|
Franciscus Piroulle
François, France or Franciscus Piroulle (died 1663) was a theologian in the Habsburg Netherlands and the Prince-Bishopric of Liège. Life Piroulle was born in Limbourg ( Duchy of Limburg) and studied at Leuven University, where he graduated with a licentiate in philosophy in 1607 and later as Licentiate in Sacred Theology.Alphonse Roersch, "Piroulle, François", '' Biographie Nationale de Belgique''vol. 17(Brussels, 1903), 658-660. From 1613 to 1621 he taught at Lily College, Leuven. In 1621 he moved to Bruges, where he had been appointed to a canonry of St. Donatian's Cathedral on 4 May 1620. On 11 January 1634 he delivered the funerary oration for the Infanta Isabella in the cathedral.''Oratio funebris in obitum augustae et felicis memoriae Isabellae Clarae Eugeniae Hispaniarum infantis'' (Bruges, Nicolaes Breyghel, 1634)On Google Books In 1637 he was appointed canon and cantor of St Paul's minster in Liège. Around 1645 he was appointed professor and president of the Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
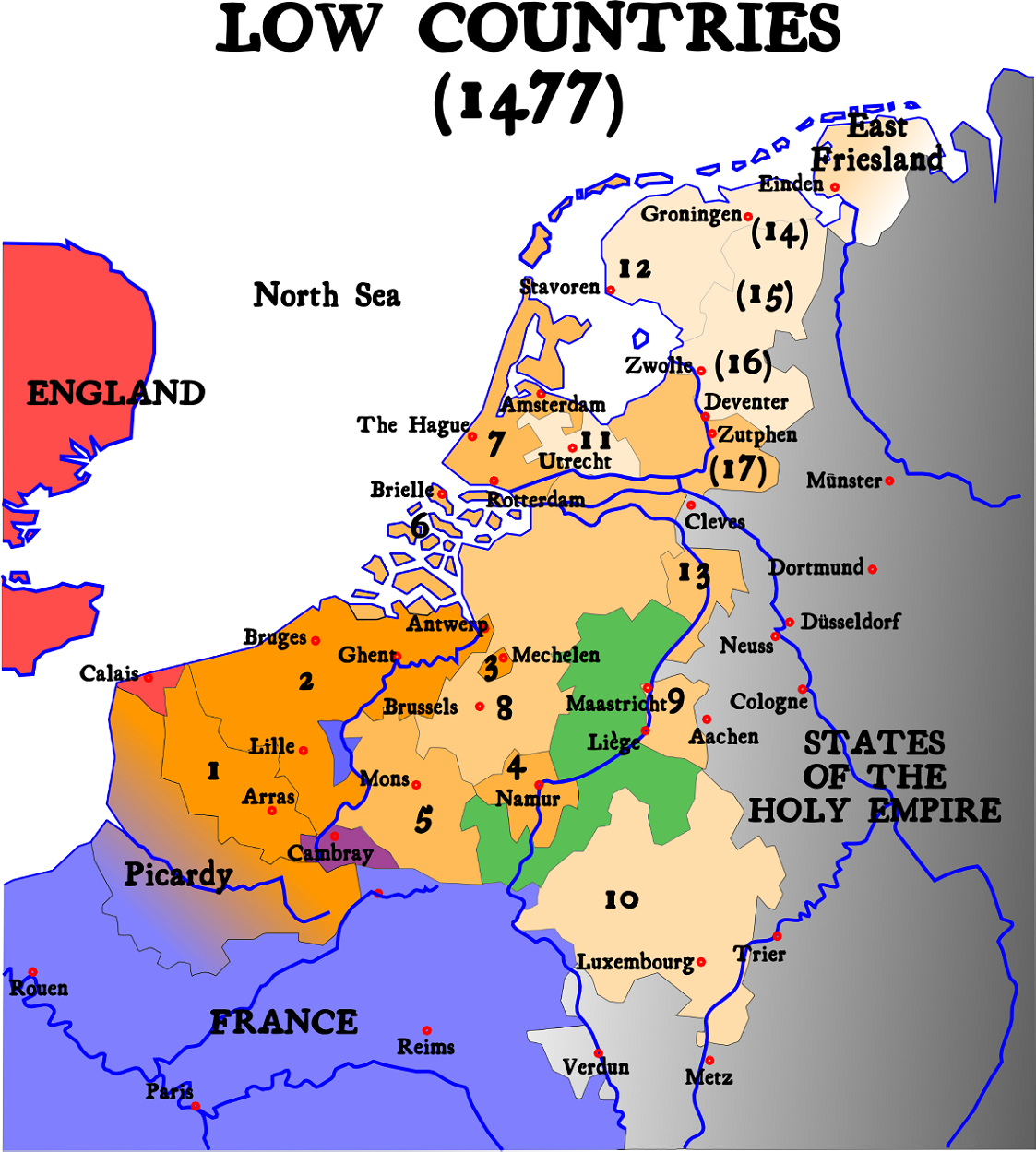
Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands was the Renaissance period fiefs in the Low Countries held by the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. The rule began in 1482, when the last House of Valois-Burgundy, Valois-Burgundy ruler of the Netherlands, Mary of Burgundy, Mary, wife of Maximilian I of Austria, died. Their grandson, Emperor Charles V, was born in the Habsburg Netherlands and made Brussels one of his capitals. Becoming known as the Seventeen Provinces in 1549, they were held by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556, known as the Spanish Netherlands from that time on. In 1581, in the midst of the Dutch Revolt, the Seven United Provinces seceded from the rest of this territory to form the Dutch Republic. The remaining Spanish Southern Netherlands became the Austrian Netherlands in 1714, after Austrian acquisition under the Treaty of Rastatt. De facto Habsburg rule ended with the annexation by the revolutionary French First Republic in 1795. Austria, however, did not relinquish its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantor (Christianity)
In Christianity, the cantor, sometimes called the precentor or the protopsaltes (; from ), is the chief singer, and usually instructor, employed at a church, with responsibilities for the choir and the preparation of the Mass or worship service. Generally, a cantor must be competent to choose and conduct the vocals for the choir, to start any chant on demand, and to be able to identify and correct the missteps of singers placed under them. A cantor may be held accountable for the immediate rendering of the music, showing the course of the melody by movements of the hand(s) (''cheironomia''), similar to a conductor. Western Christianity Roman Catholicism Before and after the Second Vatican Council, a ''cantor'' in the Roman Catholic Church was the leading singer of the choir, a ''bona fide'' clerical role. The medieval cantor of the papal Schola Cantorum was called ''Prior scholae'' or ''Primicerius''. In medieval cathedrals, the cantor or precentor directed the music and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clergy From The Spanish Netherlands
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the terms used for individual clergy are clergyman, clergywoman, clergyperson, churchman, and cleric, while clerk in holy orders has a long history but is rarely used. In Christianity, the specific names and roles of the clergy vary by denomination and there is a wide range of formal and informal clergy positions, including deacons, elders, priests, bishops, preachers, pastors, presbyters, ministers, and the pope. In Islam, a religious leader is often known formally or informally as an imam, caliph, qadi, mufti, mullah, muezzin, or ayatollah. In the Jewish tradition, a religious leader is often a rabbi (teacher) or hazzan (cantor). Etymology The word ''cleric'' comes from the ecclesiastical Latin ''Clericus'', for those belonging to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old University Of Leuven Alumni
Old or OLD may refer to: Places *Old, Baranya, Hungary *Old, Northamptonshire, England *Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD) *OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, Maine, United States People *Old (surname) Music *OLD (band), a grindcore/industrial metal group * ''Old'' (Danny Brown album), a 2013 album by Danny Brown * ''Old'' (Starflyer 59 album), a 2003 album by Starflyer 59 * "Old" (song), a 1995 song by Machine Head *''Old LP'', a 2019 album by That Dog Other uses * ''Old'' (film), a 2021 American thriller film *''Oxford Latin Dictionary'' *Online dating *Over-Locknut Distance (or Dimension), a measurement of a bicycle wheel and frame *Old age See also *List of people known as the Old * * *Olde, a list of people with the surname *Olds (other) Olds may refer to: People * The olds, a jocular and irreverent online nickname for older adults * Bert Olds (1891–1953), Australian rules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Limbourg
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1663 Deaths
Events January–March * January 10 – The Royal African Company is granted a Royal Charter by Charles II of England. * January 23 – The Treaty of Ghilajharighat is signed in India between representatives of the Mughal Empire and the independent Ahom Kingdom (in what is now the Assam state), with the Mughals ending their occupation of the Ahom capital of Garhgaon, in return for payment by Ahom in silver and gold for costs of the occupation, and King Sutamla of Ahom sending one of his daughters to be part of the harem of Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb. * February 5 - A magnitude 7.3 to 7.9 earthquake hits Canada's Quebec Province. * February 8 – English pirates led by Christopher Myngs and Edward Mansvelt carry out the sack of Campeche in Mexico, looting the town during a two week occupation that ends on February 23. * February 10 – The army of the Kingdom of Siam (now Thailand) captures Chiang Mai from the Kingdom of Burma (now Myanmar), using it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century Births
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The 16th century is regarded by historians as the century which saw the rise of Western civilization and the Islamic gunpowder empires. The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocesan Seminary Of Liège
The Diocesan Seminary of Liège (in French: ''Séminaire épiscopal'' or ''Grand Séminaire de Liège''), now also Espace Prémontrés, is an educational institution in the Diocese of Liège, founded in 1592. History The seminary was first founded by Ernest of Bavaria in 1592 to train diocesan clergy in line with the decrees of the Council of Trent. The papal breve of foundation was dated 5 March 1592, and the seminary was formally opened on 28 May that year, in the buildings of the former Hôpital Saint-Mathieu. In 1605, the seminary opened a dependent college, Liège College, at the University of Leuven. In 1786, after the suppression of the Society of Jesus, the seminary moved into the vacated premises of the Jesuit college. Teaching was suspended during the French period In Northern European historiography, the term French period (french: Période française, german: Franzosenzeit, nl, Franse tijd) refers to the period between 1794 and 1815 during which most of Northern E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
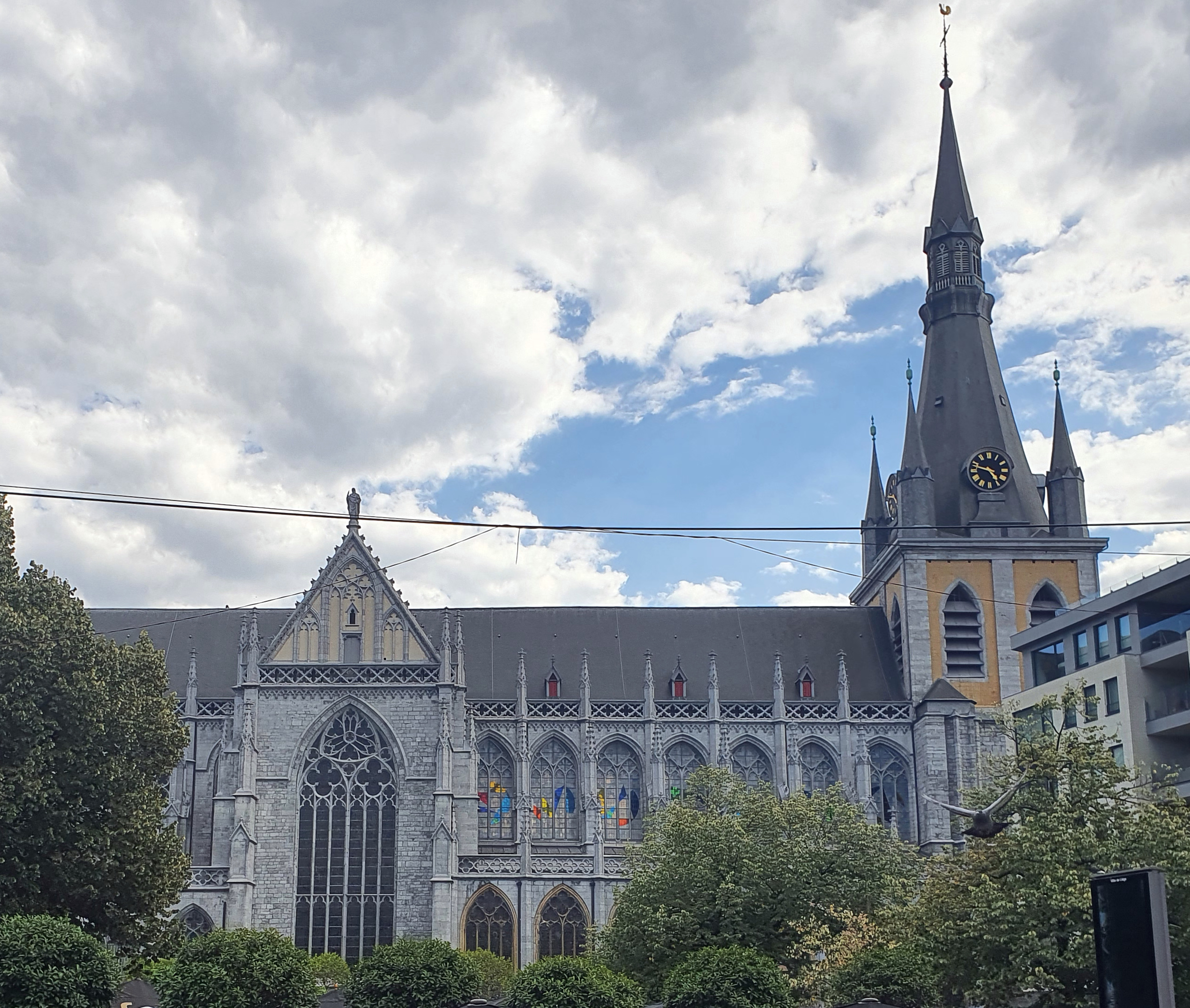
Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège. The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far from borders with the Netherlands (Maastricht is about to the north) and with Germany (Aachen is about north-east). In Liège, the Meuse meets the river Ourthe. The city is part of the '' sillon industriel'', the former industrial backbone of Wallonia. It still is the principal economic and cultural centre of the region. The municipality consists of the following districts: Angleur, , Chênée, , Grivegnée, Jupille-sur-Meuse, Liège, Rocourt, and Wandre. In November 2012, Liège had 198,280 inhabitants. The metropolitan area, including the outer commuter zone, covers an area of 1,879 km2 (725 sq mi) and had a total population of 749,110 on 1 January 2008. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liège Cathedral
Liège Cathedral, otherwise St. Paul's Cathedral, Liège, in Liège, Belgium, is part of the religious heritage of Liège. Founded in the 10th century, it was rebuilt from the 13th to the 15th century and restored in the mid-19th century. It became a Catholic cathedral in the 19th century due to the destruction of Saint Lambert's Cathedral in 1795. It is the seat of the Diocese of Liège. St. Paul's Cathedral During the French Revolution the ancient cathedral of Liège, St. Lambert's, was destroyed. After the revolution the former collegiate church of St. Paul's was elevated in rank, becoming the current Liège Cathedral. History The present cathedral was formerly one among the Seven collegiate churches of Liège – St. Peter's, Holy Cross, St. Paul's, St. John's, St. Denis's, St. Martin's and St. Bartholomew's – which until the Liège Revolution of 1789 together comprised the "secondary clergy" of the First Estate in the Prince-bishopric of Liège (the "primary c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolaes Breyghel
Nicolaes Breyghel (died 1669), Latinized Nicolaus Breyghelius, was a leading printer and bookseller in 17th-century Bruges in the Habsburg Netherlands. He was the first publisher of a weekly newspaper in the city. Career Breyghel, originally from Cologne, trained as a printer in Antwerp in the early 17th century, becoming a freeman of the city and a master of the Guild of Saint Luke in 1624. In 1625 he set up shop in Bruges, his relocation expenses reimbursed by the city council.Arthur der Weduwen, ''Dutch and Flemish Newspapers of the Seventeenth Century'' (Brill: Leiden and Boston, 2017), pp. 468-470. Much of his work was printing official publications for the city, but by 1637 he was also publishing the city's first newspaper, ''Nieuwe Tydinghen uyt verscheyde ghewesten''. This was printed weekly, usually on Tuesdays. Between 1640 and 1658 he repeatedly held office in the booksellers' guild. He died on 17 April 1669. Publications Books * 1625: Olivier de Wree, ''De vermaerde oor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince-Bishopric Of Liège
The Prince-Bishopric of Liège or Principality of Liège was an Hochstift, ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that was situated for the most part in present-day Belgium. It was an Imperial State, Imperial Estate, so the List of bishops and prince-bishops of Liège, bishop of Liège, as its prince, had a seat and a vote in the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet. The Prince-Bishopric of Liège should not be confused with the Diocese of Liège, which was larger and over which the prince-bishop exercised only the usual responsibilities of a bishop. The bishops of Liège acquired their status as prince-bishops between 980 and 985 when Bishop Notker of Liège, who had been the bishop since 972, received secular control of the County of Huy from Otto II, Holy Roman Emperor. From 1500, the prince-bishopric belonged to the Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle. Its territory included most of the present Belgian provinces of Liège (province), Liège and Limbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1938.jpg)




