|
French Foreign Legion (other)
The French Foreign Legion (french: Légion étrangère) is a corps of the French Army which comprises several specialties: infantry, cavalry, engineers, airborne troops. It was created in 1831 to allow foreign nationals into the French Army. It formed part of the Armée d’Afrique, the French Army's units associated with France's colonial project in Africa, until the end of the Algerian war in 1962. Legionnaires are highly trained soldiers and the Legion is unique in that it is open to foreign recruits willing to serve in the French Armed Forces. The Legion is today known as a unit whose training focuses on traditional military skills and on its strong esprit de corps, as its men come from different countries with different cultures. Consequently, training is often described as not only physically challenging, but also very stressful psychologically. French citizenship may be applied for after three years' service. Any soldier who is wounded during a battle for France can imm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grenade (insignia)
A grenade insignia is a form of emblem which represents a stylized old style of hand grenade, with a rising flame. This symbol is used as a charge (heraldry), charge in heraldry and is also featured on the uniforms of numerous military units. Military usage The insignia is featured on the uniforms of such military units as the: *French French Foreign Legion, Foreign Legion *Italian Carabinieri *Italian Fanteria *Italian Cavalleria *Italian Trasmissioni *Italian Granatieri di Sardegna *Italian Trasporti e Materiali *Italian Engineers Corps *Italian Bersaglieri *Dutch Koninklijke Marechaussee *Finnish Defence Forces, Finnish artillery *The Grenadiers Regiment of the Indian Army *British and Commonwealth Grenadier Guards Regiments *British Royal Regiment of Fusiliers *Royal Canadian Engineers *Commissioned Officers of the British Royal Engineers *Commissioned Officers of the British Honourable Artillery Company *Commissioned Officers of the British Royal Artillery (collar badge) *No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
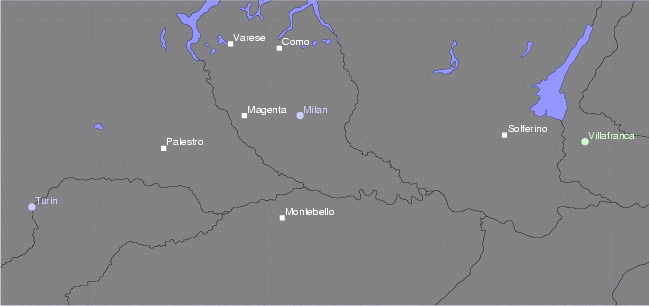
Second Italian War Of Independence
The Second Italian War of Independence, also called the Franco-Austrian War, the Austro-Sardinian War or Italian War of 1859 ( it, Seconda guerra d'indipendenza italiana; french: Campagne d'Italie), was fought by the Second French Empire and the Savoyard Kingdom of Sardinia against the Austrian Empire in 1859 and played a crucial part in the process of Italian Unification. A year prior to the war, in the Plombières Agreement, France agreed to support Sardinia's efforts to expel Austria from Italy in return for territorial compensation in the form of the Duchy of Savoy and the County of Nice. The two states signed a military alliance in January 1859. Sardinia mobilised its army on 9 March 1859, and Austria mobilized on 9 April. On 23 April, Austria delivered an ultimatum to Sardinia demanding its demobilization. Upon Sardinia's refusal, the war began on 26 April. Austria invaded Sardinia three days later, and France declared war on Austria on 3 May. The Austrian invasion wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indochina War
The First Indochina War (generally known as the Indochina War in France, and as the Anti-French Resistance War in Vietnam) began in French Indochina from 19 December 1946 to 20 July 1954 between France and Việt Minh (Democratic Republic of Vietnam), and their respective allies. Việt Minh was led by Võ Nguyên Giáp and Hồ Chí Minh. Most of the fighting took place in Tonkin in Northern Vietnam, although the conflict engulfed the entire country and also extended into the neighboring French Indochina protectorates of Laos and Cambodia. At the Potsdam Conference in July 1945, the Combined Chiefs of Staff decided that Indochina south of latitude 16° north was to be included in the Southeast Asia Command under British Admiral Mountbatten. The Japanese forces located south of that line surrendered to him and those to the north surrendered to Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek. In September 1945, Chinese forces entered Tonkin, and a small British task force landed at city of Saigo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria–Lebanon Campaign
The Syria–Lebanon campaign, also known as Operation Exporter, was the Allied invasion of Syria and Lebanon (then controlled by Vichy France) in June and July 1941, during the Second World War. The French had ceded autonomy to Syria in September 1936, with the right to maintain armed forces and two airfields in the territory. On 1 April 1941, the Iraqi coup d'état had occurred and Iraq had come under the control of Iraqi nationalists led by Rashid Ali, who appealed for Italian and German support. The Anglo-Iraqi War (2–31 May 1941) led to the overthrow of the Ali regime and the installation of a pro-British government. During this conflict, key Vichy figure Admiral François Darlan had allowed German aircraft to use Vichy airfields in Syria for attacks against the British in Iraq. The British invaded Syria and Lebanon in June, to prevent Nazi Germany from using the Vichy French-controlled Syrian Republic and French Lebanon as bases for attacks on Egypt, during an invasion s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rif War
The Rif War () was an armed conflict fought from 1921 to 1926 between Spain (joined by History of France, France in 1924) and the Berbers, Berber tribes of the mountainous Rif region of northern Morocco. Led by Abd el-Krim, the Riffians at first inflicted several defeats on the Spanish forces by using guerrilla tactics and captured European weapons. After France's military intervention against Abd el-Krim's forces and the major landing of Spanish troops at Alhucemas landing, Al Hoceima, considered the first amphibious landing in history to involve the use of tanks and aircraft, Abd el-Krim surrendered and was taken into exile. In July 1909, Spanish workers constructing a rail-bridge providing access to iron mines near Melilla were attacked by Rifian tribesmen. This incident led to the summoning of reinforcements from Spain itself. A series of skirmishes over the following weeks cost the Spanish over a thousand casualties. By September, the Spanish Army had 40,000 troops in n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Levant
The Army of the Levant (french: Armée du Levant) identifies the armed forces of France and then Vichy France which occupied, and were in part recruited from, the French Mandated territories in the Levant during the interwar period and early World War II. The locally recruited Syrian and Lebanese units of this force were designated as the Special Troops of the Levant (''Troupes Spéciales du Levant''). Origins In September 1919, Lloyd George and Georges Clemenceau entered an agreement to replace the British troops occupying Cilicia with French soldiers. The first elements of this new army came from the former 156th Infantry Division (french: 156ème Division d'Infanterie) of the Allied Army of the Orient, under General . This division from Cilicia included a metropolitan regiment, the 412th Infantry Regiment (french: 412ème Régiment d'Infanterie), a colonial regiment, the 17th Senegalese Tirailleurs (french: 17ème Régiment de tirailleurs sénégalais), a French Armenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandingo Wars
Mandinka, Mandika, Mandinkha, Mandinko, or Mandingo may refer to: Media * ''Mandingo'' (novel), a bestselling novel published in 1957 * ''Mandingo'' (film), a 1975 film based on the eponymous 1957 novel * ''Mandingo (play)'', a play by Jack Kirkland * "Mandinka" (song), by Sinead O'Connor from her 1987 album ''The Lion and the Cobra'' People * Mandingo people of Sierra Leone * Mandingo Wars (1883–1898), between France and the Wassoulou Empire of the Mandingo * Mandinka language * Mandinka people of West Africa * Wassoulou Empire, also known as the Mandinka Empire * Madinkhaya, an eastern variant of the Syriac alphabet * Mandingo, a stereotype of African American men See also * ''Django Unchained ''Django Unchained'' () is a 2012 American revisionist Western film written and directed by Quentin Tarantino, starring Jamie Foxx, Christoph Waltz, Leonardo DiCaprio, Kerry Washington, and Samuel L. Jackson, with Walton Goggins, Dennis Chri ...'', which features Manding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Madagascar Expedition
The Second Madagascar expedition was a French military intervention which took place in 1894–95, sealing the conquest of the Merina Kingdom on the island of Madagascar by France. It was the last phase of the Franco-Hova War and followed the First Madagascar expedition of 1883–85. Background Madagascar was at the time an independent country, ruled from the capital of Antananarivo by the Merina dynasty from the central highlands. The French invasion was triggered by the refusal of Queen Ranavalona III to accept a protectorate treaty from France, despite the signature of the Franco- Hova Treaty of 1885 following the First Madagascar expedition. Resident-general Charles Le Myre de Vilers broke negotiation and effectively declared war on the Malagasy monarchy. The expedition An expeditionary corps was sent under General Jacques Duchesne. First, the harbor of Toamasina on the east coast, and Mahajanga on the west coast, were bombarded and occupied in December 1894 and Janua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Franco-Dahomean War
The Second Franco-Dahomean War, which raged from 1892 to 1894, was a major conflict between France, led by General Alfred-Amédée Dodds, and Dahomey under King Béhanzin. The French emerged triumphant and incorporated Dahomey into their growing colonial territory of French West Africa. Background In 1890, the Fon kingdom of Dahomey and the French Third Republic had gone to war in what was remembered as the First Franco-Dahomean War over the former's rights to certain territories, specifically those in the Ouémé Valley. The Fon ceased hostilities with the French after two military defeats, withdrawing their forces and signing a treaty conceding to all of France's demands. However, Dahomey remained a potent force in the area and quickly re-armed with modern weapons in anticipation of a second, decisive conflict. ''Casus belli'' After re-arming and regrouping, the Fon returned to raiding the Ouémé Valley, the same valley fought over in the first war with France. Vic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sino-French War
The Sino-French War (, french: Guerre franco-chinoise, vi, Chiến tranh Pháp-Thanh), also known as the Tonkin War and Tonquin War, was a limited conflict fought from August 1884 to April 1885. There was no declaration of war. The Chinese armies performed better than its List of Chinese wars and battles#Qing dynasty (1644–1912), other nineteenth-century wars and the war ended with French retreat on land and the momentum in China's favor. However lack of foreign support, French naval supremacy, and northern threats posed by Russia and Japan forced China to enter negotiations. China ceded its sphere of influence in Tonkin (northern Vietnam) to France and recognized all the French treaties with Annam (French protectorate), Annam turning it into a French protectorate. The war strengthened the dominance of Empress Dowager Cixi over the Chinese government, but brought down the government of Prime Minister Jules Ferry in Paris. Both sides ratified the Treaty of Tientsin (1885), Trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


_-_Fondo_Car-Kutxa_Fototeka.jpg)


