|
Frančesko Micalović
Frančesko Ratkov Micalović was an early 16th-century Ragusan printer who printed the first books on vernacular language of population of contemporary Ragusa (modern-day Dubrovnik). Micalović prepared Cyrillic script types and organized printing of prayer books in Venice in 1512. These prayer books are known as ''Molitvenik'' and ''Officio''. Micalović was obliged to collect printed books and to sell them in his shop which he was to open in Dubrovnik and in Ottoman Serbia. In sources, the language of these prayer books and the script in which it is printed is referred to as Bosnian, Ragusan, Serbian, Croatian, or Serbo-Croatian, depending on the point of view of its authors, and the Cyrillic script used to print them is in sources referred to as Bosančica. Family Frančesko Micalović's birth name was Ivan. His grandfather was a book trader. Frančesko's father was Ratko Vukosalić whose nickname was Micalović. Ratko Vukosalić belonged to a group of Ragusans who had ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
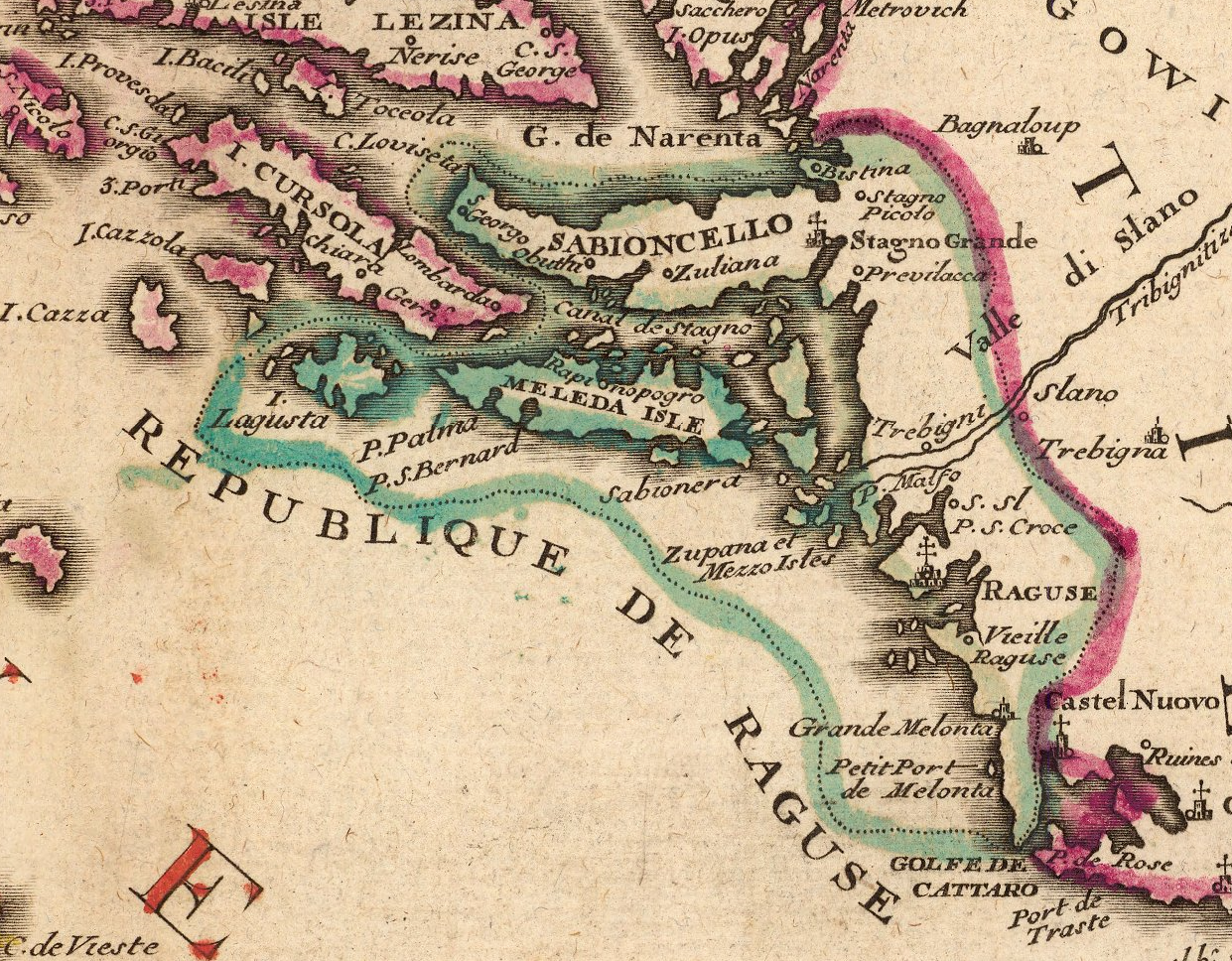
Ragusan Republic
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost Croatia) that carried that name from 1358 until 1808. It reached its commercial peak in the 15th and the 16th centuries, before being conquered by Napoleon's French Empire and formally annexed by the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy in 1808. It had a population of about 30,000 people, of whom 5,000 lived within the city walls. Its motto was "'", a Latin phrase which can be translated as "Liberty is not well sold for all the gold". Names Originally named ' (Latin for "Ragusan municipality" or "community"), in the 14th century it was renamed ' (Latin for ''Ragusan Republic''), first mentioned in 1385. It was nevertheless a Republic under its previous name, although its Rector was appointed by Venice rather than by Ragusa's own Major Council. In Italian it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
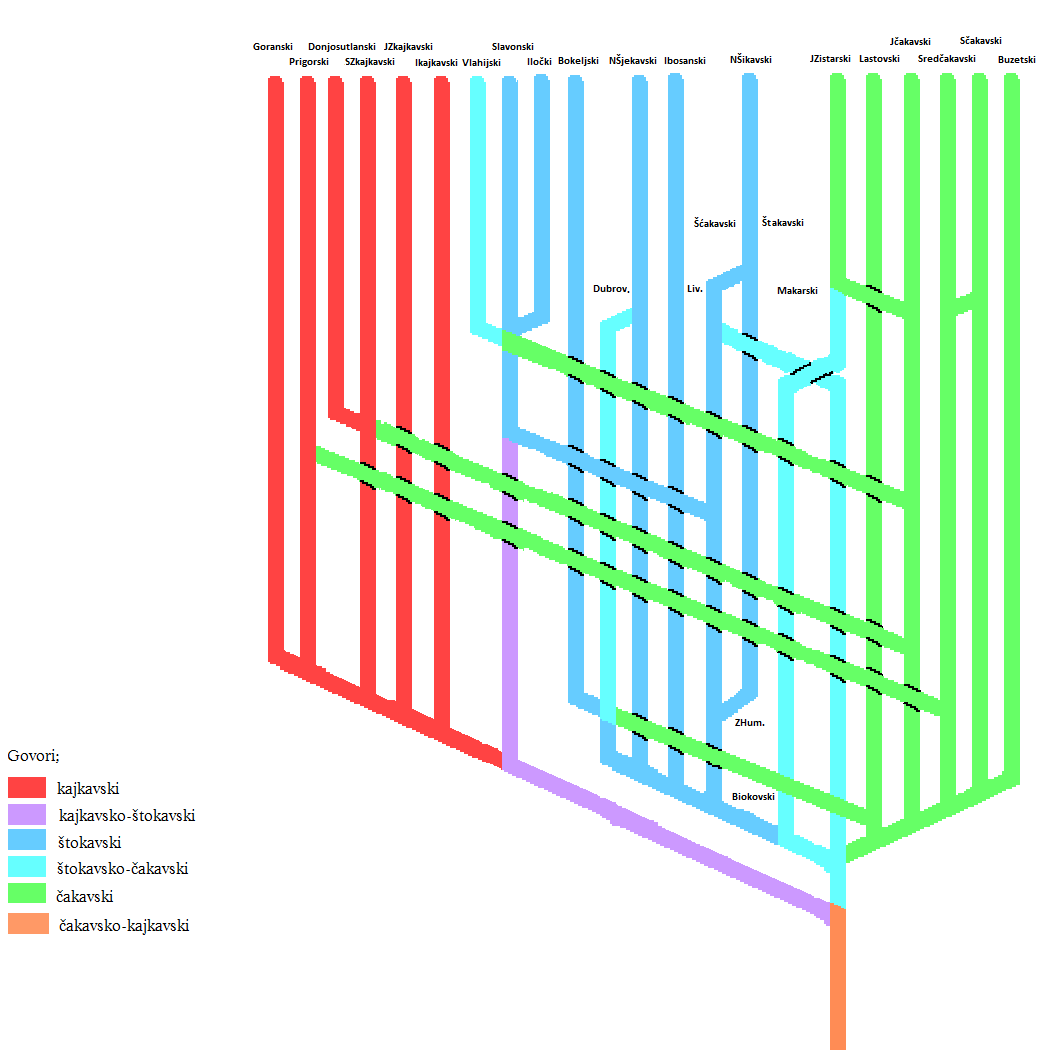
Chakavian Dialect
Chakavian or Čakavian (, , , proper name: or own name: ''čokovski, čakavski, čekavski'') is a South Slavic supradialect or language spoken by Croats along the Adriatic coast, in the historical regions of Dalmatia, Istria, Croatian Littoral and parts of coastal and southern Central Croatia (now collectively referred to as Adriatic Croatia or Littoral Croatia), as well as by the Burgenland Croats as Burgenland Croatian in southeastern Austria, northwestern Hungary and southwestern Slovakia as well as few municipalities in southern Slovenia on the border with Croatia. Chakavian represents the basis for early literary standards in Croatia, and until the modern age was simply known and understood, along with the Kajkavian and Shtokavian idioms in Croatia, as the Croatian language (''hrvatski jezik''). Legal and liturgical to literary texts until the 16th century, including literary work by "the father of Croatian literature" Marko Marulić and the first Croatian dict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragica Malić
Dragica (Cyrillic: Драгица) is a South Slavic feminine given name. Those bearing it include: * Dragica Basletić (1916—1976), Croatian gymnast * Dragica Cepernić (1981— ), Croatian football player * Dragica Džono (1987— ), Croatian handball player * Dragica Đurić (1963— ), former Yugoslav handball player * Dragica Kresoja (1986— ), Macedonian handball player * Dragica Mitrova (1987— ), Macedonian handball player * Dragica Ponorac, Montenegrin diplomat * Dragica Sekulić (1980— ), Montenegrin politician * Dragica Vasileska Dragica Vasileska (also published as Dragica Vasileska-Kafedziska) is an electrical engineer whose research involves what she calls "computational electronics": simulation and modeling of the physics of semiconductor devices, including integrated ..., Macedonian scientist References See also * {{Given name Slavic feminine given names Croatian feminine given names Feminine given names Serbian feminine given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vatican Croatian Prayer Book
The Vatican Croatian Prayer Book () is a Croatian vernacular prayer book and the example of Shtokavian vernacular literary dialect. Written between 1380 and 1400 in Dubrovnik as a transcript and transliteration from older texts composed in a mixture of Church Slavonic and Chakavian dialect and written down in Glagolitic with some Cyrillic script, it retained a few phonological and morphological features found in the original manuscripts. The book contains the following parts: Offices of the Virgin Mary according to the rites of the Roman Church; seven penitentiary psalms; Offices of the Holy Cross; Offices for the dead; Offices of the Holy Spirit as well as numerous prayers. The script is the Roman Gothic, embroidered with luxuriantly outlined initials and miniatures. The name of the prayer book reflects the fact that it is held in the Vatican library. The text has become widely known from 1859, when influential Croatian historian Franjo Rački drew attention to it, but the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatian Language
Croatian (; ) is the standard language, standardised Variety (linguistics)#Standard varieties, variety of the Serbo-Croatian pluricentric language mainly used by Croats. It is the national official language and literary standard of Croatia, one of the official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, the Serbian province of Vojvodina, the European Union and a recognized minority language elsewhere in Serbia and other neighbouring countries. In the mid-18th century, the first attempts to provide a Croatian literary standard began on the basis of the Neo-Shtokavian dialect that served as a supraregional lingua franca – pushing back regional Chakavian, Kajkavian, and Shtokavian vernaculars. The decisive role was played by Croatian Vukovians, who cemented the usage of Ijekavian Neo-Shtokavian as the literary standard in the late 19th and the beginning of the 20th century, in addition to designing a phonological orthography. Croatian is written in Gaj's Latin alphabet. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stjepan Ivšić
Stjepan Ivšić (; 13 August 1884 – 14 January 1962) was a Croatian linguist, Slavicist, and accentologist. Biography Ivšić was born on 13 August 1884 in Orahovica. After finishing primary school in Orahovica, he attended secondary school in Osijek and Požega. At the Faculty of Philosophy at the University of Zagreb he studied Croatian and classical philology, and later specialized at the universities in Kraków, Prague, Saint Petersburg, Moscow, and Kyiv. He received his Ph.D. in 1913 with the thesis ''Prilog za slavenski akcenat'' (A Contribution on the Slavic Accent). He served as a professor at the secondary school in Gornji Grad in Zagreb from 1909 to 1915, and thenceforth as a professor of Slavic Studies at the Faculty of Philosophy in Zagreb. The focal point of Ivšić's research was Croatian Štokavian subdialects, on which he published several very important studies (''Šaptinovačko narječje'', 1907; ''Današnji posavski govor'', 1913). He was especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serb Catholic Movement In Dubrovnik
The Serb-Catholic movement in Dubrovnik ( sh-Cyrl-Latn, separator=" / ", Дубровачки србокатолички покрет, Dubrovački srbokatolički pokret) was a cultural and political movement of people from Dubrovnik who, while Catholic, declared themselves Serbs, while Dubrovnik was part of the Habsburg-ruled Kingdom of Dalmatia in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Initially spearheaded by intellectuals who espoused strong pro-Serbian sentiments, there were two prominent incarnations of the movement: an early pan-Slavic phase under Matija Ban and Medo Pucić that corresponded to the Illyrian movement, and a later, more Serbian nationalist group that was active between the 1880s and 1908, including a large number of Dubrovnik intellectuals at the time. The movement, whose adherents are known as Serb-Catholics () or Catholic Serbs (), largely disappeared with the creation of Yugoslavia. Background Ragusa was founded in the 7th century by refugees from Epidaurum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Slavonic Language
Church Slavonic is the conservative Slavic liturgical language used by the Eastern Orthodox Church in Belarus, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Poland, Russia, Ukraine, Serbia, the Czech Republic and Slovakia, Slovenia and Croatia. The language appears also in the services of the Russian Orthodox Church Outside of Russia, the American Carpatho-Russian Orthodox Diocese, and occasionally in the services of the Orthodox Church in America. In addition, Church Slavonic is used by some churches which consider themselves Orthodox but are not in communion with the Orthodox Church, such as the Montenegrin Orthodox Church and the Russian True Orthodox Church. The Russian Old Believers and the Co-Believers also use Church Slavonic. Church Slavonic is also used by Greek Catholic Churches in Slavic countries, for example the Croatian, Slovak and Ruthenian Greek Catholics, as well as by the Roman Catholic Church (Croatian and Czech recensions). In the past, Church Slavon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oktoih
The ''Cetinje Octoechos'' ( or ''Cetinjski oktoih'') is a Serbian Orthodox liturgical book printed Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and Printmaking, images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabon ... in 1494 in Cetinje, the capital of the Principality of Zeta (present-day Montenegro). It is the first incunabulum written in the Serbian language, Serbian recension of Church Slavonic, as well as the first book printed in Cyrillic script, Cyrillic in Southeast Europe. The Octoechos (liturgy), octoechos was produced under the direction of Hieromonk Makarije at the Crnojević printing house, which was founded in 1493 by Đurađ Crnojević, the ruler of Zeta. Printed in two instalments, its first volume contains the hymns to be sung to the first four tones of the Octoechos, Octoechos system of musical modes, and the hymns for the remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milan Rešetar
Milan Rešetar (February 1, 1860 – January 14, 1942) was a linguist, historian and literary critic from Dubrovnik. Biography Rešetar was born in Dubrovnik. After the gymnasium in Dubrovnik, he studied classical philology and Slavic languages in Vienna and Graz. He worked as a high-school professor in Koper, Zadar and Split, and later a professor of Slavic studies on the universities of Vienna and Zagreb). He also edited the Croatian edition of "''List drevnih zakona''" magazine. Rešetar was a student of Vatroslav Jagić. He was a notable member of the Serb-Catholic movement in Dubrovnik. After retirement, he moved to Florence where he died 1942. The main areas of his works included dialectology and accentology of South Slavic languages, as well as philologically impeccable editions of 15th to 18th century writers for the Yugoslav Academy of Sciences and Arts. He was one of founders of South Slavic dialectology, investigating features of Štokavian dialects (''Der Štoka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and surpass the ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. Associated with great social change in most fields and disciplines, including Renaissance art, art, Renaissance architecture, architecture, politics, Renaissance literature, literature, Renaissance exploration, exploration and Science in the Renaissance, science, the Renaissance was first centered in the Republic of Florence, then spread to the Italian Renaissance, rest of Italy and later throughout Europe. The term ''rinascita'' ("rebirth") first appeared in ''Lives of the Artists'' () by Giorgio Vasari, while the corresponding French word was adopted into English as the term for this period during the 1830s. The Renaissance's intellectual basis was founded in its version of Renaiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dejan Medaković
Dejan Medaković ( sr-cyr, Дејан Медаковић; 7 July 1922 – 1 July 2008) was a Serbian art historian, writer and academician. Medaković had served as President of the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts from 1998 to 2003, as Dean of the University of Belgrade Faculty of Philosophy (1971–1973) and was a member of the Matica srpska as well as other scholarly associations. Life Dejan Medaković was born on 7 July 1922 in Zagreb (then the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (now Croatia) in an ethnic Serb family. His father, Đorđe Medaković, was an economist; his mother, Anastazija, a housewife. His paternal grandfather, Bogdan Medaković, had been a political leader of Serbs in Croatia during the Austro-Hungarian reign, president of the Serb Independent Party and president of the Croat-Serb Coalition and Speaker of the Croatian Sabor from 1908 to 1918. Dejan Medaković's great-grandfather Danilo had lived in the Kingdom of Serbia and held various posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |