|
Frederick Barlee
Sir Frederick Palgrave Barlee (6 February 1827 – 8 August 1884) was Colonial Secretary of Western Australia from 1855 to 1875; Lieutenant-Governor of the British Honduras (now Belize) from 1877 to 1882; and Administrator of Trinidad in 1884. Frederick Barlee was born in Worlingworth, Suffolk, England on 6 February 1827. He was educated privately and at local schools, and in 1845 he entered the public service as a clerk to the Ordnance Department in Chatham and Woolwich. In 1851, Barlee married Jane Oseland. Later that year he was posted to Sierra Leone, where he served initially as a barrack-master and storekeeper. In 1853 he became clerk to the Executive and Legislative Councils, and private secretary to the Governor of Sierra Leone Arthur Edward Kennedy. In 1855, Kennedy was appointed Governor of Western Australia, and he arranged for Barlee to be appointed Colonial Secretary. Both men arrived in Western Australia in June 1855, and commenced work the following month. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worlingworth
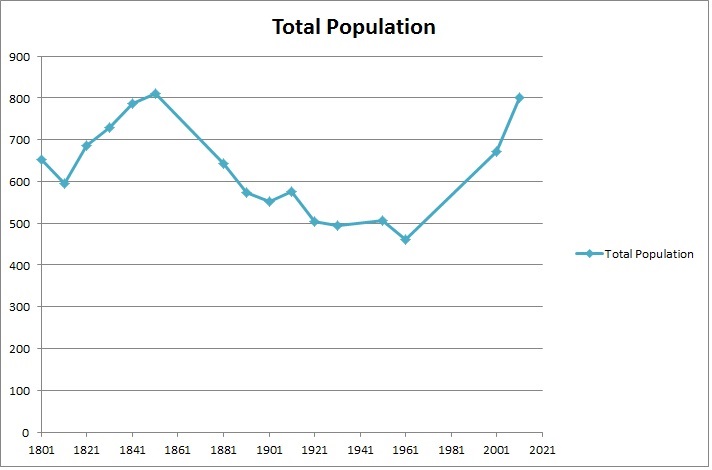
Worlingworth is a village and civil parish in the Mid Suffolk district of Suffolk in eastern England, located around ten miles south-east of Diss. In 2011 it had a total population of 802 people. The village has a primary school called Worlingworth CEVC Primary School. The school was judged by Ofsted to be 'Outstanding' in all areas in March 2016. The school's motto is "Cherish All, Achieve Together". The local church of St. Mary is a grade I listed building and the chancel, the oldest surviving part, dates to the late 13th century. Between 1908 and 1952 the village was served by Worlingworth railway station on the Mid-Suffolk Light Railway. History In Old English, the meaning of Worlingworth is an 'enclosure of the followers of Wilhere'. Broken down, 'Wilhere' is a personal name, '-ingas' means 'the people of' or 'the people called after' and 'worð' is for 'an enclosure'. The Domesday book states Worlingworth to be "quite large", with a population of 32 households, made up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Australian Legislative Council
The Western Australian Legislative Council is the upper house of the Parliament of Western Australia, a state of Australia. It is regarded as a house of review for legislation passed by the Legislative Assembly, the lower house. The two Houses of Parliament sit in Parliament House in the state capital, Perth. Effective on 20 May 2005, for the election of members of the Legislative Council, the State was divided into 6 electoral regions by community of interest —3 metropolitan and 3 rural—each electing 6 members to the Legislative Council.. The 2005 changes continued to maintain the previous malapportionment in favour of rural regions. Legislation was passed in 2021 to abolish these regions and increase the size of the council to 37 seats, all of which will be elected by the state-at-large. The changes will take effect in the 2025 state election. Since 2008, the Legislative Council has had 36 members. Since the 2013 state election, both houses of Parliament have had fix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasmania
) , nickname = , image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Tasmania , established_title2 = Federation , established_date2 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Abel Tasman , demonym = , capital = Hobart , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 29 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonial Office
The Colonial Office was a government department of the Kingdom of Great Britain and later of the United Kingdom, first created to deal with the colonial affairs of British North America but required also to oversee the increasing number of colonies of the British Empire. Despite its name, the Colonial Office was never responsible for all Britain's Imperial territories; for example, protectorates fell under the purview of the Foreign Office, and British India was ruled by the East India Company until 1858 (the British Raj ruled the India Office as a result of the Indian Mutiny), while the role of the Colonial Office in the affairs of the Dominions changed as time passed. It was headed by the Secretary of State for the Colonies, also known more informally as the Colonial Secretary. First Colonial Office (1768–1782) Prior to 1768, responsibility for the affairs of the British colonies was part of the duties of the Secretary of State for the Southern Department and a committe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Responsible Government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability, the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy. Governments (the equivalent of the executive branch) in Westminster democracies are responsible to parliament rather than to the monarch, or, in a colonial context, to the imperial government, and in a republican context, to the president, either in full or in part. If the parliament is bicameral, then the government is responsible first to the parliament's lower house, which is more representative than the upper house, as it usually has more members and they are always directly elected. Responsible government of parliamentary accountability manifests itself in several ways. Ministers account to Parliament for their decisions and for the performance of their departments. This requirement to make announcements and to answer questions in Parliament means that ministers must have the priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Representative Government
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy, is a types of democracy, type of democracy where elected people Representation (politics), represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern liberal democracy, Western-style democracies function as some type of representative democracy: for example, the United Kingdom (a unitary state, unitary parliamentary system, parliamentary constitutional monarchy), India (a federal parliamentary republic), France (a unitary semi-presidential system, semi-presidential republic), and the United States (a federal Presidential system, presidential republic). Representative democracy can function as an element of both the Parliamentary system, parliamentary and the presidential systems of form of government, government. It typically manifests in a lower chamber such as the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, and the Lok Sabha of India, but may be curtailed by Constitution, constitutional constraints suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Weld
Sir Frederick Aloysius Weld (9 May 1823 – 20 July 1891), was a New Zealand politician and a governor of various British colonies. He was the sixth premier of New Zealand, and later served as Governor of Western Australia, Governor of Tasmania, and Governor of the Straits Settlements. Early life Weld was born near Bridport, Dorset, England, on 9 May 1823. His mother, Christina Maria Clifford, was the daughter of Baron Clifford of Chudleigh. Both of his parents were from old recusant Catholic families. His father, Humphrey Weld of Chideock, was a member of the Weld family. Humphrey's father Thomas Weld (of Lulworth) donated the land and endowed the Jesuit college at Stonyhurst. Weld's upbringing was strongly grounded in the Catholic faith. His early years were spent with his parents in France. Later, he received a good education, studying at Stonyhurst before attending a predecessor of the University of Fribourg in Switzerland, where he studied philosophy, chemistry, language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bruce (British Army Officer)
John Bruce (25 July 1808 – 5 November 1870) was a British Army officer and acting Governor of Western Australia. Bruce was born in Athlone, Ireland, of Scottish parents. Bruce was educated privately and at the Sandhurst Military College, England; he was appointed an ensign in the 16th on 31 July 1828 and joined it in Bengal. In the early 1840s he transferred to the 18th Regiment of Foot and served in China. Bruce went to Western Australia with his regiment, and was for twenty years Staff-officer of Pensioners and Commandant of Western Australia. He was Acting Governor of the colony in February 1862, and from November 1868 to September 1869, during the interim between the departure of Governor John Hampton and the arrival of Governor Frederick Weld. Bruce died on 5 November 1870, at the age of sixty-two. Bruce had seven children, he was survived by his wife. Mount Bruce, Western Australia in the Hamersley Range The Hamersley Range is a mountainous region of the Pilbara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roebuck Bay
Roebuck Bay is a bay on the coast of the Kimberley region of Western Australia. Its entrance is bounded in the north by the town of Broome, and in the south by Bush Point and Sandy Point. It is named after , the ship captained by William Dampier when he explored the coast of north-western Australia in 1699. The Broome Bird Observatory lies on the northern coast of the bay. Description Roebuck Bay is a 550 km2 (210 mi2) tropical, marine embayment. It has red sandy beaches and areas of mangroves, with the eastern edge of the bay being made up of linear tidal creeks. It is surrounded by grasslands and pindan woodland.Protecting Ramsar Wetlands. The northern shore of the bay is dominated by a long and low red cliff, 2–6 m in height, of pindan soil which gives the beaches there their distinctive red colouration. It overlies yellowish-red Broome Sandstone of Cretaceous age which, when exposed at the base of the cliff, shows occasional fossil footprints of din ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world. Origin and use The word "town" shares an origin with the German word , the Dutch word , and the Old Norse . The original Proto-Germanic word, *''tūnan'', is thought to be an early borrowing from Proto-Celtic *''dūnom'' (cf. Old Irish , Welsh ). The original sense of the word in both Germanic and Celtic was that of a fortress or an enclosure. Cognates of ''town'' in many modern Germanic languages designate a fence or a hedge. In English and Dutch, the meaning of the word took on the sense of the space which these fences enclosed, and through which a track must run. In England, a town was a small community that could not afford or was not allowed to build walls or other larger fortifications, and built a palisade or stockade instead. In the Netherlands, this space was a garden, mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastoral
A pastoral lifestyle is that of shepherds herding livestock around open areas of land according to seasons and the changing availability of water and pasture. It lends its name to a genre of literature, art, and music (pastorale) that depicts such life in an idealized manner, typically for urban audiences. A ''pastoral'' is a work of this genre, also known as bucolic, from the Greek , from , meaning a cowherd. Literature Pastoral literature in general Pastoral is a mode of literature in which the author employs various techniques to place the complex life into a simple one. Paul Alpers distinguishes pastoral as a mode rather than a genre, and he bases this distinction on the recurring attitude of power; that is to say that pastoral literature holds a humble perspective toward nature. Thus, pastoral as a mode occurs in many types of literature (poetry, drama, etc.) as well as genres (most notably the pastoral elegy). Terry Gifford, a prominent literary theorist, define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hale School
Hale School is an independent, Anglican day and boarding school for boys, located in Wembley Downs, a western suburb of Perth, Western Australia. Named after the school founded by Bishop Mathew Blagden Hale in 1858, Hale School claims to be the oldest private boys' school in Western Australia, a claim subsequently contested by historian and former Hale School Headmaster Dr Ken Tregonning. The school was originally situated at the Cloisters on St Georges Terrace in Perth, relocated to the Pensioner Guard Barracks at the top of St George's Terrace around 1880, and then to new Havelock Street premises in 1914 in West Perth. In 1961 the School moved to its current premises in Wembley Downs. The campus now consists of a junior school for Years Pre-Primary to 6, a middle school for Years 7 & 8 and a senior school for Year 9 to 12. The school also consists of sporting grounds, and boarding facilities for regional and international students. The school is a member of the Public Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
