|
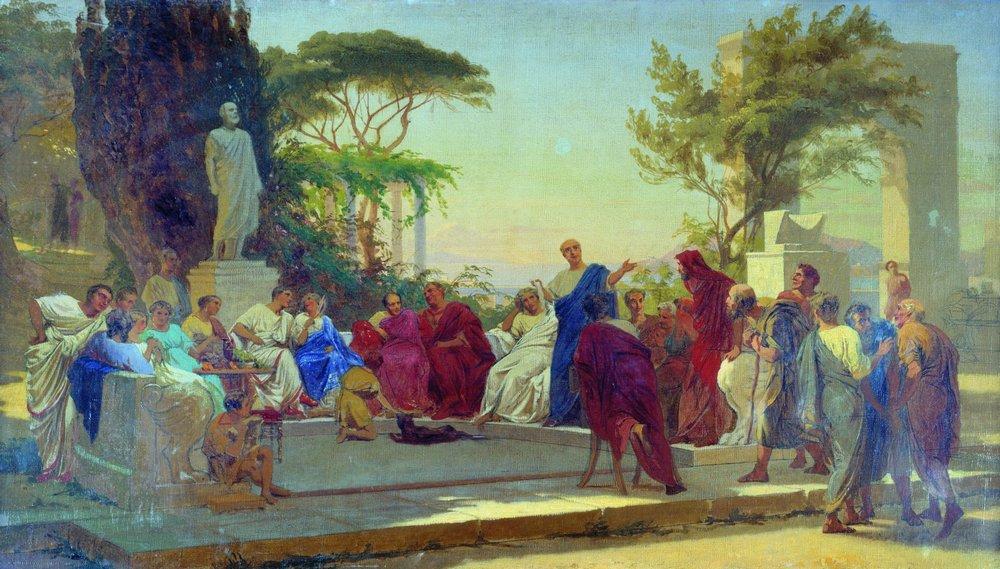
Freedmen In Ancient Rome
Freedmen in ancient Rome existed as a distinct social class ''(liberti'' or ''libertini)'', with former slaves granted freedom and rights through the legal process of manumission. The Roman practice of slavery utilized slaves for both production and domestic labour, overseen by their wealthy masters. Urban and domestic slaves especially could achieve high levels of education, acting as agents and representatives of their masters' affairs and finances. Within Roman law there was a set of practices for freeing trusted slaves, granting them a limited form of Roman citizenship or Latin rights. These freed slaves were known in Latin as ''liberti'' (freedmen), and formed a class set apart from freeborn Romans. While freedmen were barred from some forms of social mobility in Roman society, many achieved high levels of wealth and status. ''Liberti'' were an important part of the "most economically active and innovative entrepreneurial class" in the Roman Empire. The legal and social status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relief Of Publius Aiedius Amphio And Aiedia Fausta Melior Antikensammlung Berlin
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces remain attached to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb , to raise (). To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the sculpted material has been raised above the background plane. When a relief is carved into a flat surface of stone (relief sculpture) or wood (relief carving), the field is actually lowered, leaving the unsculpted areas seeming higher. The approach requires chiselling away of the background, which can be time-intensive. On the other hand, a relief saves forming the rear of a subject, and is less fragile and more securely fixed than a sculpture in the round, especially one of a standing figure where the ankles are a potential weak point, particularly in stone. In other materials such as metal, clay, plaster stucco, ceramics or papier-mâché the form can be simply added to or raised up from the background. Monumental bronze reliefs are ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimalchio
Trimalchio is a character in the 1st-century AD Roman work of fiction ''Satyricon'' by Petronius. He features as the ostentatious, nouveau-riche host in the section titled the "Cēna Trīmalchiōnis" (The Banquet of Trimalchio, often translated as "Dinner with Trimalchio"). Trimalchio is an arrogant former slave who has become quite wealthy as a wine merchant. The name "Trimalchio" is formed from the Greek prefix τρις and the Semitic מלך ( melech) in its occidental form Malchio or Malchus. The fundamental meaning of the root is "King", and the name "Trimalchio" would thus mean "Thrice King" or "greatest King". Character description His full name is "Gaius Pompeius Trimalchio Maecenatianus"; the references to Pompey and Maecenas in his name serve to enhance his ostentatious character. His wife's name is Fortunata, a former slave and chorus girl. Trimalchio is known for throwing lavish dinner parties, where his numerous slaves bring course after course of exotic delicacies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabulist
Fable is a literary genre defined as a succinct fictional story, in prose or verse, that features animals, legendary creatures, plants, inanimate objects, or forces of nature that are anthropomorphized, and that illustrates or leads to a particular moral lesson (a "moral"), which may at the end be added explicitly as a concise maxim or saying. A fable differs from a parable in that the latter ''excludes'' animals, plants, inanimate objects, and forces of nature as actors that assume speech or other powers of humankind. Conversely, an animal tale specifically includes talking animals as characters. Usage has not always been so clearly distinguished. In the King James Version of the New Testament, "" ("''mythos''") was rendered by the translators as "fable" in the First Epistle to Timothy, the Second Epistle to Timothy, the Epistle to Titus and the First Epistle of Peter. A person who writes fables is referred to as a fabulist. Global history The fable is one of the most end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonius Musa
__NOTOC__ Antonius Musa (, ''Antṓnios Moúsas'') was a Greek botanist and the Roman Emperor Augustus's physician; Antonius was a freedman who received freeborn status along with other honours. In the year 23 BC, when Augustus was seriously ill, Musa cured the illness with cold compresses and became immediately famous. ''Musa'', the plant group which includes the banana, the plantain and numerous other species, was apparently named after him.Liberty Hyde Bailey, ''The Standard Cyclopedia of Horticulture''. 1916pp. 2076–9/ref> However, ''Musa'' may be a Latinization of the Arabic name for the fruit, ''mauz'' (موز). ''Mauz'' meaning ''Musa'' is discussed in the 11th century Arabic encyclopedia ''The Canon of Medicine'', which was translated to Latin in medieval times and well known in Europe. Musa's brother was Euphorbus, physician to king Juba II of Numidia, after whom the plant ''Euphorbia'', which has given its name to a scientific genus, was originally named. A short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Julius Hyginus
Gaius Julius Hyginus (; 64 BC – AD 17) was a Latin author, a pupil of the scholar Alexander Polyhistor, and a freedman of Augustus, and reputed author of the '' Fabulae'' and the '' De astronomia'', although this is disputed. Life and works Hyginus may have originated either from Spain, or from the Egyptian city of Alexandria. He was elected superintendent of the Palatine library by Augustus according to Suetonius' ''De Grammaticis'', 20. Suetonius remarks that Hyginus fell into great poverty in his old age and was supported by the historian Clodius Licinus. Hyginus was a voluminous author: his works included topographical and biographical treatises, commentaries on Helvius Cinna and the poems of Virgil, and disquisitions on agriculture and bee-keeping. All these are lost. Attributed works Two Latin works which have survived under the name of Hyginus are a mythological handbook, known as the ''Genealogiae'' or the '' Fabulae'', and an astronomical work, entitled '' D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Polyhistor
Lucius Cornelius Alexander Polyhistor (; flourished in the first half of the 1st century BC; also called Alexander of Miletus) was a Greek scholar who was enslaved by the Romans during the Mithridatic War and taken to Rome as a tutor. After his release, he continued to live in Italy as a Roman citizen. He was so productive as a writer that he earned the surname '' Polyhistor'' (very learned). The majority of his writings are now lost, but the fragments that remain shed valuable light on antiquarian and eastern Mediterranean subjects. Among his works were historical and geographical accounts of nearly all the countries of the ancient world, and the book ''Upon the Jews'' () which excerpted many works which might otherwise be unknown. Life The Suda is the main source of information about Alexander's life. He was born in Miletus, Asia Minor, between 110 and 105 BC and educated by Crates of Mallus in Pergamon, before being captured in the Mithridatic War and brought to Rome as a sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publilius Syrus
Publilius Syrus (fl. 85–43 BC), was a Latin writer, best known for his sententiae. He was a Syrian from Antioch who was brought as a slave to Roman Italy. Syrus was brought to Rome on the same ship that brought a certain Manilius, astronomer - not the famous Manilius of the 1st century AD (see Pliny, ''NH'' X, 4-5), and Staberius Eros the grammarian. By his wit and talent, Syrus won the favour of his master, who granted him manumission and educated him. He became a member of the Publilia gens. Publilius' name, due to the palatalization of 'l' between two 'i's in the Early Middle Ages, is often presented by manuscripts (and some printed editions) in corrupt form as ' Publius', Publius being a very common Roman praenomen. Work His mimes, in which he acted, had a great success in the provincial towns of Italy and at the games given by Julius Caesar in 46 BC. Publilius was perhaps even more famous as an improviser. He received from Julius Caesar the prize in a contest, in wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terence
Publius Terentius Afer (; – ), better known in English as Terence (), was a playwright during the Roman Republic. He was the author of six Roman comedy, comedies based on Greek comedy, Greek originals by Menander or Apollodorus of Carystus. All six of Terence's plays survive complete and were originally produced between 166–160 BC. According to ancient authors, Terence was born in Carthage and was brought to Rome as a slave, where he gained an education and his freedom; around the age of 25, Terence is said to have made a voyage to the east in search of inspiration for his plays, where he died either of disease in Greece, or by shipwreck on the return voyage. However, Terence's traditional biography is often thought to consist of speculation by ancient scholars who lived too long after Terence to have access to reliable facts about his life. Terence's plays quickly became standard school texts. He ultimately secured a place as one of the four authors taught to all grammar p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livius Andronicus
Lucius Livius Andronicus (; ; ) was a Greco-Roman dramatist and epic poet of the Old Latin period during the Roman Republic. He began as an educator in the service of a noble family, producing Latin translations of Greek works, including Homer's ''Odyssey''. The translations were meant, at first, as educational devices for the school which he founded. He also wrote works for the stage—both tragedies and comedies—which are regarded as the first dramatic works written in the Latin language. His comedies were based on Greek New Comedy and featured characters in Greek costume. Thus, the Romans referred to this new genre by the term comoedia palliata or fabula palliata, meaning "cloaked comedy," the pallium being a Greek-style cloak. The Roman biographer Suetonius later coined the term "half-Greek" of Livius and Ennius (referring to their genre, not their ethnic backgrounds). The genre was imitated by later generations of playwrights, and Andronicus is accordingly regarded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeii
Pompeii ( ; ) was a city in what is now the municipality of Pompei, near Naples, in the Campania region of Italy. Along with Herculaneum, Stabiae, and Villa Boscoreale, many surrounding villas, the city was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, Pompeii offers a unique snapshot of Culture of ancient Rome, Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, as well as insight into ancient urban planning. It was a wealthy town of 10,000 to 20,000 residents at the time it was destroyed. It hosted many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and artworks, which were the main attractions for early excavators; subsequent excavations have found hundreds of private homes and businesses reflecting various architectural styles and social classes, as well as numerous public buildings. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of The Vettii
The House of the Vettii is a domus located in the Roman town Pompeii, which was preserved by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. The house is named for its owners, two successful freedmen: Aulus Vettius Conviva, an Augustalis, and Aulus Vettius Restitutus. Its careful excavation has preserved almost all of the wall frescos, which were completed following the earthquake of 62 AD, in the manner art historians term the Pompeiian Fourth Style. The House of Vetti is located in region VI, near the Vesuvian Gate, bordered by the Vicolo di Mercurio and the Vicolo dei Vettii. The house is one of the largest domus in Pompeii, spanning the entire southern section of block 15. The plan is fashioned in a typical Roman domus with the exception of a tablinum, which is not included. There are twelve mythological scenes across four cubiculum and one triclinium. The house was reopened to tourists in January 2023 after two decades of restoration. Plan The plan of the House of the Vettii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus (; 8 December 65 BC – 27 November 8 BC), Suetonius, Life of Horace commonly known in the English-speaking world as Horace (), was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus (also known as Octavian). The rhetorician Quintilian regarded his '' Odes'' as the only Latin lyrics worth reading: "He can be lofty sometimes, yet he is also full of charm and grace, versatile in his figures, and felicitously daring in his choice of words."Quintilian 10.1.96. The only other lyrical poet Quintilian thought comparable with Horace was the now obscure poet/metrical theorist, Caesius Bassus (R. Tarrant, ''Ancient Receptions of Horace'', 280) Horace also crafted elegant hexameter verses ('' Satires'' and '' Epistles'') and caustic iambic poetry ('' Epodes''). The hexameters are amusing yet serious works, friendly in tone, leading the ancient satirist Persius to comment: "as his friend laughs, Horace slyly puts his finger on his every fault; once let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |