|
Francisco De Arango Y Parreño
Francisco de Arango y Parreño (1765–1837) was a Cuban planter and intellectual. He helped to oversee colonial Cuba's transformation into a major sugar and coffee producer in the last decades of the eighteenth century and the first decades of the nineteenth century. Early life Arango y Parreño was born into a bourgeois ''Criollo'' Cuban family on May 22, 1765, in Havana, Cuba. He studied at the Real Colegio Seminario de San Carlos y San Ambrosio. Later, in the 1780s, he studied at the University of San Jeronimo. In 1787, he traveled to Madrid, where he continued his legal studies. By 1789, he had obtained a law degree. Career The outbreak of the French Revolution and the subsequent Haitian Revolution (1791–1804) opened new possibilities for Cuban planters. In the first half of the eighteenth century, Cuba's agriculture was fairly basic. The economy centered on ranching and small tobacco farms. A series of events transformed Cuba into a major plantation colony during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblioteca Nacional De España
The (National Library of Spain) is the national library of Spain. It is the largest public library in the country, and one of the largest in the world. Founded in 1711, it is an autonomous agency attached to the Ministry of Culture since 1990. Its headquarters is located on the Paseo de Recoletos in Madrid, sharing the building with the National Archaeological Museum. History The library was founded by King Philip V in 1711 as the Royal Library or Palace Public Library. The Royal Letters Patent that he granted, the predecessor of the current legal deposit requirement, made it mandatory for printers to submit a copy of every book printed in Spain to the library. In 1836, the Crown transferred the library to the Ministry of Governance and it was renamed as National Library. A year later, women were allowed access to the library for the first time, after a petition from writer Antonia Gutiérrez was granted by Queen Regent Maria Christina. During the 19th century, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
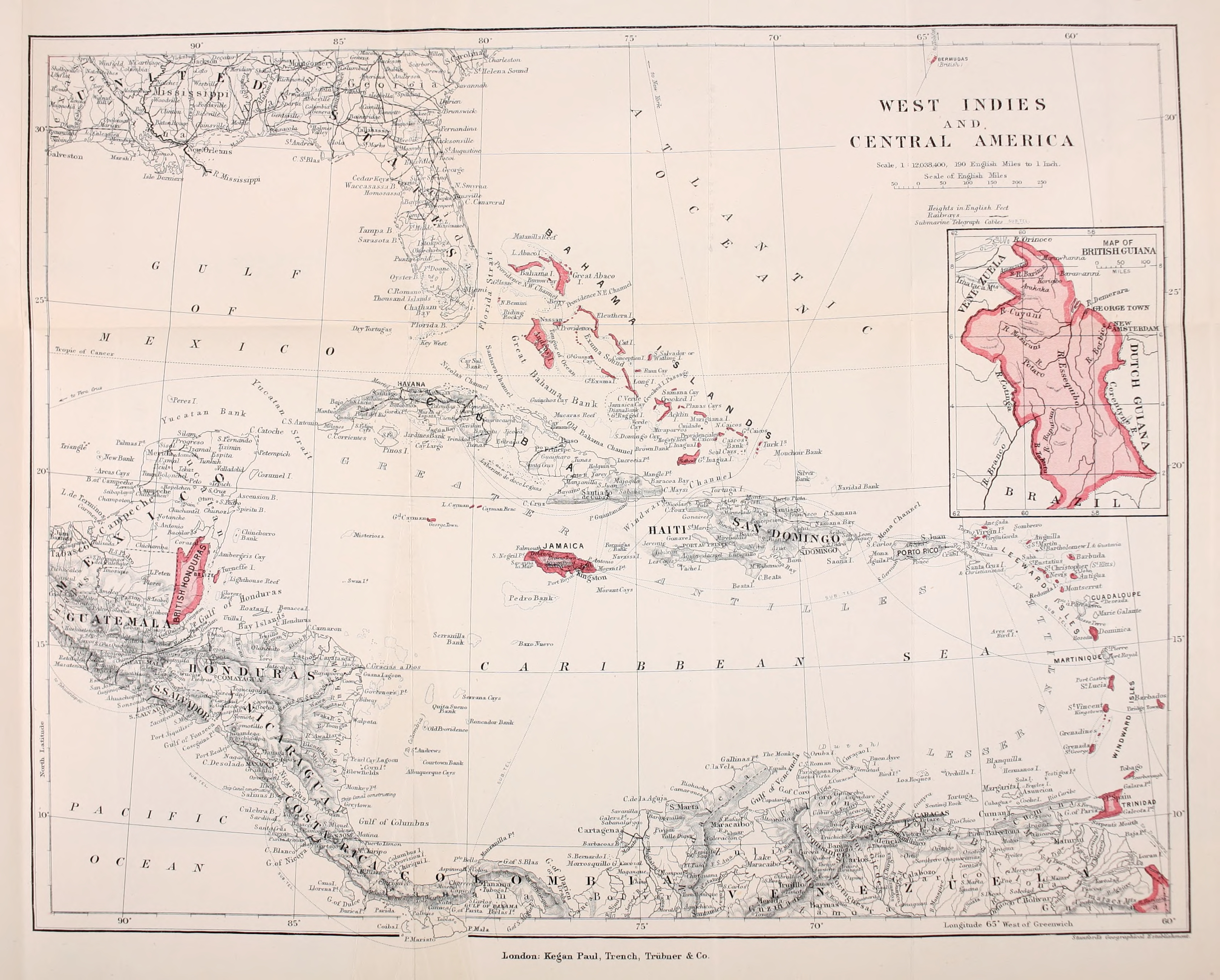
Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican Republic. Haiti is the third largest country in the Caribbean, and with an estimated population of 11.4 million, is the most populous Caribbean country. The capital and largest city is Port-au-Prince. Haiti was originally inhabited by the Taíno people. In 1492, Christopher Columbus established the first European settlement in the Americas, La Navidad, on its northeastern coast. The island was part of the Spanish Empire until 1697, when the western portion was Peace of Ryswick, ceded to France and became Saint-Domingue, dominated by sugarcane sugar plantations in the Caribbean, plantations worked by enslaved Africans. The 1791–1804 Haitian Revolution made Haiti the first sovereign state in the Caribbean, the second republic in the Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1765 Births
Events January–March * January 23 – Prince Joseph of Austria marries Princess Maria Josepha of Bavaria in Vienna. * January 29 – One week before his death, Mir Jafar, who had been enthroned as the Nawab of Bengal and ruler of the Bengali people with the support and protection of the British East India Company, abdicates in favor of his 18-year-old son, Najmuddin Ali Khan. * February 8 **Frederick the Great, the King of Prussia, issues a decree abolishing the historic punishments against unmarried women in Germany for "sex crimes", particularly the ''Hurenstrafen'' (literally "whore shaming") practices of public humiliation. ** Isaac Barré, a member of the British House of Commons for Wycombe and a veteran of the French and Indian War in the British American colonies, coins the term "Sons of Liberty" in a rebuttal to Charles Townshend's derisive description of the American colonists during the introduction of the proposed Stamp Act. Barré notes tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century Politicians
The 18th century lasted from 1 January 1701 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCI) to 31 December 1800 (MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the Atlantic Revolutions. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures. The Industrial Revolution began mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. The European colonization of the Americas and other parts of the world intensified and associated mass migrations of people grew in size as part of the Age of Sail. During the century, slave trading expanded across the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, while declining in Russia and China. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Cuban Politicians
The 19th century began on 1 January 1801 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 (MCM). It was the 9th century of the 2nd millennium. It was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanded beyond its British homeland for the first time during the 19th century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, France, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Catholic Church, in response to the growing influence and power of modernism, secularism and materialism, formed the First Vatican Council in the late 19th century to deal with such problems and confirm cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioko
Bioko (; ; ; historically known as Fernando Pó, ) is an island of Equatorial Guinea. It is located south of the coast of Cameroon, and northwest of the northernmost part of mainland Equatorial Guinea. Malabo, on the north coast of the island, is the capital city of Equatorial Guinea. Bioko's population was 335,048 at the 2015 census and it covers an area of . The island is part of the Cameroon line of volcanoes and is located off the Cameroon coast, in the Bight of Biafra portion of the Gulf of Guinea. Its geology is volcanic; its highest peak is Pico Basile at . Etymology Bioko's native name is ''Ëtulá a Ëri'' in the Bube language. For nearly 500 years, the island was known as ''Fernando Pó'' (; ), named for Portuguese navigator Fernão do Pó. Between 1973 and 1979 the island was named ''Macías Nguema Biyogo'' after the then-president of Equatorial Guinea. The current name, Bioko, dates from 1979 and is in honour of politician Cristino Seriche Bioko. Geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abolition Of Slavery
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the political movement to end slavery and liberate enslaved individuals around the world. The first country to fully outlaw slavery was France in 1315, but it was later used in its colonies. The first country to abolish and punish slavery for indigenous people was Spain with the New Laws in 1542. Under the actions of Toyotomi Hideyoshi, chattel slavery has been abolished across Japan since 1590, though other forms of forced labour were used during World War II. The first and only country to self-liberate from slavery was a former French colony, Haiti, as a result of the Revolution of 1791–1804. The British abolitionist movement began in the late 18th century, and the 1772 Somersett case established that slavery did not exist in English law. In 1807, the slave trade was made illegal throughout the British Empire, though existing slaves in British colonies were not liberated until the Slavery Abolition Act 1833. In the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. At , it is the third-largest island—after Cuba and Hispaniola—of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, west of Hispaniola (the island containing Haiti and the Dominican Republic), and southeast of the Cayman Islands (a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory). With million people, Jamaica is the third most populous English-speaking world, Anglophone country in the Americas and the fourth most populous country in the Caribbean. Kingston, Jamaica, Kingston is the country's capital and largest city. The indigenous Taíno peoples of the island gradually came under Spanish Empire, Spanish rule after the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1494. Many of the indigenous people either were killed or died of diseases, after which the Spanish brought large numbers of Africans to Jamaica as slaves. The island remained a possession of Spain, under the name Colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbados
Barbados, officially the Republic of Barbados, is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies and the easternmost island of the Caribbean region. It lies on the boundary of the South American Plate, South American and Caribbean Plate, Caribbean plates. Its capital and largest city is Bridgetown. Inhabited by Island Caribs, Kalinago people since the 13th century, and prior to that by other Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples, Barbados was claimed for the Crown of Castile by Spanish navigators in the late 15th century. It first appeared on a Spanish map in 1511. The Portuguese Empire claimed the island between 1532 and 1536, but abandoned it in 1620 with their only remnants being the introduction of wild boars intended as a supply of meat whenever the island was visited. An Kingdom of England, English ship, the ''Olive Blossom'', arrived in Barbados on 14 May 1625; its men took possession of the island in the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscovado
Muscovado is a type of partially refined to unrefined sugar with a strong molasses content and flavour, and dark brown in colour. It is technically considered either a non-centrifugal cane sugar or a centrifuged, partially refined sugar according to the process used by the manufacturer. Muscovado contains higher levels of various minerals than processed white sugar. Its main uses are in food and confectionery, and the manufacturing of rum and other forms of alcohol. The largest producer and consumer of muscovado is India. Terminology The English name "muscovado" is derived from a corruption of Portuguese ' (unrefined sugar). The Indian English names for this type of sugar are ''khandsari'' and ''khand'' (sometimes spelled ''khaand''). There is no legal definition of muscovado, and no international standards for it such as ''Codex Alimentarius'' or ''Protected Designation of Origin''. This has led to manufacturers calling various sugar products "muscovado", and has led to conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were the territories in the West Indies under British Empire, British rule, including Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, the Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Bermuda, Antigua and Barbuda, the Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, British Honduras, British Guiana and Trinidad and Tobago. The Kingdom of England first English overseas possessions, established colonies in the region during the 17th century. Financed by valuable extractive commodities such as sugar production, the colonies were also at the centre of the Atlantic slave trade, with around 2.3 million slaves being brought to the British West Indies. The colonies also served as bases to project the power of the British Empire through the Royal Navy and Britain's Merchant Marine, and to expand and protect British overseas trade. Before the decolonization of the Americas in the later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transatlantic Slave Trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Passage. Europeans established a coastal slave trade in the 15th century and trade to the Americas began in the 16th century, lasting through the 19th century. The vast majority of those who were transported in the transatlantic slave trade were from Central Africa and West Africa and had been sold by West African slave traders to European slave traders, while others had been captured directly by the slave traders in coastal raids. European slave traders gathered and imprisoned the enslaved at slave fort, forts on the African coast and then brought them to the Americas. Some Portuguese and Europeans participated in slave raids. As the National Museums Liverpool explains: "European traders captured some Africans in raids along the coast, but bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |