|
FrameNet
FrameNet is a research and resource development project based at the International Computer Science Institute (ICSI) in Berkeley, California, which has produced an electronic resource based on a theory of meaning called frame semantics. The data that FrameNet has analyzed show that the sentence "John sold a car to Mary" essentially describes the same basic situation (semantic frame) as "Mary bought a car from John", just from a different perspective. A semantic frame is a conceptual structure describing an event, relation, or object along with its participants. The FrameNet lexical database contains over 1,200 semantic ''frames'', 13,000 ''lexical units'' (a pairing of a word with a meaning; polysemous words are represented by several ''lexical units'') and 202,000 example sentences. Charles J. Fillmore, who developed the theory of frame semantics which serves as the theoretical the basis of FrameNet, founded the project in 1997 and continued to lead the effort until he died in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PropBank
PropBank is a corpus that is annotated with verbal propositions and their arguments—a "proposition bank". Although "PropBank" refers to a specific corpus produced by Martha Palmer ''et al.'', the term ''propbank'' is also coming to be used as a common noun referring to any corpus that has been annotated with propositions and their arguments. The PropBank project has played a role in recent research in natural language processing, and has been used in semantic role labelling. Comparison PropBank differs from FrameNet, the resource to which it is most frequently compared, in several ways. PropBank is a verb-oriented resource, while FrameNet is centered on the more abstract notion of frames, which generalizes descriptions across similar verbs (e.g. "describe" and "characterize") as well as nouns and other words (e.g. "description"). PropBank does not annotate events or states of affairs described using nouns. PropBank commits to annotating all verbs in a corpus, whereas the Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Role Labeling
In natural language processing, semantic role labeling (also called shallow semantic parsing or slot-filling) is the process that assigns labels to words or phrases in a sentence that indicates their semantic role in the sentence, such as that of an agent, goal, or result. It serves to find the meaning of the sentence. To do this, it detects the arguments associated with the predicate or verb of a sentence and how they are classified into their specific roles. A common example is the sentence "Mary sold the book to John." The agent is "Mary," the predicate is "sold" (or rather, "to sell,") the theme is "the book," and the recipient is "John." Another example is how "the book belongs to me" would need two labels such as "possessed" and "possessor" and "the book was sold to John" would need two other labels such as theme and recipient, despite these two clauses being similar to "subject" and "object" functions. History In 1968, the first idea for semantic role labeling was proposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Role Labeling
In natural language processing, semantic role labeling (also called shallow semantic parsing or slot-filling) is the process that assigns labels to words or phrases in a sentence that indicates their semantic role in the sentence, such as that of an agent, goal, or result. It serves to find the meaning of the sentence. To do this, it detects the arguments associated with the predicate or verb of a sentence and how they are classified into their specific roles. A common example is the sentence "Mary sold the book to John." The agent is "Mary," the predicate is "sold" (or rather, "to sell,") the theme is "the book," and the recipient is "John." Another example is how "the book belongs to me" would need two labels such as "possessed" and "possessor" and "the book was sold to John" would need two other labels such as theme and recipient, despite these two clauses being similar to "subject" and "object" functions. History In 1968, the first idea for semantic role labeling was proposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frame Semantics (linguistics)
Frame semantics is a theory of linguistic meaning developed by Charles J. Fillmore that extends his earlier case grammar. It relates linguistic semantics to encyclopedic knowledge. The basic idea is that one cannot understand the meaning of a single word without access to all the essential knowledge that relates to that word. For example, one would not be able to understand the word "sell" without knowing anything about the situation of commercial transfer, which also involves, among other things, a seller, a buyer, goods, money, the relation between the money and the goods, the relations between the seller and the goods and the money, the relation between the buyer and the goods and the money and so on. Thus, a word activates, or evokes, a frame of semantic knowledge relating to the specific concept to which it refers (or highlights, in frame semantic terminology). The idea of the encyclopedic organisation of knowledge itself is old and was discussed by Age of Enlightenment philos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Jurafsky
Daniel Jurafsky is a professor of linguistics and computer science at Stanford University, and also an author. With Daniel Gildea, he is known for developing the first automatic system for semantic role labeling (SRL). He is the author of ''The Language of Food: A Linguist Reads the Menu'' (2014) and a textbook on speech and language processing (2000). Jurafsky was given a MacArthur Fellowship in 2002. Education Jurafsky received his B.A in linguistics (1983) and Ph.D. in computer science (1992), both at University of California, Berkeley; and then a postdoc at International Computer Science Institute, Berkeley (1992–1995). Academic life He is the author of ''The Language of Food: A Linguist Reads the Menu'' (W. W. Norton & Company, 2014). With James H. Martin, he wrote the textbook ''Speech and Language Processing: An Introduction to Natural Language Processing, Computational Linguistics, and Speech Recognition'' (Prentice Hall, 2000). The first automatic system for semant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frame Language
Frames are an artificial intelligence data structure used to divide knowledge into substructures by representing " stereotyped situations". They were proposed by Marvin Minsky in his 1974 article "A Framework for Representing Knowledge". Frames are the primary data structure used in artificial intelligence frame languages; they are stored as ontologies of sets. Frames are also an extensive part of knowledge representation and reasoning schemes. They were originally derived from semantic networks and are therefore part of structure-based knowledge representations. According to Russell and Norvig's "Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach", structural representations assemble " ..acts about particular objects and event types and arrange the types into a large taxonomic hierarchy analogous to a biological taxonomy". Frame structure The frame contains information on how to use the frame, what to expect next, and what to do when these expectations are not met. Some information in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
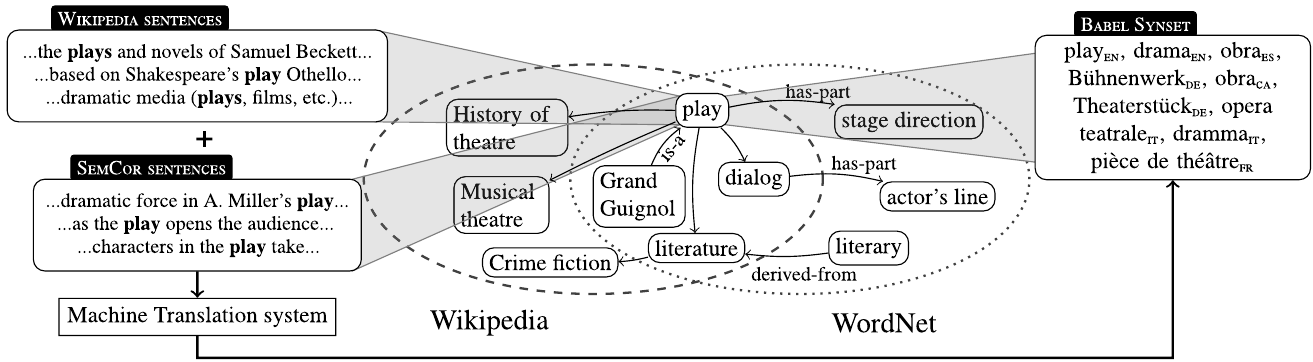
BabelNet
BabelNet is a multilingual lexicalized semantic network and ontology developed at the NLP group of the Sapienza University of Rome.R. Navigli and S. P Ponzetto. 2012BabelNet: The Automatic Construction, Evaluation and Application of a Wide-Coverage Multilingual Semantic Network Artificial Intelligence, 193, Elsevier, pp. 217-250. BabelNet was automatically created by linking Wikipedia to the most popular computational lexicon of the English language, WordNet. The integration is done using an automatic mapping and by filling in lexical gaps in resource-poor languages by using statistical machine translation. The result is an encyclopedic dictionary that provides concepts and named entities lexicalized in many languages and connected with large amounts of semantic relations. Additional lexicalizations and definitions are added by linking to free-license wordnets, OmegaWiki, the English Wiktionary, Wikidata, FrameNet, VerbNet and others. Similarly to WordNet, BabelNet groups words i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Computer Science Institute
The International Computer Science Institute (ICSI) is an independent, non-profit research organization located in Berkeley, California, United States. Since its founding in 1988, ICSI has maintained an affiliation agreement with the University of California, Berkeley, where several of its members hold faculty appointments. Research areas ICSI's research activities include Internet architecture, network security, network routing, speech and speaker recognition, spoken and text-based natural language processing, computer vision, multimedia, privacy and biological system modeling. Research groups and leaders * The Institute's director iDr. Lea Shanley * SIGCOMM Award winner Professor Scott Shenker, one of thmost-cited authors in computer science is the Chief Scientist and head of the New Initiatives group. * SIGCOMM Award winner Professor Vern Paxson, who leads network security efforts and who previously chaired the Internet Research Task Force. * Professor Jerry Feldman is the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Dictionaries
An online dictionary is a dictionary that is accessible via the Internet through a web browser. They can be made available in a number of ways: free, free with a paid subscription for extended or more professional content, or a paid-only service. Many dictionaries have been digitized from their print versions and are available at online libraries. Some online dictionaries are organized as lists of words, similar to a glossary, while others offer search features, reverse lookups, and additional language tools and content such as verb conjugations, grammar references, and discussion forums. The variety of online dictionaries for specialized topics is enormous, covering a wide range of fields such as computing, business and investing, along with almost any other class of trade, science, art, or common interest with its own terminology. Selected online dictionaries The following is a concise list of online English dictionaries whose definitions are based upon well-established content. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertext
Hypertext is E-text, text displayed on a computer display or other electronic devices with references (hyperlinks) to other text that the reader can immediately access. Hypertext documents are interconnected by hyperlinks, which are typically activated by a mouse (computing), mouse click, keypress set, or screen touch. Apart from text, the term "hypertext" is also sometimes used to describe tables, images, and other presentational content formats with integrated hyperlinks. Hypertext is one of the key underlying concepts of the World Wide Web, where Web pages are often written in the Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). As implemented on the Web, hypertext enables the easy-to-use publication of information over the Internet. Etymology The English prefix "hyper-" comes from the Greek language, Greek prefix "ὑπερ-" and means "over" or "beyond"; it has a common origin with the prefix "super-" which comes from Latin. It signifies the overcoming of the previous linear con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Internet
The history of the Internet has its origin in information theory and the efforts of scientists and engineers to build and interconnect computer networks. The Internet Protocol Suite, the set of rules used to communicate between networks and devices on the Internet, arose from research and development in the United States and involved international collaboration, particularly with researchers in the United Kingdom and France. Computer science was an emerging discipline in the late 1950s that began to consider time-sharing between computer users, and later, the possibility of achieving this over wide area networks. J. C. R. Licklider developed the idea of a universal network at the Information Processing Techniques Office (IPTO) of the United States Department of Defense (DoD) Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA). Independently, Paul Baran at the RAND Corporation proposed a distributed network based on data in message blocks in the early 1960s, and Donald Davies conceived o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Linguistics
Corpus linguistics is the study of language, study of a language as that language is expressed in its text corpus (plural ''corpora''), its body of "real world" text. Corpus linguistics proposes that a reliable analysis of a language is more feasible with corpora collected in the field—the natural context ("realia") of that language—with minimal experimental interference. The text-corpus method uses the body of texts written in any natural language to derive the set of abstract rules which govern that language. Those results can be used to explore the relationships between that subject language and other languages which have undergone a similar analysis. The first such corpora were manually derived from source texts, but now that work is automated. Corpora have not only been used for linguistics research, they have also been used to compile dictionaries (starting with ''The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language'' in 1969) and grammar guides, such as ''A Compreh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |