|
Francis Kelly (Canadian Politician)
Francis Kelly (May 1806 – 19 April 1879) was a Canadian surveyor, business agent, farmer, and politician, noted for his long service as a member of the government of Prince Edward Island (PEI), and as an advocate for Catholic issues on PEI during the period of Canadian Confederation. His Life Prior to Politics Born in Mulloloughan, County Monaghan, Ireland, Kelly was schooled in Dublin, and worked as a teacher and law clerk before emigrating to PEI with his wife, Catherine Lennon, in May, 1835, ten years before the Great Famine. Kelly settled at Fort Augustus, Price Edward Island, not far from the province's capital of Charlottetown. Kelly was hired by the Reverend John McDonald as an assayer and business agent, for whom he worked until May 1846. Political career Interested in politics, Kelly made two attempts at election to the House of Assembly for the third district of Queens County in the 1840s. He was defeated in those first two attempts, but was elected to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
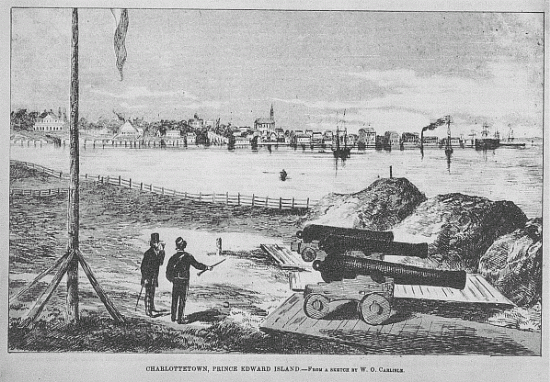
Charlottetown In The Late 19th Century
Charlottetown is the capital and largest city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Prince Edward Island, and the county seat of Queens County, Prince Edward Island, Queens County. Named after Queen Charlotte, Charlottetown was an unincorporated town until it was incorporated as a city in 1855. It was the site of the famous Charlottetown Conference in 1864, the first gathering of Canadian and Maritime statesmen to discuss the proposed Maritime Union. This conference led, instead, to the union of British North American colonies in 1867, which was the beginning of the Canadian confederation. PEI, however, did not join Confederation until 1873. From this, the city adopted as its motto ''Cunabula Foederis'', "Birthplace of Confederation". The population of Charlottetown is estimated to be 40,500 (2022); this forms the centre of a census agglomeration of 83,063 (2021), which is roughly half of the province's population (160,302). History Early history ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premier Of Prince Edward Island
The premier of Prince Edward Island is the first minister and head of government for the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Prince Edward Island. The current premier of Prince Edward Island is Dennis King (politician), Dennis King, from the Progressive Conservative Party of Prince Edward Island, Progressive Conservative Party. See also * Prime Minister of Canada * Premier (Canada) * List of premiers of Prince Edward Island References External links * Premiers of Prince Edward Island, * {{PrinceEdwardIsland-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Commissioner Of Crown Lands
Chief may refer to: Title or rank Military and law enforcement * Chief master sergeant, the ninth, and highest, enlisted rank in the U.S. Air Force and U.S. Space Force * Chief of police, the head of a police department * Chief of the boat, the senior enlisted sailor on a U.S. Navy submarine * Chief petty officer, a non-commissioned officer or equivalent in many navies * Chief warrant officer, a military rank Other titles * Chief of the Name, head of a family or clan * Chief mate, or Chief officer, the highest senior officer in the deck department on a merchant vessel * Chief of staff, the leader of a complex organization * Fire chief, top rank in a fire department * Scottish clan chief, the head of a Scottish clan * Tribal chief, a leader of a tribal form of government * Chief, IRS-CI, the head and chief executive of U.S. Internal Revenue Service, Criminal Investigation Places * Chief Mountain, Montana, United States * Stawamus Chief or the Chief, a granite dome in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Edward Island Progressive Conservative Party
The Progressive Conservative Party of Prince Edward Island is one of three major political parties on Prince Edward Island. The party and its rival, the Liberals, have alternated in power since responsible government was granted in 1851. History The policies of the Liberals and Progressive Conservatives (PCs) are very similar. The major differences are in their allegiances to federal parties and in personalities. The PC Party began as the Conservative Party of Prince Edward Island, and changed its name in 1942 to reflect the development of the federal Progressive Conservative Party. The Progressive Conservatives formed the government in Prince Edward Island under Premier Pat Binns, starting in 1996. The party lost its bid for a fourth mandate in 2007. In October 2010, following the resignation of Binns as party leader (in 2007), a leadership election was held. Jim Bagnall became interim leader of the party in 2010 when previous interim leader MLA Olive Crane resigned the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Colledge Pope
James Colledge Pope, (June 11, 1826 – May 8, 1885) was a land proprietor and politician on Prince Edward Island (PEI), Canada. He served as premier of the colony from 1865 to 1867, and from 1870 to 1873. He was premier of PEI in 1873 when the island joined Canadian confederation. He was born in Bedeque, Prince Edward Island, the son of Joseph Pope and Lucy Colledge. Pope was a successful businessman who was at one point the island's third largest shipowner. He entered PEI politics in 1857 when the island was still a colony of the United Kingdom. He was a member of the Conservative Party, and defended the rights of landowners against growing demands by tenant farmers for land reform. Pope was named to the Executive Council in 1859, joining the Conservative government of Edward Palmer. In 1865, he became Premier after a dispute over Canadian confederation resulted in Palmer and John Hamilton Gray resigning from the Executive Council. While not hostile to confederation, Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Poore Haythorne
Robert Poore Haythorne (2 December 1815 – 7 May 1891) was a Prince Edward Island politician and premier. He was born in England to a prominent family, his father having been mayor of Bristol on several occasions. Haythorne arrived in Prince Edward Island at the age of 25 and, with his brother, acquired ownership of 10,000 ac (4,000 ha) of land. When the land question became a major issue in the 1860s Haythorne who had been a progressive farmer and a reformer decided to sell his land to his tenants for $2.00/ac ($4.94/ha). His former tenants asked him to run for a seat on the legislative council (which was by then an elected body) in 1867 and he did so winning the seat as a PEI Liberal Party, Liberal. Haythorne joined the Liberal government of George Coles (politician), George Coles and became Premier in 1869 after Coles retired and his successor, Joseph Hensley accepted a judicial appointment. Politically, Haythorne became skeptical of Canadian confederation and his govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Separate School
In Canada, a separate school is a type of school that has constitutional status in three provinces (Ontario, Alberta and Saskatchewan) and statutory status in the three territories ( Northwest Territories, Yukon and Nunavut). In these Canadian jurisdictions, a separate school is one operated by a civil authority—a separate school board—with a mandate enshrined in the Canadian Constitution (for the three provinces) or in federal statutes (for the three territories). In these six jurisdictions a civil electorate, composed of the members of the minority faith, elects separate school trustees according to the province's or territory's local authorities election legislation. These trustees are legally accountable to their electorate and to the provincial or territorial government. No church has a constitutional, legal, or proprietary interest in a separate school. The constitutionally provided mandate of a separate school jurisdiction and of a separate school is to provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic School
Catholic schools are pre-primary, primary and secondary educational institutions administered under the aegis or in association with the Catholic Church. , the Catholic Church operates the world's largest religious, non-governmental school system. In 2016, the church supported 43,800 secondary schools and 95,200 primary schools. The schools include religious education alongside secular subjects in their curriculum. Background Across Europe, North America, Australia and New Zealand, the main historical driver for the establishment of Catholic schools was Irish immigration. Historically, the establishment of Catholic schools in Europe encountered various struggles following the creation of the Church of England in the Elizabethan Religious settlements of 1558–63. Anti-Catholicism in this period encouraged Catholics to create modern Catholic education systems to preserve their traditions. The Relief Acts of 1782 and the Catholic Emancipation Act of 1829 later increased the pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts established by England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as "the empire on which the sun never sets", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established large overse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel O'Connell
Daniel O'Connell (I) ( ga, Dónall Ó Conaill; 6 August 1775 – 15 May 1847), hailed in his time as The Liberator, was the acknowledged political leader of Ireland's Roman Catholic majority in the first half of the 19th century. His mobilization of Catholic Ireland, down to the poorest class of tenant farmers, secured the final installment of Catholic emancipation in 1829 and allowed him to take a seat in the Parliament of the United Kingdom, United Kingdom Parliament to which he had been twice elected. At Palace of Westminster, Westminster, O'Connell championed liberal and reform causes (he was internationally renowned as an Abolitionism, abolitionist) but he failed in his declared objective for Ireland—the restoration of a separate Irish Parliament through the repeal of the Acts of Union 1800, 1800 Act of Union. Against the backdrop of a growing agrarian crisis and, in his final years, of the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine, O'Connell contended with dissension at home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of regular, full-time military personnel; or, historically, to members of a warrior-nobility class (e.g. knights or samurai). Generally unable to hold ground against regular forces, militias commonly support regular troops by skirmishing, holding fortifications, or conducting irregular warfare, instead of undertaking offensive campaigns by themselves. Local civilian laws often limit militias to serve only in their home region, and to serve only for a limited time; this further reduces their use in long military campaigns. Beginning in the late 20th century, some militias (in particular officially recognized and sanctioned militias of a government) act as professional forces, while still being "part-time" or "on-call" organizations. For instan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |