|
Freeze (breakdancing Move)
A freeze is a b-boying technique that involves halting all body motion, often in an interesting or balance-intensive position. It is implied that the position is hit and held from motion as if freezing in motion, or into ice. Freezes often incorporate various twists and distortions of the body into stylish and often difficult positions. Spins are often combined with freezes, and the spins are usually done in the form of highkicks. Various handstands ("inverts", "Nikes", and "pikes") can be frozen, and skilled breakers sometimes incorporate the technique of ''threading'' into handstands by forming a loop with one arm and leg, then "threading" the other leg in and out of the loop. Variants There are many different variations of freezes. A common naming convention categorizes freezes based on what part of the body is in contact with the ground. First Freezes were chin freaks, Tracks, Splits, deadman freeze, chairs. Thus a "headstand freeze" is done with only the breaker's he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakdance
Breakdancing, also called breaking or b-boying/b-girling, is an athletic style of street dance originating from the African American and Puerto Rican communities in the United States. While diverse in the amount of variation available in the dance, breakdancing mainly consists of four kinds of movement: toprock, downrock, power moves and freezes. Breakdancing is typically set to songs containing drum breaks, especially in hip-hop, funk, soul music and breakbeat music, although modern trends allow for much wider varieties of music along certain ranges of tempo and beat patterns. The modern dance elements of breakdancing originated among the poor youth of New York during the early 1970s, where it was introduced as breaking. It is closely attributed to the birth of hip-hop, as DJs developed rhythmic breaks for dancers. The dance form has since expanded globally, with an array of organizations and independent competitions supporting its growth. Breaking will now be featured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headstand
The headstand, or sometimes head stand, is a pose that is an inversion posture of standing head down. The technique is used in different settings such as yoga, breakdancing, acrobatics and beginner gymnastics. Health risks If the headstand is not done perfectly, the performer is likely to suffer head injury from standing on the head. In yoga The yoga headstand, Shirshasana, may be balanced and symmetrical from all perspectives, even though not always in a legs-vertical position. The asana has many variations, several of them asymmetrical. File:Shirshasana.jpg, Yoga headstand, Shirshasana File:Unkown Headstand 1.jpg, alt=Unknown Headstand 1, With feet as in Baddha Konasana File:Mr-yoga-sideways-bound-angle-headstand-1.jpg, A variation See also * handstand __NOTOC__ A handstand is the act of supporting the body in a stable, inverted vertical position by balancing on the hands. In a basic handstand, the body is held straight with arms and legs fully extended, with hands sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Float (breakdance Move)
The float (turtle) is a b-boying move originally coming from basic Gymnastics alongside variants specifically the Turtle. Though it appears to demand great strength, the float actually requires balance above all because the breaker's weight is supported on the elbows which are firmly planted (" stabbed") into the lower abdomen near the anterior superior iliac spine. Stationary floats are often employed as freeze poses. On the other hand, breakers can "walk" with floats by shifting weight from one hand to the other and thus moving in a straight line or circle. These moving floats can be made to spin very fast and become the first power moves Power moves are dance moves which are loosely defined as moves relying on speed, momentum, and acrobatic elements for performance. They are prominent in B-boying, often the centerpieces of routines featuring the other elements (toprock, downrock, ... that were done in the 80's. Variants *Crab - The Crab is a specific term for a two-handed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
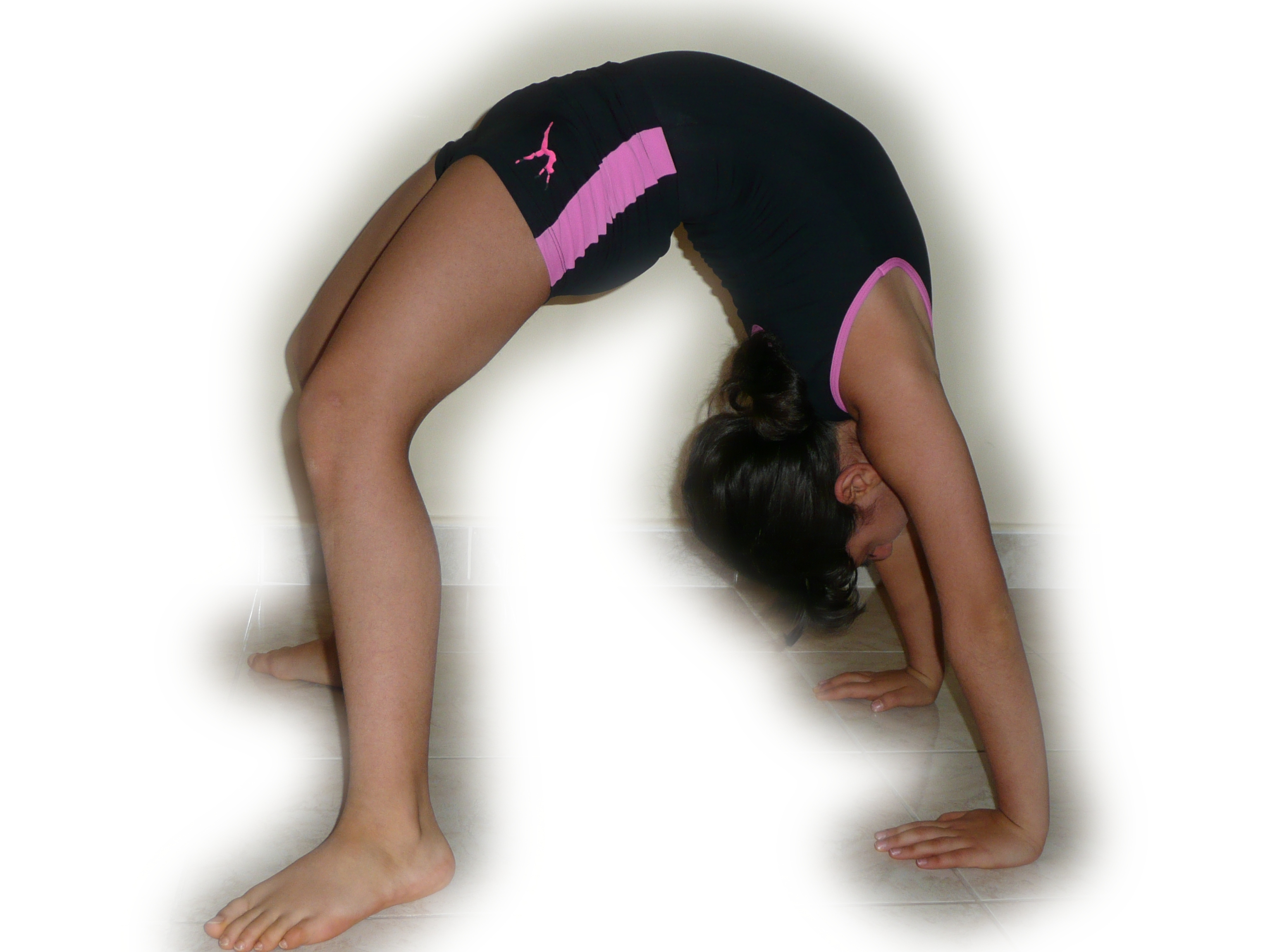
Bridge (exercise)
The bridge (also called gymnastic bridge) is an exercise. Many variations of this exercise are employed throughout the world, most commonly the balancing of the body on the hands and the feet. It is intended to improve lower back and gluteus strength. Examples of bridging in sportive or self-defense applications are seen in Kung Fu, Judo, Brazilian jiu jitsu, Capoeira, mixed martial arts, and wrestling. In yoga, this particular pose is called Chakrasana, Urdhva Dhanurasana, or Wheel, while the Westernized nickname "Bridge pose" refers to a less rigorous supine backbend called Setu Bandha Sarvangasana, in which the body is fairly straight from knees to shoulders, and most of the bend is in the knees. Variations The bridging exercise is not a singular movement, but includes a wide range of variations and progressions. There is no single agreed upon "standard" variation of the bridge like with other common bodyweight exercises. Bridge hold The bridge hold is a static variat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stab (breakdance Move)
The stab is a breakdance technique necessary to perform many downrock and power moves. It is not a distinct move, but is incorporated into many breakdance moves including the turtle, cricket, jackhammer, crab-walk, hand glide, some versions of the windmill, and many other floats and freezes. It allows the breakdancer's entire weight to be supported by bony structures while expending minimal muscular energy to maintain balance. The stab is accomplished by placing the olecranon process of the elbow firmly against the bones or tensed muscles of the abdomen, side, or back. Perhaps the most basic stab places the elbow against the anterior superior iliac spine. Meanwhile, the hand is placed against the ground. The radius and ulna are held perpendicular In elementary geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle (90 degrees or π/2 radians). The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the ''perpendicular symbol'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planche (exercise)
A planche is a skill in gymnastics and calisthenics in which the body is held parallel to the ground, while being supported above the floor by straight arms. It is a move that requires significant strength and balance. There are many variations of a planche, although only two are accredited in artistic gymnastics: the straddle planche, and the full planche. Depending on the event, it can range from a B to a D skill, and must be held for at least two seconds. As an example, on gymnastic rings, the straddle planche is a B move, and the full planche is a C move. On floor, straddle/full is A/B. The main muscle used in this exercise is the anterior deltoid, but the abdominals, chest, shoulders, upper back, lower back, and glutes also play important roles. As the planche is a demanding position, athletes train for it with a progression of simpler moves, advancing to the next when they have gained mastery of the intermediate positions. A typical training progression usually consists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
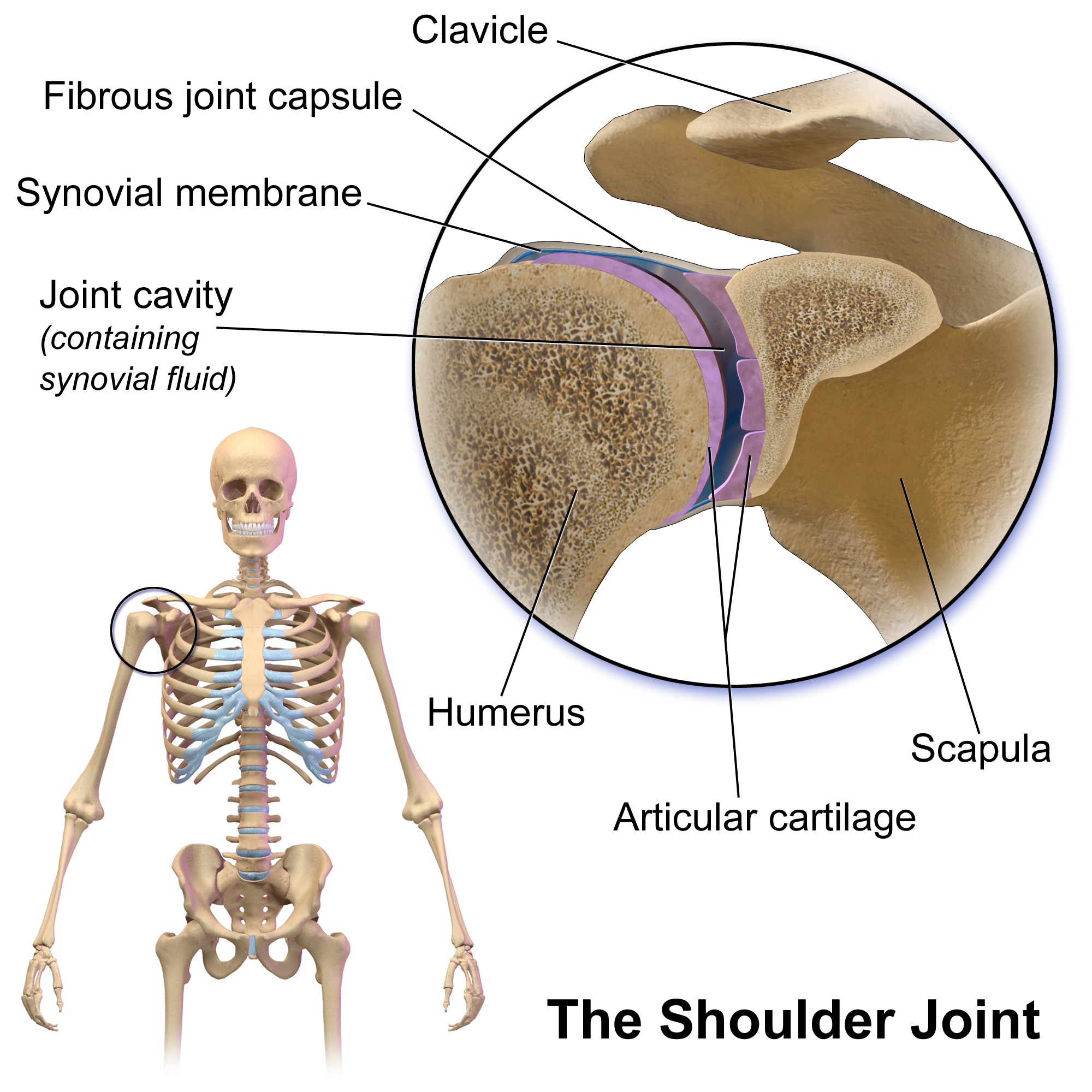
Shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is the major joint of the shoulder, but can more broadly include the acromioclavicular joint. In human anatomy, the shoulder joint comprises the part of the body where the humerus attaches to the scapula, and the head sits in the glenoid cavity. The shoulder is the group of structures in the region of the joint. The shoulder joint is the main joint of the shoulder. It is a ball and socket joint that allows the arm to rotate in a circular fashion or to hinge out and up away from the body. The joint capsule is a soft tissue envelope that encircles the glenohumeral joint and attaches to the scapula, humerus, and head of the biceps. It is lined by a thin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbow-joint
The elbow is the region between the arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term ''elbow'' is specifically used for humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates forelimb plus joint is used. The name for the elbow in Latin is ''cubitus'', and so the word cubital is used in some elbow-related terms, as in ''cubital nodes'' for example. Structure Joint The elbow joint has three different portions surrounded by a common joint capsule. These are joints between the three bones of the elbow, the humerus of the upper arm, and the radius and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
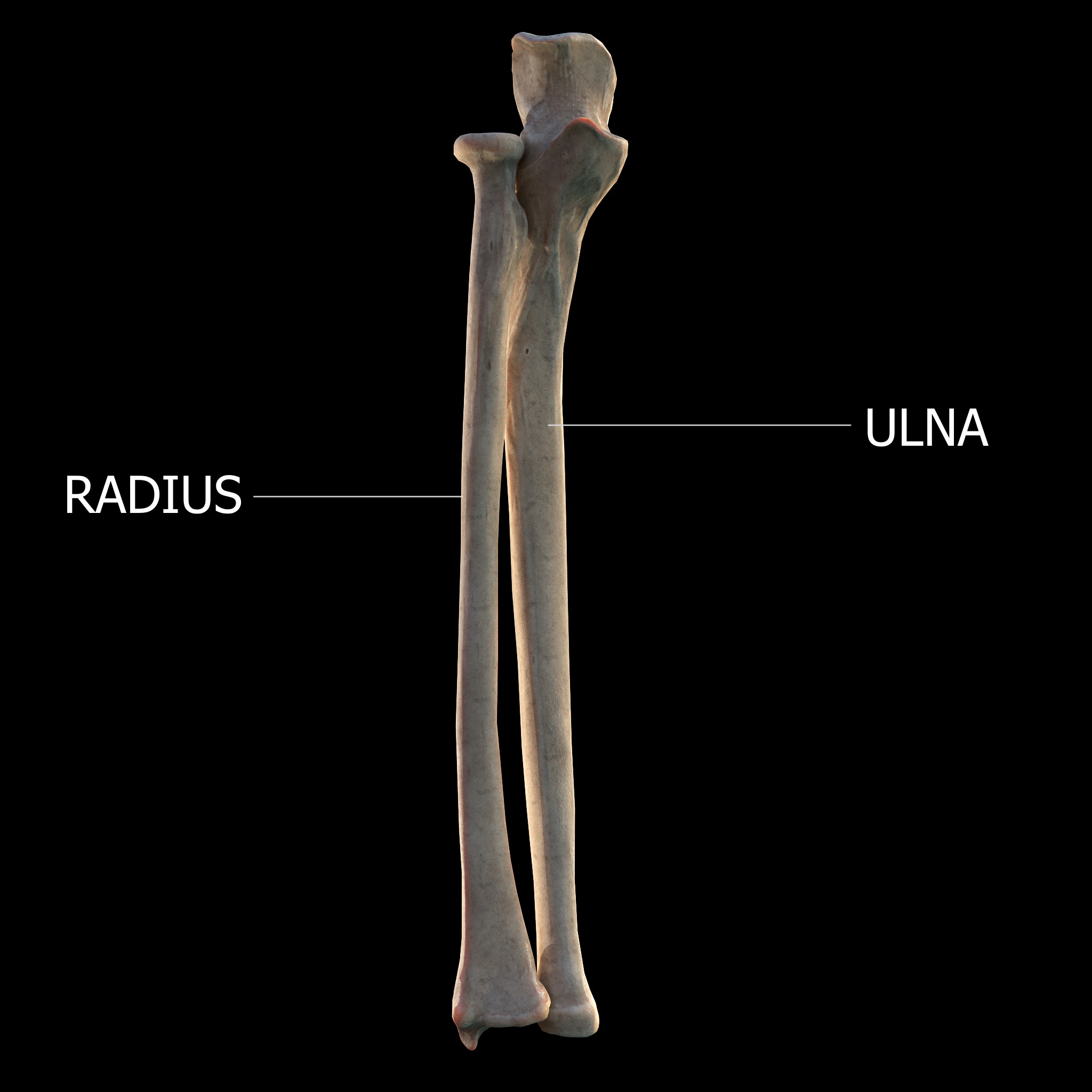
Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow (brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
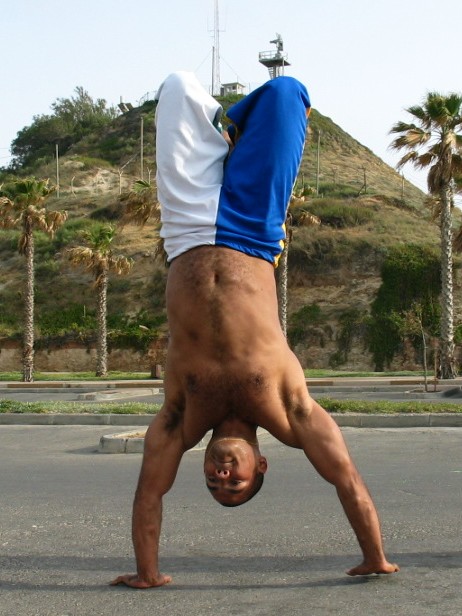
Handstand
__NOTOC__ A handstand is the act of supporting the body in a stable, inverted vertical position by balancing on the hands. In a basic handstand, the body is held straight with arms and legs fully extended, with hands spaced approximately shoulder-width apart and the legs together. There are many variations of handstands, all of which require the performer to possess adequate balance and upper body strength. Kinematics Handstands use the wrist flexor muscles as well as the anterior deltoid, pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi, biceps brachii, and trapezius descendens. It is considered demanding in terms of both the muscle and joint requirement. According to a 2017 study most handbalancers use wrist movement to maintain balance in a handstand. Another study found that handbalancers who were also expert gymnasts had better coordination than those at an intermediate level of gymnastics. More advanced practitioners also altered their center of pressure less to change the center of mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kick (breakdance Move)
A kick is a b-boy move that generally constitutes a one-handed handstand with the legs and free arm in some stylish position. Kicks can be employed as freezes, in which case they are held as long as possible. Alternatively, they can be executed quickly and powerfully to impress onlookers. Kicks are often named after letters or symbols whose form they imitate. The hand used for the stand is the "standing hand" and the leg on the same side of the body is the "standing leg." The other pair of appendages are the "free" hand and leg. Variants Some notable kicks include: *Airchair - Similar in appearance to a kick, the airchair is sometimes considered a float Float may refer to: Arts and entertainment Music Albums * ''Float'' (Aesop Rock album), 2000 * ''Float'' (Flogging Molly album), 2008 * ''Float'' (Styles P album), 2013 Songs * "Float" (Tim and the Glory Boys song), 2022 * "Float", by Bush ... because it employs a stab. The position of the legs and free arm varies. *G-Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |