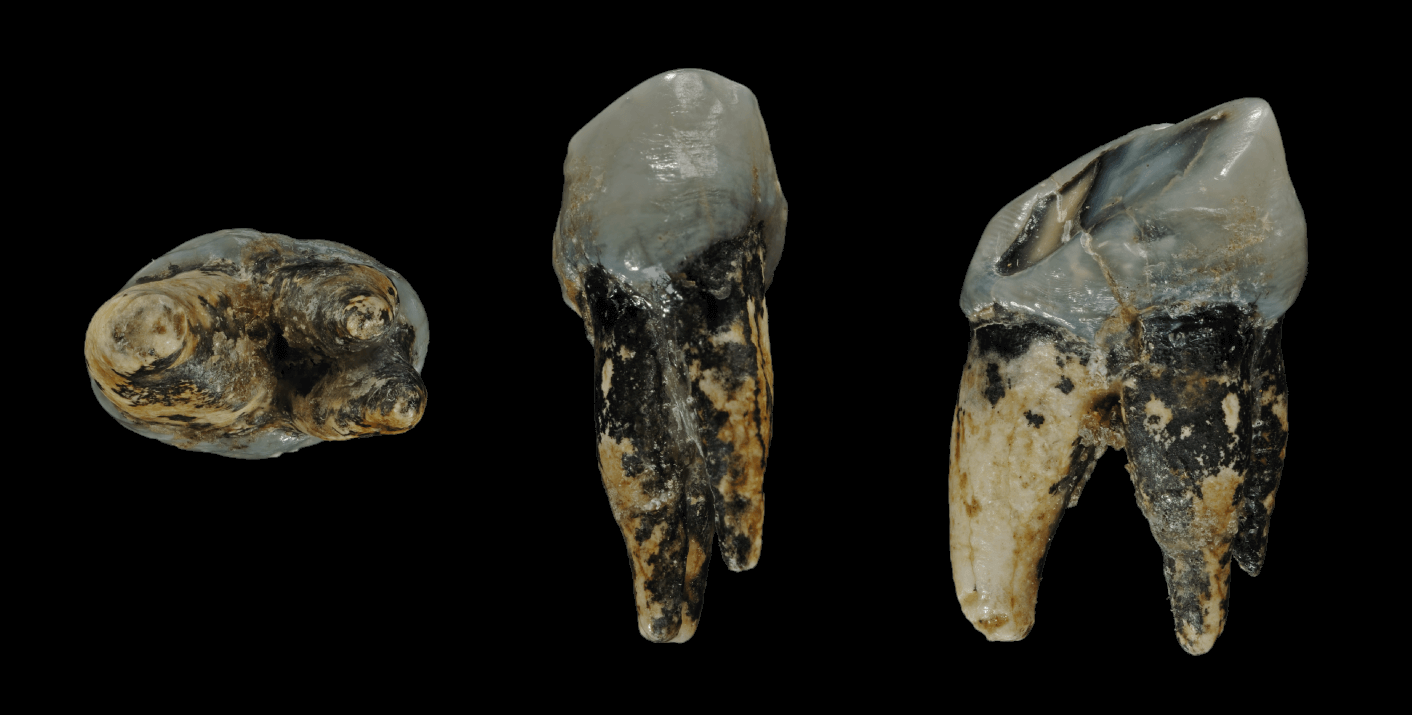
Neanderthal 1
Feldhofer 1 or Neanderthal 1 is the scientific name of the 40,000-year-old type specimen fossil of the species ''Homo neanderthalensis'', found in August 1856 in a German cave, the Kleine Feldhofer Grotte in the Neandertal valley, east of Düsseldorf. In 1864 the fossil's description was first published in a scientific magazine and officially named. William King: ''The Reputed Fossil Man of the Neanderthal''. In: ''Quarterly Journal of Science''. Band 1, 1864, S. 88–97Volltext (PDF; 356 kB)/ref> However, the find was not the first Neanderthal fossil discovery. Other Neanderthal fossils had been discovered earlier, but their true nature and significance had not been recognized, and therefore no separate species' name was assigned. The discovery was made by limestone quarry miners. Neanderthal 1 consists of a skullcap, two femora, the three right arm bones, two of the left arm bones, ilium, and fragments of a scapula and ribs. The fossils were given to Johann Carl Fuhlro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuhlrott
Prof. Dr. Johann Carl Fuhlrott (31 December 1803, Leinefelde, Germany – 17 October 1877, Wuppertal) was an early German paleoanthropologist. He is famous for recognizing the significance of the bones of Neanderthal 1, a Neanderthal specimen discovered by German laborers who were digging for limestone in Neander valley (''Neanderthal'' in German) in August 1856. Originally disregarded, Fuhlrott, to his eternal credit, had the insight to recognize them for what they were: the remains of a previously unknown type of human. Biography His parents were the innkeeper Johannes Philipp Fuhlrott and his wife Maria Magdalena, née Nussbaum. His parents had died by the time he was ten and he was raised by his uncle, the Catholic priest Carl Bernhard Fuhlrott, in Seulingen. In 1835 he married Josepha Amalia Kellner (1812–1850), with whom he had six children. After studying mathematics and natural sciences at the University of Bonn, Fuhlrott became a teacher at the Gymnasium in Elberfeld ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Schaaffhausen
Hermann Schaaffhausen (19 July 1816, Koblenz – 26 January 1893, Bonn) was a German anatomist, anthropologist, and paleoanthropologist. Biography Hermann Schaaffhausen was the son of Josef Hubert Schaaffhausen and Anna Maria Wachendorf. He studied medicine at the University of Berlin and received his doctorate degree in 1839, and became a Professor of Anatomy at the University of Bonn. Schaaffhausen soon became involved in research in physical anthropology and the study of prehistoric humans in Europe. He is best known for his study of the Neanderthal fossils (together with J.C. Fuhlrott). He was a member of several scientific societies, including the Naturhistorischen Vereins der preussischen Rheinlande und Westphalens (Natural History Society of the Rhineland and Westphalia) located in Bonn, the Vereins von Alterthumsfreunden im Rheinlande (Association of the Friends of Antiquity in the Rhineland), and was an honorary member of the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Anthropologie, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neandertal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the "causes of Neanderthal disappearance about 40,000 years ago remain highly contested," demographic factors such as small population size, inbreeding and genetic drift, are considered probable factors. Other scholars have proposed competitive replacement, assimilation into the modern human genome (bred into extinction), great climatic change, disease, or a combination of these factors. It is unclear when the line of Neanderthals split from that of modern humans; studies have produced various intervals ranging from 315,000 to more than 800,000 years ago. The date of divergence of Neanderthals from their ancestor '' H. heidelbergensis'' is also unclear. The oldest potential Neanderthal bones date to 430,000 years ago, but the classificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the "causes of Neanderthal disappearance about 40,000 years ago remain highly contested," demographic factors such as small population size, inbreeding and genetic drift, are considered probable factors. Other scholars have proposed competitive replacement, assimilation into the modern human genome (bred into extinction), great climatic change, disease, or a combination of these factors. It is unclear when the line of Neanderthals split from that of modern humans; studies have produced various intervals ranging from 315,000 to more than 800,000 years ago. The date of divergence of Neanderthals from their ancestor ''H. heidelbergensis'' is also unclear. The oldest potential Neanderthal bones date to 430,000 years ago, but the classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leinefelde
Leinefelde-Worbis is a town in the district of Eichsfeld, in northwestern Thuringia, Germany. The town was formed on March 16, 2004, from the former independent towns Leinefelde and Worbis along with the municipalities of Breitenbach and Wintzingerode. In July 2018 the former municipality of Hundeshagen, and in January 2019 Kallmerode was merged into Leinefelde-Worbis. The population before the amalgamation was 14,387 for Leinefelde, 5,541 for Worbis, 1,021 for Breitenbach and 614 for Wintzingerode. The 10 parts of Leinefelde-Worbis are Leinefelde, Worbis, Breitenbach, Kirchohmfeld, Birkungen, Beuren, Hundeshagen, Kaltohmfeld, Wintzingrode, Kallmerode and Breitenholz. Transport Leinefelde station is located on the Halle–Hann. Münden and the Gotha–Leinefelde railways. Bear sanctuary Since 1997 Worbis has become known for its bear sanctuary, the Alternativer Bärenpark Worbis, which is operated by the German animal welfare organisation ''Aktion Tier – Menschen für Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoanthropology
Paleoanthropology or paleo-anthropology is a branch of paleontology and anthropology which seeks to understand the early development of anatomically modern humans, a process known as hominization, through the reconstruction of evolutionary kinship lines within the family Hominidae, working from biological evidence (such as petrified skeletal remains, bone fragments, footprints) and cultural evidence (such as stone tools, artifacts, and settlement localities). The field draws from and combines primatology, paleontology, biological anthropology, and cultural anthropology. As technologies and methods advance, genetics plays an ever-increasing role, in particular to examine and compare DNA structure as a vital tool of research of the evolutionary kinship lines of related species and genera. Etymology The term paleoanthropology derives from Greek palaiós (παλαιός) "old, ancient", ánthrōpos (ἄνθρωπος) "man, human" and the suffix -logía (-λογία) "study of". Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoanthropology
Paleoanthropology or paleo-anthropology is a branch of paleontology and anthropology which seeks to understand the early development of anatomically modern humans, a process known as hominization, through the reconstruction of evolutionary kinship lines within the family Hominidae, working from biological evidence (such as petrified skeletal remains, bone fragments, footprints) and cultural evidence (such as stone tools, artifacts, and settlement localities). The field draws from and combines primatology, paleontology, biological anthropology, and cultural anthropology. As technologies and methods advance, genetics plays an ever-increasing role, in particular to examine and compare DNA structure as a vital tool of research of the evolutionary kinship lines of related species and genera. Etymology The term paleoanthropology derives from Greek palaiós (παλαιός) "old, ancient", ánthrōpos (ἄνθρωπος) "man, human" and the suffix -logía (-λογία) "study of". Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Hominina Fossils
The following tables give an overview of notable finds of hominin fossils and remains relating to human evolution, beginning with the formation of the tribe Hominini (the divergence of the human and chimpanzee lineages) in the late Miocene, roughly 7 to 8 million years ago. As there are thousands of fossils, mostly fragmentary, often consisting of single bones or isolated teeth with complete skulls and skeletons rare, this overview is not complete, but show some of the most important findings. The fossils are arranged by approximate age as determined by radiometric dating and/or incremental dating and the species name represents current consensus; if there is no clear scientific consensus the other possible classifications are indicated. The early fossils shown are not considered ancestors to ''Homo sapiens'' but are closely related to ancestors and are therefore important to the study of the lineage. After 1.5 million years ago (extinction of '' Paranthropus''), all fossils sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Anthropologists
German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) **Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman times) * German language **any of the Germanic languages * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (other) * Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Leinefelde-Worbis
A person (plural, : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal obligation, legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1877 Deaths
Events January–March * January 1 – Queen Victoria is proclaimed ''Empress of India'' by the ''Royal Titles Act 1876'', introduced by Benjamin Disraeli, the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom . * January 8 – Great Sioux War of 1876 – Battle of Wolf Mountain: Crazy Horse and his warriors fight their last battle with the United States Cavalry in Montana. * January 20 – The Conference of Constantinople ends, with Ottoman Turkey rejecting proposals of internal reform and Balkan provisions. * January 29 – The Satsuma Rebellion, a revolt of disaffected samurai in Japan, breaks out against the new imperial government; it lasts until September, when it is crushed by a professionally led army of draftees. * February 17 – Major General Charles George Gordon of the British Army is appointed Governor-General of the Sudan. * March – ''The Nineteenth Century'' magazine is founded in London. * March 2 – Compromise of 1877: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_1938.jpg)