|
Francis Sempill
Francis Sempill (c. 1616 – March 1682) was a Scottish poet, the son of Robert Sempill the younger. No details of his education are known. His fidelity to the Stuarts involved him in money difficulties, to meet which he alienated portions of his estates to his son. Before 1677 he was appointed sheriff-depute of Renfrewshire. He died at Paisley in March 1682. Sempill wrote many occasional pieces, and his fame as a wit was widespread. Among his most important works is the ''Banishment of Poverty'', which contains some biographical details. The Blythsome Wedding, long attributed to Francis Sempill, has been more recently asserted to be the work of Sir William Scott of Thirlestane. Sempill's claim to the authorship of the celebrated song "She raise and let me in", and of the ballad "Maggie Lauder", has been discussed at considerable length. It seems probable that he had some share in both. "Maggie Lauder" is still fairly well known in Scotland. It has been performed by The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Sempill The Younger
Robert Sempill, the younger (1595?–1663?), Scottish poet, son of James Sempill, was educated at the University of Glasgow, having matriculated in March 1613. During the Civil War he fought for the Stuarts, and seems to have suffered heavy pecuniary losses under the Commonwealth. He died between 1660 and 1669. He married Mary, daughter of Sir Thomas Lyon of Auldbar. His son, Francis Sempill, was also a writer. His reputation is based on the Scots ballad, "The Life and Death of Habbie Simpson, Piper of Kilbarchan", written c. 1640. It is an interesting picture of the times; and it gave fresh vogue to the popular six-lined stanza which was much used later by Allan Ramsay, Robert Fergusson and Robert Burns (see particularly, Burns's ''Poor Mailie's Elegy''). Two broadside copies were printed before 1700, and it appeared in James Watson's ''Collection of Poems'' (1706–1710). Sempill is supposed to be the author also of an epitaph on Sawney Briggs, nephew to Habbie Simp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Stuart
The House of Stuart, originally spelt Stewart, was a royal house of Scotland, England, Ireland and later Great Britain. The family name comes from the office of High Steward of Scotland, which had been held by the family progenitor Walter fitz Alan (c. 1150). The name Stewart and variations had become established as a family name by the time of his grandson Walter Stewart. The first monarch of the Stewart line was Robert II, whose male-line descendants were kings and queens in Scotland from 1371, and of England and Great Britain from 1603, until 1714. Mary, Queen of Scots, was brought up in France where she adopted the French spelling of the name Stuart. In 1503, James IV married Margaret Tudor, thus linking the royal houses of Scotland and England. Elizabeth I of England died without issue in 1603, and James IV's great-grandson (and Mary's only son) James VI of Scotland succeeded to the thrones of England and Ireland as James I in the Union of the Crowns. The Stuarts were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
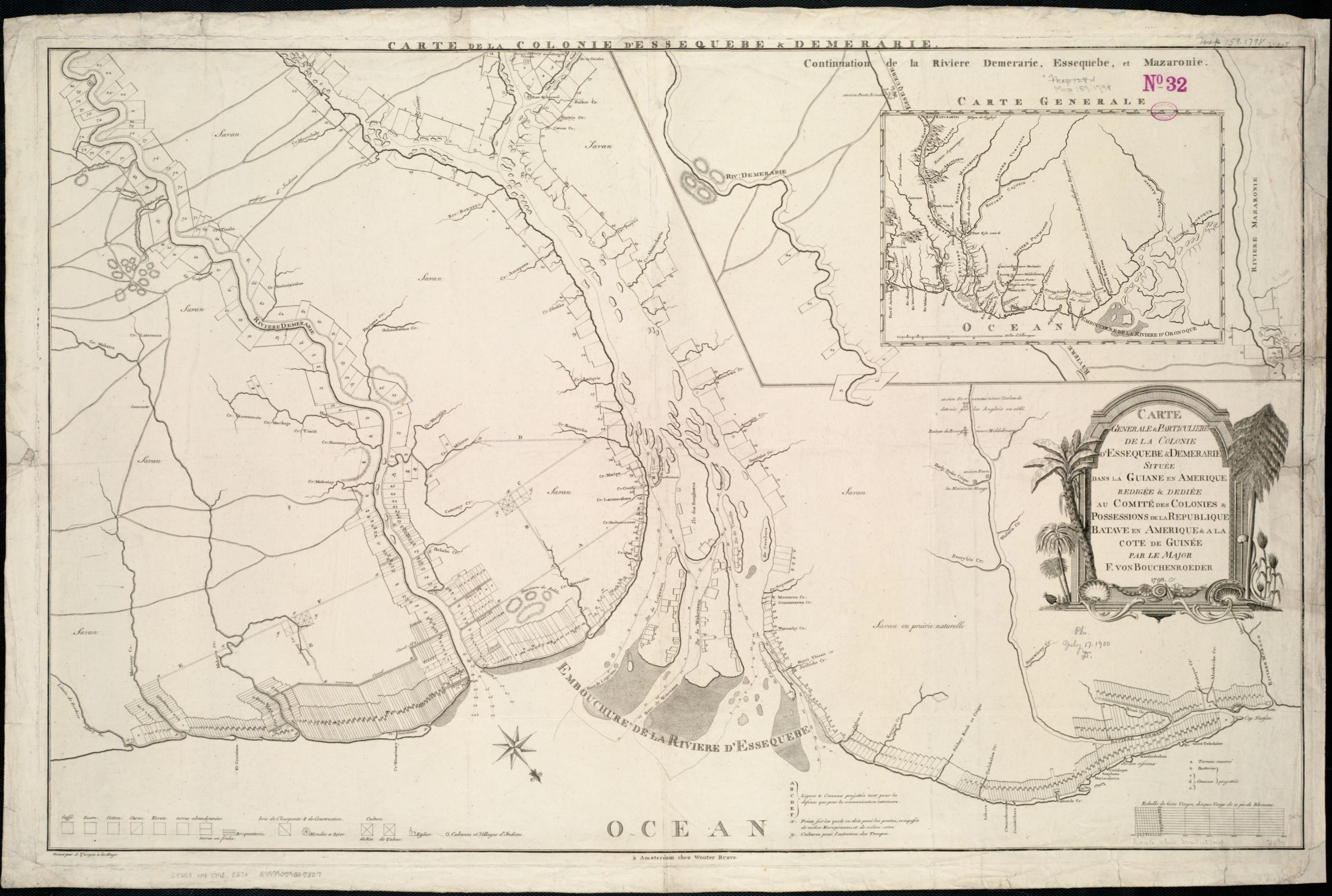
Renfrewshire
Renfrewshire () ( sco, Renfrewshire; gd, Siorrachd Rinn Friù) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland. Located in the west central Lowlands, it is one of three council areas contained within the boundaries of the historic county of Renfrewshire, the others being East Renfrewshire to the east and Inverclyde to the west. It also shares borders with Glasgow, North Ayrshire and West Dunbartonshire, and lies on the southern bank of the River Clyde. The term Renfrewshire may also be used to refer to the historic county, also known as the County of Renfrew or Greater Renfrewshire, with origins in the 16th century. The larger Renfrewshire, containing Renfrewshire, Inverclyde and East Renfrewshire, remains in use as a registration county and lieutenancy area as well as a joint valuation board area for electoral registration and local tax valuation purposes. The town of Paisley is the area's main settlement and centre of local government and contains the historic county town, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paisley, Scotland
Paisley ( ; sco, Paisley, gd, Pàislig ) is a large town situated in the west central Lowlands of Scotland. Located north of the Gleniffer Braes, the town borders the city of Glasgow to the east, and straddles the banks of the White Cart Water, a tributary of the River Clyde. Paisley serves as the administrative centre for the Renfrewshire council area, and is the largest town in the historic county of the same name. It is often cited as "Scotland's largest town" and is the fifth largest settlement in the country, although it does not have city status. The town became prominent in the 12th century, with the establishment of Paisley Abbey, an important religious hub which formerly had control over other local churches. By the 19th century, Paisley was a centre of the weaving industry, giving its name to the Paisley shawl and the Paisley pattern. The town's associations with political radicalism were highlighted by its involvement in the Radical War of 1820, with striki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir William Scott Of Thirlestane
Sir William Scott, 2nd Baronet of Thirlestane (c.1670 – 8 October 1725) was a Scottish lawyer, known as a neo-Latin poet. Life He was the eldest son of Francis Scott, 1st Baronet of Thirlestane, Selkirkshire, and Lady Henrietta, daughter of William Kerr, 3rd Earl of Lothian, who married in 1673. Francis built a large tenement in Edinburgh in 1679 at Elphinstone Court near the Scottish mint. William trained as a lawyer in Edinburgh and was admitted a member of the Faculty of Advocates on 25 February 1702. On 20 May 1719 Scott executed a deed of entail of his lands of Thirlestane. Thirlestane in Selkirkshire should not be confused with Thirlestane in Roxburghshire, which is associated with the Kerrs, and later the Scott-Kerrs of Chatto and Sunlaws. Such confusion has led to the assumption that the Kerrs of Chatto are buried in Greyfriars. This is not the case. The Kerrs and Scott-Kerrs of Chatto and Sunlaws are buried at Sunlaws and Roxburgh, and possibly Hownam. He died ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Corries
The Corries were a Scottish folk group that emerged from the Scottish folk revival of the early 1960s. The group was a trio from their formation until 1966 when founder Bill Smith left the band but Roy Williamson and Ronnie Browne continued as a duo until Williamson's death in 1990. They are particularly known for the song "Flower of Scotland", written by Williamson, which has become an unofficial national anthem of Scotland. History Early years In the early 1960s, Bill Smith (born in 1936 in Edinburgh), Ron Cruikshank and Andy Turner had formed a trio called The Corrie Voices. The trio was named after Smith's daughter, Corrie Smith, but because a corrie is a deep bowl in a mountain, the name was particularly appropriate as it evokes imagery of the Scottish landscape. After Turner dropped out in 1962, Roy Williamson teamed up with Smith and Cruikshank to form the Corrie Folk Trio. Their first performance was in the Waverley Bar in St Mary's Street, Edinburgh. After a few we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dick Gaughan
Richard Peter Gaughan (born 17 May 1948) is a Scottish musician, singer and songwriter, particularly of folk and social protest songs. He is regarded as one of Scotland's leading singer-songwriters. Early years Gaughan was born in Glasgow's Royal Maternity Hospital while his father was working in Glasgow as an engine driver. He spent the first year-and-a-half of his life in Rutherglen, South Lanarkshire, after which the whole family moved to Leith, a port on the outskirts of Edinburgh. The eldest of three children, Gaughan grew up surrounded by the music of both Scotland and Ireland. His mother, a Highland Scot from Lochaber who spoke Gaelic, had as a child won a silver medal for singing at a Gaelic Mòd. His father, a native of Leith, played guitar. His Irish-born paternal grandfather (a native of Erris, County Mayo) played the fiddle and his paternal grandmother, a Glaswegian born to Irish parents, played button accordion and sang. The family experienced considerable pover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Paterson (journalist)
James Paterson (18 May 1805 – 6 May 1876) was a Scottish journalist on numerous newspapers, writer and antiquary. His works are popular history, rather than scholarly. Life He was the son of James Paterson, farmer at Struthers, Ayrshire, where he was born on 18 May 1805; his father then had money troubles and gave up his farm. Paterson received an education, and then was apprenticed to a printer at the office of the Kilmarnock ''Mirror''. Subsequently he was transferred to the ''Courier'' office in Ayr. On completing his apprenticeship, Paterson went to Glasgow, where he joined the ''Scots Times''. In 1826 he returned to Kilmarnock, took a shop as stationer and printer, and in partnership with other gentlemen started the Kilmarnock ''Chronicle''. Its first number appeared on 4 May 1831, during the agitation for the Great Reform Bill, and the paper closed in May 1832. In 1835 Paterson left Kilmarnock for Dublin, where for some time he acted as correspondent of the Glasgow ''Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1616 Births
Events January–June * January ** Six-year-old António Vieira arrives from Portugal, with his parents, in Bahia (present-day Salvador) in Colonial Brazil, where he will become a diplomat, noted author, leading figure of the Church, and protector of Brazilian indigenous peoples, in an age of intolerance. ** Officials in Württemberg charge astronomer Johannes Kepler with practicing "forbidden arts" (witchcraft). His mother had also been so charged and spent 14 months in prison. * January 1 – King James I of England attends the masque ''The Golden Age Restored'', a satire by Ben Jonson on fallen court favorite the Robert Carr, 1st Earl of Somerset, Earl of Somerset. The king asks for a repeat performance on January 6. * January 3 – In the court of James I of England, the king's favorite George Villiers, 1st Duke of Buckingham, George Villiers becomes Master of the Horse (encouraging development of the thoroughbred horse); on April 24 he receives the Order of the Gart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1682 Deaths
Year 168 ( CLXVIII) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Apronianus and Paullus (or, less frequently, year 921 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 168 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Marcus Aurelius and his adopted brother Lucius Verus leave Rome, and establish their headquarters at Aquileia. * The Roman army crosses the Alps into Pannonia, and subdues the Marcomanni at Carnuntum, north of the Danube. Asia * Emperor Ling of Han succeeds Emperor Huan of Han as the emperor of the Chinese Han Dynasty; the first year of the ''Jianning'' era. Births * Cao Ren, Chinese general (d. 223) * Gu Yong, Chinese chancellor (d. 243) * Li Tong, Chinese general (d. 209) Deaths * Anicetus, pope of Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century Scottish Writers
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easily k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Songwriters
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including: *Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland *Scottish English *Scottish national identity, the Scottish identity and common culture *Scottish people, a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland *Scots language, a West Germanic language spoken in lowland Scotland *Symphony No. 3 (Mendelssohn), a symphony by Felix Mendelssohn known as ''the Scottish'' See also *Scotch (other) *Scotland (other) *Scots (other) *Scottian (other) *Schottische The schottische is a partnered country dance that apparently originated in Bohemia. It was popular in Victorian era ballrooms as a part of the Bohemian folk-dance craze and left its traces in folk music of countries such as Argentina ("chotis"Span ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ca:Escocès ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |