|
Fructose-bisphosphatase 2
Fructose-bisphosphatase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''FBP2'' gene. Function This gene encodes a gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In vertebrat ... regulatory enzyme which catalyzes the hydrolysis of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate and inorganic phosphate. References Further reading * * * * {{gene-9-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
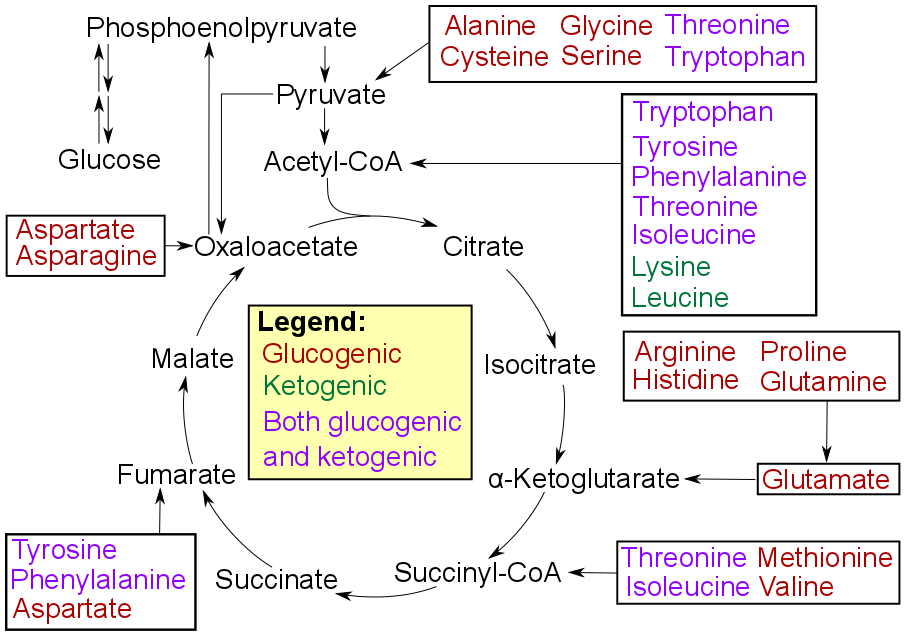
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys. It is one of two primary mechanisms – the other being degradation of glycogen ( glycogenolysis) – used by humans and many other animals to maintain blood sugar levels, avoiding low levels (hypoglycemia). In ruminants, because dietary carbohydrates tend to be metabolized by rumen organisms, gluconeogenesis occurs regardless of fasting, low-carbohydrate diets, exercise, etc. In many other animals, the process occurs during periods of fasting, starvation, low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise. In humans, substrates for gluconeogenesis may come from any non-carbohydrate sources that can be converted to pyruvate or intermediates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, abbreviated Fru-2,6-''P''2, is a metabolite that allosterically affects the activity of the enzymes phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK-1) and fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase-1) to regulate glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. Fru-2,6-''P''2 itself is synthesized and broken down by the bifunctional enzyme phosphofructokinase 2/ fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (PFK-2/FBPase-2). The synthesis of Fru-2,6-''P''2 is performed through a bifunctional enzyme containing both PFK-2 and FBPase-2, which is dephosphorylated, allowing the PFK-2 portion to phosphorylate fructose 6-phosphate using ATP. The breakdown of Fru-2,6-''P''2 is catalyzed by the phosphorylation of the bifunctional enzyme, which allows FBPase-2 to dephosphorylate fructose 2,6-bisphosphate to produce fructose 6-phosphate and Pi. Effects on glucose metabolism Fru-2,6-''P''2 strongly activates glucose breakdown in glycolysis through allosteric modulation (activation) of phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK-1). Elevate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fructose 6-phosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate (sometimes called the Neuberg ester) is a derivative of fructose, which has been phosphorylated at the 6-hydroxy group. It is one of several possible fructosephosphates. The β-D-form of this compound is very common in cells. The great majority of glucose is converted to fructose 6-phosphate upon entering a cell. Fructose is predominantly converted to fructose 1-phosphate by fructokinase following cellular import. History The name ''Neuberg ester'' comes from the German biochemist Carl Neuberg. In 1918, he found that the compound (later identified as fructose 6-phosphate) was beproduced by mild acid hydrolysis of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate.Fruton, Joseph S. ''Proteins, Enzymes, Genes: The Interplay of Chemistry and Biology''. Yale University Press: New Haven, 1999. p 292 In glycolysis Fructose 6-phosphate lies within the glycolysis metabolic pathway and is produced by isomerisation of glucose 6-phosphate. It is in turn further phosphorylated to fructose-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |