|
Friction Acoustics
Solid bodies in contact that undergo shear relative motion (friction) radiate energy. Part of this energy is radiated directly into the surrounding fluid media, and another part radiates throughout the solid bides and the connecting boundary conditions. The coupling of structural vibration and acoustic radiation takes is rooted in the mechanism of atomic oscillations, by which kinetic energy is translated to thermal energy. This field involves principles of acoustics, solid mechanics, contact dynamics, and tribology Tribology is the science and engineering of interacting surfaces in relative motion. It includes the study and application of the principles of friction, lubrication and wear. Tribology is highly interdisciplinary, drawing on many academic f .... Coupling and Stick-Slip Vibrational energy induced by either kinetic or breakaway friction can cause modal excitation of a subset of the contacting bodies or the vibratory coupling of the multiple bodies, depending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
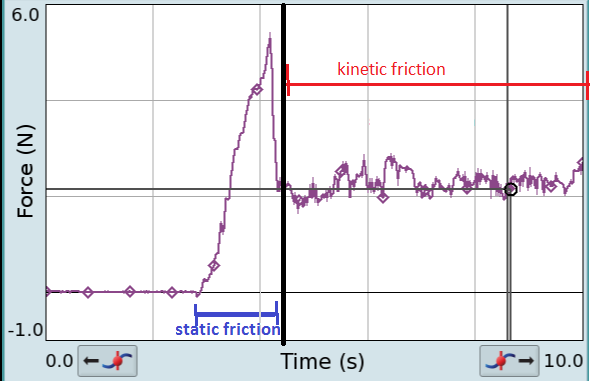
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: *Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into ''static friction'' ("stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and ''kinetic friction'' between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features, known as asperities (see Figure 1). *Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other. *Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces. *Skin friction is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body. *Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics technology may be called an acoustical engineer. The application of acoustics is present in almost all aspects of modern society with the most obvious being the audio and noise control industries. Hearing is one of the most crucial means of survival in the animal world and speech is one of the most distinctive characteristics of human development and culture. Accordingly, the science of acoustics spreads across many facets of human society—music, medicine, architecture, industrial production, warfare and more. Likewise, animal species such as songbirds and frogs use sound and hearing as a key element of mating rituals or for marking territories. Art, craft, science and technology have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Mechanics
Solid mechanics, also known as mechanics of solids, is the branch of continuum mechanics that studies the behavior of solid materials, especially their motion and deformation under the action of forces, temperature changes, phase changes, and other external or internal agents. Solid mechanics is fundamental for civil, aerospace, nuclear, biomedical and mechanical engineering, for geology, and for many branches of physics such as materials science. It has specific applications in many other areas, such as understanding the anatomy of living beings, and the design of dental prostheses and surgical implants. One of the most common practical applications of solid mechanics is the Euler–Bernoulli beam equation. Solid mechanics extensively uses tensors to describe stresses, strains, and the relationship between them. Solid mechanics is a vast subject because of the wide range of solid materials available, such as steel, wood, concrete, biological materials, textiles, geologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Dynamics
Contact dynamics deals with the motion of multibody systems subjected to unilateral contacts and friction. Such systems are omnipresent in many multibody dynamics applications. Consider for example * Contacts between wheels and ground in vehicle dynamics * Squealing of brakes due to friction induced oscillations * Motion of many particles, spheres which fall in a funnel, mixing processes (granular media) * Clockworks * Walking machines * Arbitrary machines with limit stops, friction. *Anatomic tissues (skin, iris/lens, eyelids/anterior ocular surface, joint cartilages, vascular endothelium/blood cells, muscles/tendons, et cetera) In the following it is discussed how such mechanical systems with unilateral contacts and friction can be modeled and how the time evolution of such systems can be obtained by numerical integration. In addition, some examples are given. Modeling The two main approaches for modeling mechanical systems with unilateral contacts and friction are the regulari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribology
Tribology is the science and engineering of interacting surfaces in relative motion. It includes the study and application of the principles of friction, lubrication and wear. Tribology is highly interdisciplinary, drawing on many academic fields, including physics, chemistry, materials science, mathematics, biology and engineering. People who work in the field of tribology are referred to as ''tribologists''. The fundamental objects of study in tribology are tribosystems, which are physical systems of contacting surfaces. In lubricated tribosystems, contact stress can create tribofilms. Subfields of tribology include biotribology, nanotribology, space tribology and tribotronics. Etymology The word ''tribology'' derives from the Greek root τριβ- of the verb , '' tribo'', "I rub" in classic Greek, and the suffix '' -logy'' from , ''-logia'' "study of", "knowledge of". Peter Jost coined the word in 1966, in the eponymous report which highlighted the cost of friction, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stick-slip
The stick–slip phenomenon, also known as the slip–stick phenomenon or simply stick–slip, is the spontaneous jerking motion that can occur while two objects are sliding over each other. Cause Below is a simple, heuristic description of stick–slip phenomena using classical mechanics that is relevant for engineering descriptions. However, in actuality, there is little consensus in academia regarding the actual physical description of stick–slip which follows the lack of understanding about friction phenomena in general. The generally agreed upon view is that stick–slip behavior results from common phonon modes (at the interface between the substrate and the slider) that are pinned in an undulating potential well landscape that un-pin (slip) and pin (stick) primarily influenced by thermal fluctuations. However, stick–slip frictional behaviour is encountered over a wide range of length scales from the atomic up to the tectonic, and there is no single underlying physical m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: *Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into ''static friction'' ("stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and ''kinetic friction'' between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features, known as asperities (see Figure 1). *Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other. *Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces. *Skin friction is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body. *Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)