|
Franz Breit (obstetrician)
Franz Breit (1 July 1817, in Mieders – 17 August 1868, in Tübingen) was an Austrian obstetrician. He studied medicine in Vienna, Prague and Padua,ADB: Breit, Franz Xaver at and was later an and assistant to professor of the maternity clinic at the |
Mieders
Mieders is a municipality in the southern part of the district Innsbruck-Land in the Austrian state of Tyrol. It is located on the right side of the Stubaital 10.60 km south of Innsbruck. History Founded in 1100, the scattered village is located on a gently rising slope of the valley at the foot of the 2718 m high Serles. Inhabited from the early Middle Ages, the centre has houses decorated with baroque frescoes. Population Tourism Two seasonal tourist resorts are located directly at the bottom of the skiing and hiking area Serlesbahnen. The slopes are also known for a summer alpine coaster (monorail), which extends from the top station to the base station of the gondola, leading through the lower wooded slopes of the forest, parallel to the route of the cable car. Transportation The town of Innsbruck is connected by a bus line. Neighboring municipalities *Fulpmes * Mühlbachl *Schönberg im Stubaital *Telfes Telfes (officially Telfes im Stubai) is a village in the distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignaz Semmelweis
Ignaz Philipp Semmelweis (; hu, Semmelweis Ignác Fülöp ; 1 July 1818 – 13 August 1865) was a Hungarian physician and scientist, who was an early pioneer of antiseptic procedures. Described as the "saviour of mothers", he discovered that the incidence of puerperal fever (also known as "childbed fever") could be drastically reduced by requiring hand disinfection in obstetrical clinics. Puerperal fever was common in mid-19th-century hospitals and often fatal. He proposed the practice of washing hands with chlorinated lime solutions in 1847 while working in Vienna General Hospital's First Obstetrical Clinic, where doctors' wards had three times the mortality of midwives' wards. He published a book of his findings in '' Etiology, Concept and Prophylaxis of Childbed Fever''. Despite various publications of results where hand-washing reduced mortality to below 1%, Semmelweis's observations conflicted with the established scientific and medical opinions of the time and his idea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Innsbruck-Land District
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1868 Deaths
Events January–March * January 2 – British Expedition to Abyssinia: Robert Napier leads an expedition to free captive British officials and missionaries. * January 3 – The 15-year-old Mutsuhito, Emperor Meiji of Japan, declares the ''Meiji Restoration'', his own restoration to full power, under the influence of supporters from the Chōshū and Satsuma Domains, and against the supporters of the Tokugawa shogunate, triggering the Boshin War. * January 5 – Paraguayan War: Brazilian Army commander Luís Alves de Lima e Silva, Duke of Caxias enters Asunción, Paraguay's capital. Some days later he declares the war is over. Nevertheless, Francisco Solano López, Paraguay's president, prepares guerrillas to fight in the countryside. * January 7 – The Arkansas constitutional convention meets in Little Rock. * January 9 – Penal transportation from Britain to Australia ends, with arrival of the convict ship ''Hougoumont'' in Western Australi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1817 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – Sailing through the Sandwich Islands, Otto von Kotzebue discovers New Year Island. * January 19 – An army of 5,423 soldiers, led by General José de San Martín, starts crossing the Andes from Argentina, to liberate Chile and then Peru. * January 20 – Ram Mohan Roy and David Hare found Hindu College, Calcutta, offering instructions in Western languages and subjects. * February 12 – Battle of Chacabuco: The Argentine–Chilean patriotic army defeats the Spanish. * March 3 ** President James Madison vetoes John C. Calhoun's Bonus Bill. ** The U.S. Congress passes a law to split the Mississippi Territory, after Mississippi drafts a constitution, creating the Alabama Territory, effective in August. * March 4 – James Monroe is sworn in as the fifth President of the United States. * March 21 – The flag of the Pernambucan Revolt is publicly blessed by the dean of Recife Cathedral, Brazil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerperium
The postpartum (or postnatal) period begins after childbirth and is typically considered to end within 6 weeks as the mother's body, including hormone levels and uterus size, returns to a non-pregnant state. The terms puerperium, puerperal period, or immediate postpartum period are commonly used to refer to the first six weeks following childbirth. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes the postnatal period as the most critical and yet the most neglected phase in the lives of mothers and babies; most maternal and infant mortality, newborn deaths occur during this period. In scientific literature, the term is commonly abbreviated to P''x'', where ''x'' is a number; for example, "day P5" should be read as "the fifth day after birth". This is not to be confused with the medical nomenclature that uses G P to stand for number and outcomes of pregnancy (gravidity and parity). A female giving birth in a hospital may leave as soon as they are medically stable, which can be as ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
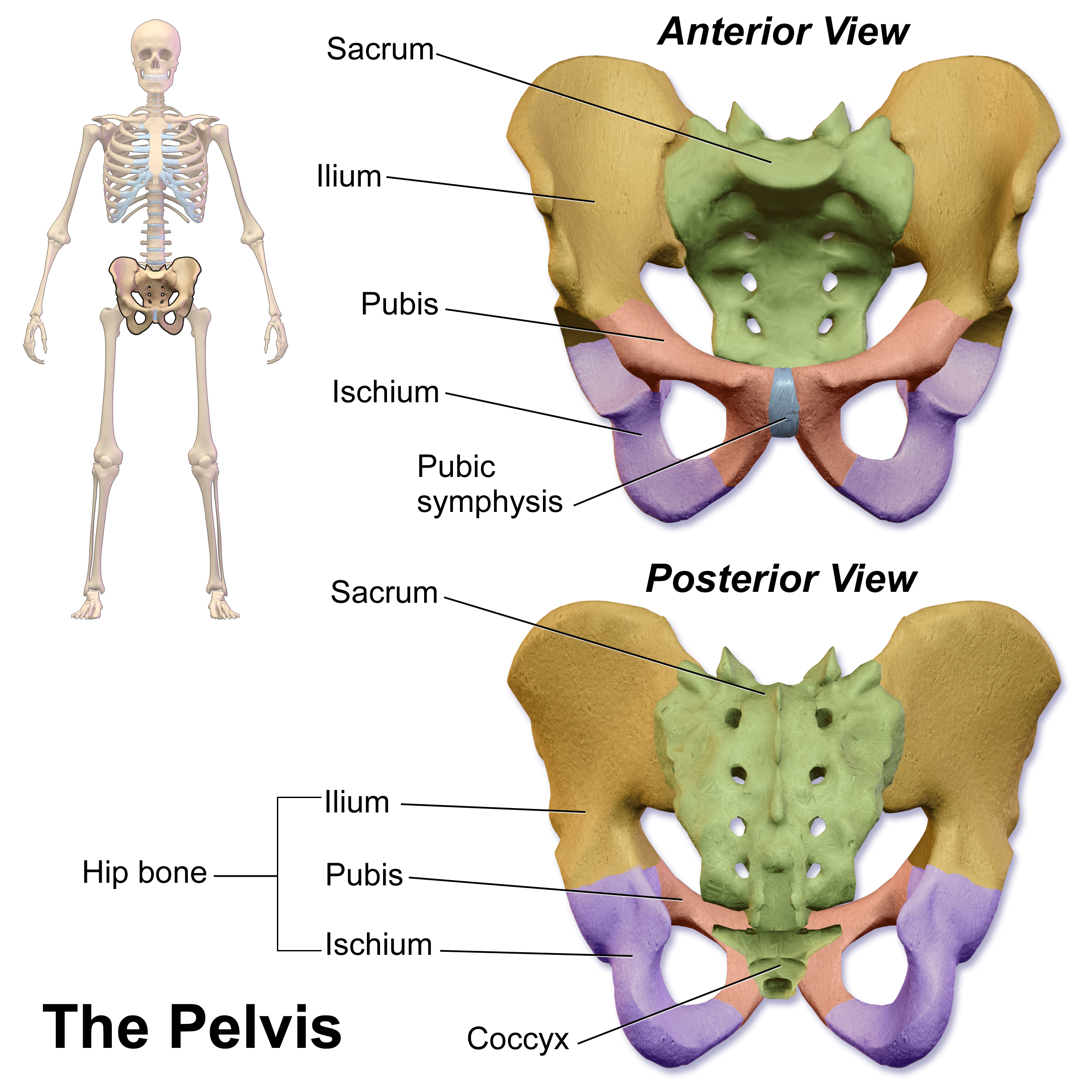
Symphysis Pubis
The pubic symphysis is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior pubic ramus, superior rami of the pubis of the pubis (bone), hip bones. It is in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubic symphysis. In females, the pubic symphysis is close to the clitoris. In most adults it can be moved roughly 2 mm and with 1 degree rotation. This increases for women at the time of childbirth. The name comes from the Greek word ''symphysis'', meaning 'growing together'. Structure The pubic symphysis is a Synovium, nonsynovial Amphiarthrosis, amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by fibrocartilage and may contain a fluid-filled cavity; the center is Blood vessel, avascular, possibly due to the nature of the compressive forces passing through this joint, which may lead to harmful vascular disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Reinhold August Wunderlich
Carl Reinhold August Wunderlich (4 August 1815, Sulz am Neckar – 25 September 1877, Leipzig) was a German physician, pioneer psychiatrist, and medical professor. He is known for his measurement of mean normal human body temperature of 37 °C (98.6 °F), now known more accurately to be about 36.8 °C (98.2 °F). He attended grammar school in Stuttgart and at the age of eighteen he began his medical studies at University of Tübingen, where he completed his final exams in 1837. In 1838 he worked as assistant at St Catharine's Hospital in Stuttgart, and wrote his MD thesis. Two years later he wrote his MD habilitation on internal medicine at University of Tübingen. In 1846, he was appointed Professor ( ordentlicher Professor) and head of the general hospital at Tübingen. He moved to Leipzig University as Professor and Medical Director of the university hospital four years later. There he introduced clinical pedagogy, combined with a rigorous methodol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Roser
Wilhelm Roser (26 March 1817 – 16 December 1888) was a German surgeon and ophthalmologist. He was born in Stuttgart and died in Marburg. In 1839 he received his medical doctorate from the University of Tübingen, and afterwards continued his education in Würzburg, Halle, Vienna and Paris. In 1841 he returned to Tübingen, where he was habilitated for surgery. In 1846 he practiced medicine in Reutlingen, and later succeeded Eduard Zeis (1807–1868) as professor of surgery at the University of Marburg. Roser would remain at Marburg for the remainder of his career. With his lifelong friends, clinician Carl Wunderlich (1815–1877) and neurologist Wilhelm Griesinger (1817–1868), he founded a journal of physiological medicine titled ''Archiv für physiologische Heilkunde''. He published over 150 medical papers, and was the author of ''Handbuch der anatomischen Chirurgie'', a textbook on anatomical surgery that ran through eight editions, and was translated into French and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Lumpe (obstetrician)
Eduard Lumpe (1813–1876) was an obstetrician working in Vienna General Hospital as assistant to professor Johann Klein. He is mainly known for compiling a list of causes for childbed fever in 1845, reflecting the (in retrospect: limited) insights at the time. The disease was predominantly epidemic, i.e. due to miasmatic influences. Other causal factors included: general deprivation, worry, shame, attempted abortion, fear of death, dietary disorders, exposure to cold, local miasmas and difficult delivery. Ignaz Semmelweis ridiculed Lumpe's work. Lumpe's work reflected mainstream views, see for instance the work of Charles Delucena Meigs Charles Delucena Meigs (February 19, 1792 – June 22, 1869) was an American obstetrician of the nineteenth century who is remembered for his opposition to obstetrical anesthesia and to advocating the idea that physicians' hands could not transmi ...Meigs(1854):179ff for a similar American account in 1854. References * * * Notes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Tübingen
The University of Tübingen, officially the Eberhard Karl University of Tübingen (german: Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen; la, Universitas Eberhardina Carolina), is a public research university located in the city of Tübingen, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The University of Tübingen is one of eleven German Excellence Universities. The University of Tübingen is especially known as a centre for the study of plant biology, medicine, law, archeology, ancient cultures, philosophy, theology, and religious studies as well as more recently as center of excellence for artificial intelligence. The university's noted alumni include presidents, EU Commissioners, and judges of the Federal Constitutional Court. The university is associated with eleven Nobel laureates, especially in the fields of medicine and chemistry. History The University of Tübingen was founded in 1477 by Count Eberhard V (Eberhard im Bart, 1445–1496), later the first Duke of Württemberg, a civic and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tübingen
Tübingen (, , Swabian: ''Dibenga'') is a traditional university city in central Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated south of the state capital, Stuttgart, and developed on both sides of the Neckar and Ammer rivers. about one in three of the 90,000 people living in Tübingen is a student. As of the 2018/2019 winter semester, 27,665 students attend the Eberhard Karls University of Tübingen. The city has the lowest median age in Germany, in part due to its status as a university city. As of December 31, 2015, the average age of a citizen of Tübingen is 39.1 years. The city is known for its veganism and environmentalism. Immediately north of the city lies the Schönbuch, a densely wooded nature park. The Swabian Alb mountains rise about (beeline Tübingen City to Roßberg - 869 m) to the southeast of Tübingen. The Ammer and Steinlach rivers are tributaries of the Neckar river, which flows in an easterly direction through the city, just south of the medieval old t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_1938.jpg)