|
Fuchseck
The Fuchseck is a 762m high mountain on the northern edge of the Swabian Alb in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The mountain is surrounded by the towns of Gammelshausen, Eschenbach, Schlat and Bad Ditzenbach. The summit is on the municipal border of Schlat in the Göppingen District Göppingen ( Swabian: ''Geppenge'' or ''Gebbenga'') is a town in southern Germany, part of the Stuttgart Region of Baden-Württemberg. It is the capital of the district Göppingen. Göppingen is home to the toy company Märklin, and it is the b .... The mountain is popular for its hiking and mountain biking opportunities. Nearby mountains include the Wasserberg and Sielenwang. Mountains and hills of Baden-Württemberg Mountains and hills of the Swabian Jura {{BadenWurttemberg-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eschenbach (Göppingen)
Eschenbach is a municipality in the district of Göppingen in Baden-Württemberg in Germany. Geography Geographical location Eschenbach is located in the valley of the river of the same name, at the foot of the Swabian Jura. The district town Göppingen is 6 kilometers away. Overview With an area of 480 ha Eschenbach is one of the smallest villages in the district of Göppingen. Through its location in the area before the Swabian Jura the municipality has however developed from a farming community to a municipality with around 2,200 inhabitants. Neighboring communities Since 1970, the municipality forms together with the neighboring community Heiningen the ''Gemeindeverwaltungsverband Voralb''. (Administration Unit Voralb). Municipality arrangement Eschenbach includes the village Eschenbach, the hamlet Lotenberg (also to community Heiningen) and the homestead Iltishof and the dialed villages Hag and Bürstenhof. History Early history The probable beginning of settlement for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schlat
Schlat is a municipality in the district of Göppingen in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. History Schlat changed owners several times during the Middle Ages. Barbara von Schlat, a local noblewoman, sold a third of the town in 1410 to Adelberg Abbey, which already controlled nearby properties donated to it by the County of Württemberg. The other two thirds of the town were inherited by the . As a result of the Protestant Reformation in the Holy Roman Empire, Adelberg Abbey was secularized and its holdings seized by the Duchy of Württemberg, which purchased the Liebenstein's portion of Schlat in 1789. The portions of Schlat were until 1807 divided between a district based out of the old abbey and . The Oberamt was reorganized as a Landkreis in 1938 and Schlat remained in its jurisdiction. The town grew after World War II to its east and south. Geography The municipality (''Gemeinde'') of Schlat is located at the center of the district of Göppingen, in the German state of Baden-W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
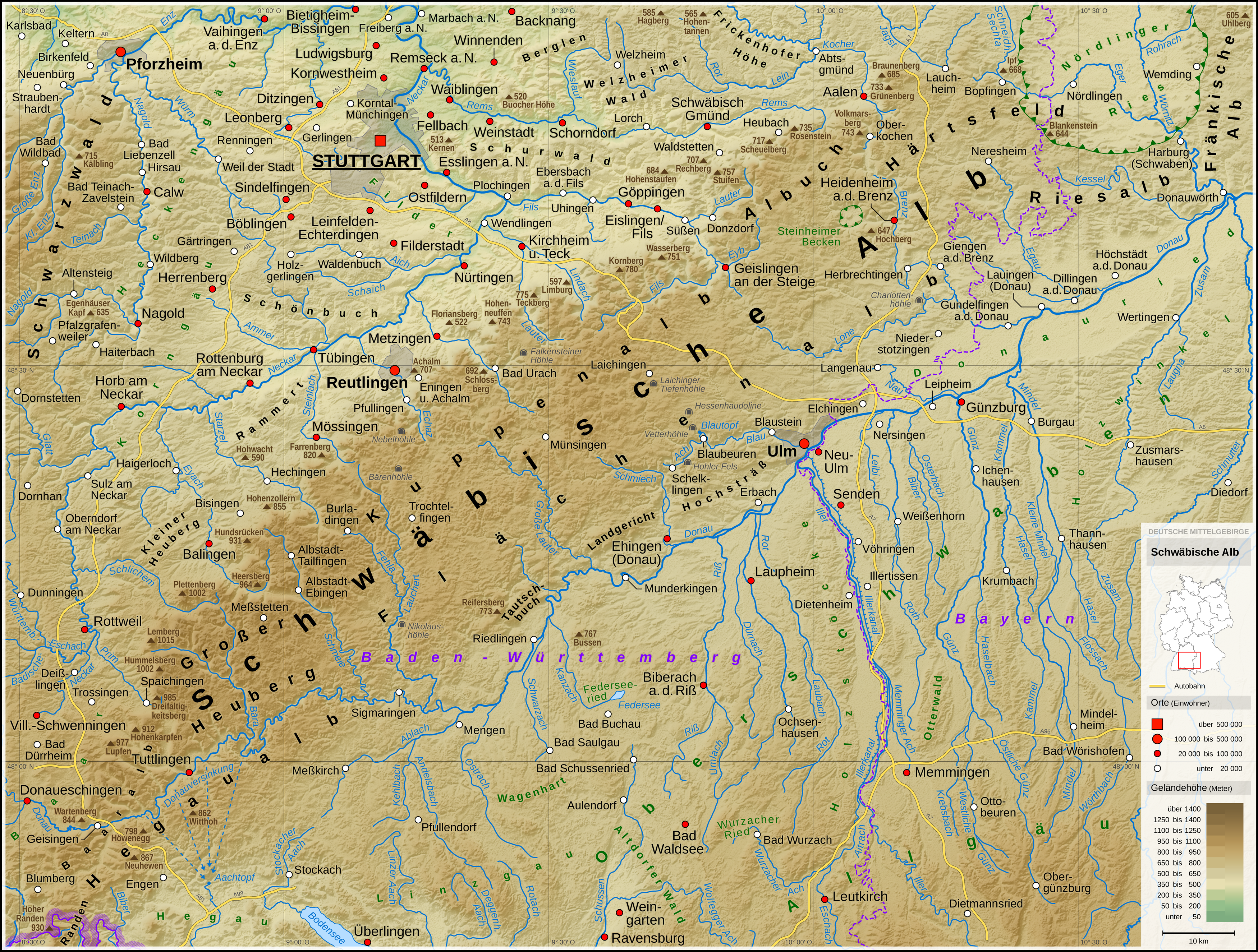
Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a total area of nearly , it is the third-largest German state by both area (behind Bavaria and Lower Saxony) and population (behind North Rhine-Westphalia and Bavaria). As a federated state, Baden-Württemberg is a partly-sovereign parliamentary republic. The largest city in Baden-Württemberg is the state capital of Stuttgart, followed by Mannheim and Karlsruhe. Other major cities are Freiburg im Breisgau, Heidelberg, Heilbronn, Pforzheim, Reutlingen, Tübingen, and Ulm. What is now Baden-Württemberg was formerly the historical territories of Baden, Prussian Hohenzollern, and Württemberg. Baden-Württemberg became a state of West Germany in April 1952 by the merger of Württemberg-Baden, South Baden, and Württemberg-Hohenzollern. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swabian Alb
The Swabian Jura (german: Schwäbische Alb , more rarely ), sometimes also named Swabian Alps in English, is a mountain range in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, extending from southwest to northeast and in width. It is named after the region of Swabia. The Swabian Jura occupies the region bounded by the Danube in the southeast and the upper Neckar in the northwest. In the southwest it rises to the higher mountains of the Black Forest. The highest mountain of the region is the Lemberg (). The area's profile resembles a high plateau, which slowly falls away to the southeast. The northwestern edge is a steep escarpment (called the Albtrauf or Albanstieg, rising up , covered with forests), while the top is flat or gently rolling. In economic and cultural terms, the Swabian Jura includes regions just around the mountain range. It is a popular recreation area. Geology The geology of the Swabian Jura is mostly limestone, which formed the seabed during the Jurassic period. The sea r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gammelshausen
Gammelshausen is a town in the district of Göppingen in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. History Gammelshausen was purchased by the County of Württemberg in 1321 but then in 1479 passed out of Württemberg's control and into that of the with Dürnau. Gammelshausen returned to Württemberg in 1806, when it was mediatized to the Kingdom of Württemberg and assigned to the district of Göppingen. After World War II, Gammelshausen began a period of urban growth that has since the turn of the millennium two areas to the town's southeast established in the 1970s. A redevelopment of the town center began in 2009 and was scheduled to conclude in 2017. Geography The municipality (''Gemeinde'') of Gammelshausen is located in the district of Göppingen, in Baden-Württemberg, one of the 16 States of the Federal Republic of Germany. Gammelshausen is physically located in the of the Swabian Jura. Elevation above sea level in the municipal area ranges from a high of Normalnull (NN) to a low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Ditzenbach
Bad Ditzenbach ( Swabian: ''Ditzebach'') is a municipality in the district of Göppingen in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. History The townships of Ditzenbach, , and were, until German mediatization in 1806, possessions of the House of Helfenstein. They were awarded to the Kingdom of Württemberg, a state that had come to control most of the surrounding territory between 1422 and 1455. The town was placed within Württemberg's administrative structure in until 1810, when it was transferred to . The nearby village of Auendorf had already mostly been a possession of Württemberg before mediatization. Auendorf and Gosbach were assigned to until transfer in 1808 to Oberamt Wiesensteig. Auendorf moved to in 1810 and in the same year Gosbach joined Ditzenbach in Oberamt Geislingen. The three townships were placed in the district of Göppingen in 1938. The three townships were merged into a new municipality, Bad Ditzenbach, on 1 January 1975. Bad Ditzenbach In 1560, a spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Göppingen (district)
Göppingen is a Districts of Germany, ''Landkreis'' (district) in the middle of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Neighboring districts are Rems-Murr, Ostalbkreis, Heidenheim (district), Heidenheim, Alb-Donau (district), Alb-Donau, Reutlingen (district), Reutlingen and Esslingen (district), Esslingen. History In 1817, Württemberg was divided into four kreise (districts), the southeastern one of which was named Donaukreis. The four kreise were in turn divided into oberämter. In Donaukreis, the most northern of these oberämter were Göppingen and, to its east, Geislingen. In 1938, the four kreise were abolished, and Geislingen was merged with Göppingen. During the communal reform of 1973 the district was not changed much, only a few municipalities from the districts Schwäbisch Gmünd and Ulm were added. The district is sometimes called ''Stauferkreis'', because the Hohenstaufen, Staufen family had their roots in this area. However, when that family had no heir anymore, the land b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains And Hills Of Baden-Württemberg
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are Monadnock, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountain formation, Mountains are formed through Tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |