|
Frankland, Western Australia
Frankland River is a small town and locality in the Shire of Cranbrook, Great Southern region of Western Australia. The town is situated approximately from the state's capital, Perth, approximately north west of Albany, southwest of Kojonup, north of Rocky Gully and east of Manjimup. Frankland derives its name from its location 6 km east of the Frankland River. At the 2006 census, Frankland had a population of 380. History Frankland River was named by the surgeon Thomas Braidwood Wilson in 1829. Wilson, who was on his way to Sydney, left Albany to explore the hinterland while his ship, ''Governor Phillip'', was being repaired.''The Albany Advertiser'', 8 January 1969 He named Frankland River and Mount Frankland after George Frankland (1800–38), who was the surveyor-general in Van Diemen's Land in 1829. Wilson's explorations helped to show that conditions in the interior were suitable for farming and settlers soon began to move inland. The area was settled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral District Of Roe
Roe is an Electoral districts of Western Australia, electoral district of the Western Australian Legislative Assembly, Legislative Assembly of Western Australia. It takes in rural areas in the south of the state. Roe was re-created for the 2017 Western Australian state election, 2017 state election, having previously been in existence from 1950 to 1983 and from 1989 to 2008. It had a notional 16.7-point majority for the National Party of Australia (WA), National Party against the Liberal Party of Australia (Western Australian Division), Liberal Party, based on the results of the 2013 Western Australian state election, 2013 state election. Geography In its current incarnation, Roe includes portions of four regions of Western Australia – the South West (Western Australia), South West, the Wheatbelt (Western Australia), Wheatbelt, the Great Southern (Western Australia), Great Southern and Goldfields-Esperance. There are eighteen Local government areas of Western Australia, local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
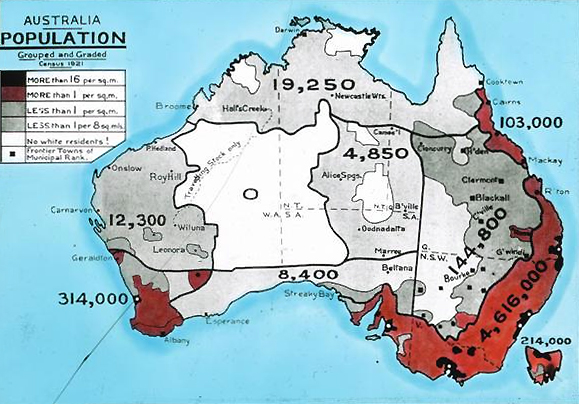
Census In Australia
The Census in Australia, officially the Census of Population and Housing, is the national census in Australia that occurs every five years. The census collects key demographic, social and economic data from all people in Australia on census night, including overseas visitors and residents of States and territories of Australia#External territories, Australian external territories, only excluding foreign diplomats. The census is the largest and most significant statistical event in Australia and is run by the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). Every person must complete the census, although some personal questions are not compulsory. The penalty for failing to complete the census after being directed to by the Australian Statistician is one federal penalty unit, or . The ''Australian Bureau of Statistics Act 1975'' and ''Census and Statistics Act 1905'' authorise the ABS to collect, store, and share anonymised data. The 1911 Australian census, first Australian census was held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Southern (wine Region)
The Great Southern wine region is in Western Australia's Great Southern region. It comprises an area from east to west and over from north to south, and is Australia's largest wine region Wines are produced in significant growing regions where vineyards are planted. Wine grapes berries mostly grow between the 30th and the 50th degrees of latitude, in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, typically in regions of Mediterranea .... It has five nominated subregions for wine, the Porongurup, Western Australia, Porongurups, Mount Barker, Western Australia, Mount Barker, Albany, Western Australia, Albany, Denmark, Western Australia, Denmark and Frankland, Western Australia, Frankland River under the geographical indications legislation as determined by the Australian Wine and Brandy Corporation. The vineyards spread throughout the area known for production of high quality vines have significant variations of terroir and climate dictated in part by the distance however the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Southern Railway (Western Australia)
The Great Southern Railway was a railway company that operated from Beverley to Albany in Western Australia between 1889 and 1896. In 1896 the Western Australian Government Railways took over the company, and kept the name for the route. Land development The Great Southern Railway project was directly tied in with developments of lands related to agriculture. Construction The ''Beverley-Albany Railway Act 1884'', an act by the Western Australian Legislative Council and the Governor of Western Australia, assented to on 13 September 1884, authorised the construction of the railway line from Beverley to Albany. The first sods for the gauge railway were turned on 20 October 1886. This occurred simultaneously at Beverley and Albany by Lady Broome and the Governor A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Nunijup
Lake Nunijup is an ephemeral salt lake located in the Great Southern (Western Australia), Great Southern region of Western Australia, approximately south west of Cranbrook, Western Australia, Cranbrook and north west of Mount Barker, Western Australia, Mount Barker. Description The lake is part of the Bow River (Western Australia), Bow River sub-catchment and the Kent River catchment. The surrounding landscape is composed of lakes and swamps with lunettes situated over tertiary alluvium, colluvium and sand with underlying laterite also present. Quaternary swamp and lake deposits are also found within the Frankland, Western Australia, Frankland district. Small amounts of brackish water can be received from the south western flanks of the Stirling Range that can flow into the lake. The area receives around of rainfall per annum and loses around from evaporation. The annual inflow to the lake between 1973 and 2001 was , of which about 70% evaporated and 26% seeped through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corymbia Calophylla
''Corymbia calophylla'', commonly known as marri, is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to the southwest of Western Australia. It is a tree or Mallee (habit), mallee with rough bark on part or all of the trunk, lance-shaped adult leaves, branched clusters of cup-shaped or pear-shaped flower buds, each branch with three or seven buds, white to pink flowers, and relatively large oval to urn-shaped fruit, colloquially known as ''honky nuts''. Marri wood has had many uses, both for Aboriginal people, and in the construction industry. Description ''Corymbia calophylla'' is a large tree, or a mallee in poor soil, that typically grows to a height of , but can reach over . The largest known individual specimen is tall, has a girth and a wood volume of . The trunk of the tree may grow up to wide, the branches becoming large, thick and rambling. It has rough, tessellated, grey-brown to red-brown bark that extends over the length of the trunk and branc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalyptus Marginata
''Eucalyptus marginata'', commonly known as jarrah, in Noongar language and historically as Swan River mahogany, is a plant in the Myrtus, myrtle Family (biology), family, Myrtaceae and is endemism, endemic to the Southwest Australia, south-west of Western Australia. It is a tree with rough, fibrous bark, leaves with a distinct midvein, white flowers and relatively large, more or less spherical fruit. Its hard, dense timber is insect resistant although the tree is susceptible to Phytophthora cinnamomi, dieback. The timber has been utilised for Cabinetry, cabinet-making, flooring and Railroad tie, railway sleepers. Description Jarrah is a tree which sometimes grows to a height of up to with a diameter at breast height, DBH of , but more usually with a DBH of up to . Less commonly it can be a small Mallee (habit), mallee to high. Older specimens have a lignotuber and roots that extend down as far as . It is a stringybark with rough, greyish-brown, vertically grooved, fibrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wandoo
Wandoo is the common name for a number of Western Australian ''Eucalyptus'' species, all of which have smooth white bark. The original "wandoo" is ''Eucalyptus wandoo''. Additional species have been given this name because of a perceived likeness with ''E. wandoo''. These include * ''Eucalyptus redunca'' (wandoo) * ''Eucalyptus accedens'' (wandoo, or powder-bark wandoo) * ''Eucalyptus capillosa'' (wheatbelt wandoo) * '' Eucalyptus lane-poolei'' (salmonbark wandoo) * '' Eucalyptus livida'' (mallee wandoo) * ''Eucalyptus nigrifunda ''Eucalyptus nigrifunda'', commonly known as desert wandoo, is a species of tree that is endemic to a small area in central Western Australia. It has smooth reddish brown bark with some rough, flaky black bark near the base of the trunk, lance-sh ...'' (desert wandoo) {{Plant common name Eucalyptus Rosids of Western Australia Myrtales of Australia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Townsite
A townsite is a legal subdivision of land for the development of a town or community. In the historical development of the United States, Canada, and other former British colonial nations, the filing of a townsite plat (United States) or plan (Canada) was often the first legal act in the establishment of a new town or community. Townsites in British Columbia Numerous townsites were filed in British Columbia, Canada, in the early 19th century. Some of those filed in what is now Metro Vancouver included: * Granville Townsite, 1870 (Gastown, Vancouver) *Hastings Townsite, 1869 (Vancouver) * Moodyville Townsite, 1865 (City of North Vancouver) *New Westminster Townsite, 1860 (original capital of Colony of British Columbia, now New Westminster) * North Vancouver Townsite, 1907North Vancouver Official Community Plan 2002, Chapter 2, Historical overview (City of North Vancouver) * Port Mann Townsite, 1911 (Surrey) * Steveston Townsite, 1889 (Richmond) Although most of these townsites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania during the European exploration of Australia, European exploration and colonisation of Australia in the 19th century. The Aboriginal Tasmanians, Aboriginal-inhabited island was first visited by the Dutch ship captained by Abel Tasman in 1642, working under the sponsorship of Anthony van Diemen, the Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies. The British retained the name when they established a settlement in 1803 before it became a separate colony in 1825. Its Penal colony, penal colonies became notorious destinations for the Convicts in Australia, transportation of convicts due to the harsh environment, isolation and reputation for being escape-proof. The name was changed to Tasmania on 1st January 1856 to disassociate the island from its convict past and to honour its discoverer, Abel Tasman. The old name had become a byword for horror in England because of the severity of its convict settlements such as Macq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Frankland
George Frankland (1800 – 30 December 1838) was an English surveyor and Surveyor-General of Van Diemen's Land (now Tasmania). In 1823, Frankland was appointed surveyor-general at Poona, India, where he became acquainted with Edward Dumaresq. In 1827 Frankland arrived in Van Diemen's Land as first assistant surveyor, in March 1828 he became Surveyor General of Tasmania. Frankland soon began a trigonometric survey of the island, but suffered some criticism due to his slow progress. John Helder Wedge and James Erskine Calder criticized Frankland's ability as a surveyor. Frankland travelled on several expeditions and recorded his observations, considering it his duty ''"to observe and record every remarkable fact connected with the Natural history of the island whose surface and native production have, in a manner, been placed so peculiarly in his custody."'' Frankland made sketches of some of the country he explored and did the artwork for the proclamation to encourage peacef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydney, Australia
Sydney is the capital city of the state of New South Wales and the most populous city in Australia. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about 80 km (50 mi) from the Pacific Ocean in the east to the Blue Mountains in the west, and about 80 km (50 mi) from Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park and the Hawkesbury River in the north and north-west, to the Royal National Park and Macarthur in the south and south-west. Greater Sydney consists of 658 suburbs, spread across 33 local government areas. Residents of the city are colloquially known as "Sydneysiders". The estimated population in June 2024 was 5,557,233, which is about 66% of the state's population. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2017. The city's nicknames include the Emerald City and the Harbour City. There is evidence that Aboriginal Australians inhabited the Greater Sydney region at least 30,000 years ago, and their engravings and cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |