|
Frame-dragging
Frame-dragging is an effect on spacetime, predicted by Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, that is due to non-static stationary distributions of mass–energy. A stationary field is one that is in a steady state, but the masses causing that field may be non-static — rotating, for instance. More generally, the subject that deals with the effects caused by mass–energy currents is known as gravitoelectromagnetism, which is analogous to the magnetism of classical electromagnetism. The first frame-dragging effect was derived in 1918, in the framework of general relativity, by the Austrian physicists Josef Lense and Hans Thirring, and is also known as the Lense–Thirring effect. They predicted that the rotation of a massive object would distort the spacetime metric, making the orbit of a nearby test particle precess. This does not happen in Newtonian mechanics for which the gravitational field of a body depends only on its mass, not on its rotation. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Probe B
Gravity Probe B (GP-B) was a satellite-based experiment to test two unverified predictions of general relativity: the geodetic effect and frame-dragging. This was to be accomplished by measuring, very precisely, tiny changes in the direction of spin of four gyroscopes contained in an Earth-orbiting satellite at of altitude, crossing directly over the poles. The satellite was launched on 20 April 2004 on a Delta II rocket. The spaceflight phase lasted until 2005; Its aim was to measure spacetime curvature near Earth, and thereby the stress–energy tensor (which is related to the distribution and the motion of matter in space) in and near Earth. This provided a test of general relativity, gravitomagnetism and related models. The principal investigator was Francis Everitt. Initial results confirmed the expected geodetic effect to an accuracy of about 1%. The expected frame-dragging effect was similar in magnitude to the current noise level (the noise being dominated by initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LARES (satellite)
LARES (Laser Relativity Satellite) is a passive satellite system of the Italian Space Agency. Mission Launch LARES was launched into orbit on 13 February 2012 at 10:00:00 UTC. It was launched on the first Vega rocket from the ESA Centre Spatial Guyanais in Kourou, French Guiana. Composition The satellite is made of THA-18N, a tungsten alloy, and houses 92 cube-corner retroreflectors, which are used to track the satellite via laser from stations on Earth. LARES's body has a diameter of about and a mass of about . LARES was inserted in a nearly circular orbit near and an inclination of 69.49 degrees. The satellite is tracked by the International Laser Ranging Service stations. The LARES satellite is the densest object known orbiting the Earth. The high density helps reduce disturbances from environmental factors such as solar radiation pressure. Scientific goals The main scientific target of the LARES mission is the measurement of the Lense–Thirring effect with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacetime
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why different observers perceive differently where and when events occur. Until the 20th century, it was assumed that the three-dimensional geometry of the universe (its spatial expression in terms of coordinates, distances, and directions) was independent of one-dimensional time. The physicist Albert Einstein helped develop the idea of spacetime as part of his theory of relativity. Prior to his pioneering work, scientists had two separate theories to explain physical phenomena: Isaac Newton's laws of physics described the motion of massive objects, while James Clerk Maxwell's electromagnetic models explained the properties of light. However, in 1905, Einstein based a work on special relativity on two postulates: * The laws of physics are invari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the ' is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second order partial differential equations. Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes classical gravity, can be seen as a prediction of general relativity for the almost flat spacetime geometry around stationary mass distributions. Some predictions of general relativity, however, are beyond Newton's law of universal gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitoelectromagnetism
Gravitoelectromagnetism, abbreviated GEM, refers to a set of formal analogies between the equations for electromagnetism and relativistic gravitation; specifically: between Maxwell's field equations and an approximation, valid under certain conditions, to the Einstein field equations for general relativity. Gravitomagnetism is a widely used term referring specifically to the kinetic effects of gravity, in analogy to the magnetic effects of moving electric charge. The most common version of GEM is valid only far from isolated sources, and for slowly moving test particles. The analogy and equations differing only by some small factors were first published in 1893, before general relativity, by Oliver Heaviside as a separate theory expanding Newton's law. Background This approximate reformulation of gravitation as described by general relativity in the weak field limit makes an apparent field appear in a frame of reference different from that of a freely moving inertial body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Laser Ranging
In satellite laser ranging (SLR) a global network of observation stations measures the round trip time of flight of ultrashort pulses of light to satellites equipped with retroreflectors. This provides instantaneous range measurements of millimeter level precision which can be accumulated to provide accurate measurement of orbits and a host of important scientific data. The laser pulse can also be reflected by the surface of a satellite without a retroreflector, which is used for tracking space debris. Satellite laser ranging is a proven geodesy, geodetic technique with significant potential for important contributions to scientific studies of the earth/atmosphere/ocean system. It is the most accurate technique currently available to determine the geocentric position of an Earth satellite, allowing for the precise calibration of radar altimeters and separation of long-term instrumentation drift from secular changes in ocean topography. Its ability to measure the variations ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central European Journal Of Physics
''Open Physics'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering all aspects of physics. It is published by De Gruyter and the editor-in-chief is Sally Seidel (University of New Mexico). Occasionally, the journal publishes special issues on a specific topic. History The journal was established in 2003 as the ''Central European Journal of Physics''. It was co-published by Versita and Springer Science+Business Media. The founding editor-in-chief was Janos Lendvai (Eötvös Loránd University), who was succeeded in 2004 by Vladimir E. Zakharov (University of Arizona and Lebedev Physical Institute) and in 2011 by Feng. In 2014 the journal was moved to De Gruyter. It obtained its current name in 2015 and simultaneously became open access. Abstracting and indexing The journals is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity And Gravitation
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry. In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The term ''general'' is used in two ways: as the generic title for all grades of general officer and as a specific rank. It originates in the 16th century, as a shortening of ''captain general'', which rank was taken from Middle French ''capitaine général''. The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. Today, the title of ''general'' is known in some countries as a four-star rank. However, different countries use different systems of stars or other insignia for senior ranks. It has a NATO rank sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
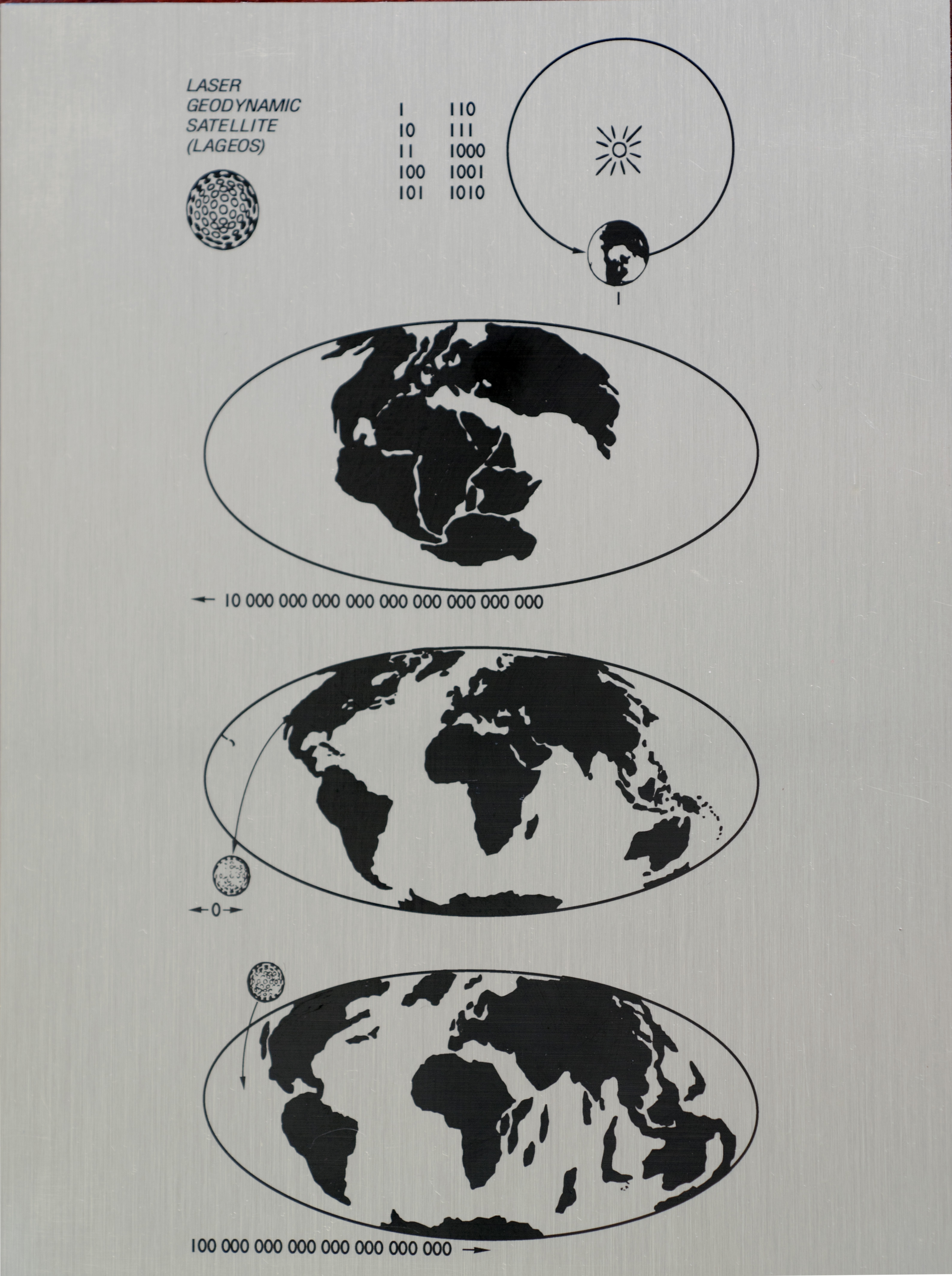
LAGEOS II
LAGEOS, Laser Geodynamics Satellite or Laser Geometric Environmental Observation Survey, are a series of two scientific research satellites designed to provide an orbiting laser ranging benchmark for geodynamical studies of the Earth. Each satellite is a high-density passive laser reflector in a very stable medium Earth orbit (MEO). Function and operation The spacecraft are aluminum-covered brass spheres with diameters of and masses of , covered with 426 cube-corner retroreflectors, giving them the appearance of giant golf balls. Of these retroreflectors, 422 are made from fused silica glass while the remaining 4 are made from germanium to obtain measurements in the infrared for experimental studies of reflectivity and satellite orientation. They have no on-board sensors or electronics, and are not attitude-controlled. They orbit at an altitude of , well above low Earth orbit and well below geostationary orbit, at orbital inclinations of 109.8 and 52.6 degrees. Measurement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperfine Structure
In atomic physics, hyperfine structure is defined by small shifts in otherwise degenerate energy levels and the resulting splittings in those energy levels of atoms, molecules, and ions, due to electromagnetic multipole interaction between the nucleus and electron clouds. In atoms, hyperfine structure arises from the energy of the nuclear magnetic dipole moment interacting with the magnetic field generated by the electrons and the energy of the nuclear electric quadrupole moment in the electric field gradient due to the distribution of charge within the atom. Molecular hyperfine structure is generally dominated by these two effects, but also includes the energy associated with the interaction between the magnetic moments associated with different magnetic nuclei in a molecule, as well as between the nuclear magnetic moments and the magnetic field generated by the rotation of the molecule. Hyperfine structure contrasts with '' fine structure'', which results from the interact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LAGEOS
LAGEOS, Laser Geodynamics Satellite or Laser Geometric Environmental Observation Survey, are a series of two scientific research satellites designed to provide an orbiting laser ranging benchmark for geodynamical studies of the Earth. Each satellite is a high-density passive laser reflector in a very stable medium Earth orbit (MEO). Function and operation The spacecraft are aluminum-covered brass spheres with diameters of and masses of , covered with 426 cube-corner retroreflectors, giving them the appearance of giant golf balls. Of these retroreflectors, 422 are made from fused silica glass while the remaining 4 are made from germanium to obtain measurements in the infrared for experimental studies of reflectivity and satellite orientation. They have no on-board sensors or electronics, and are not attitude-controlled. They orbit at an altitude of , well above low Earth orbit and well below geostationary orbit, at orbital inclinations of 109.8 and 52.6 degrees. Measurement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertia
Inertia is the idea that an object will continue its current motion until some force causes its speed or direction to change. The term is properly understood as shorthand for "the principle of inertia" as described by Newton in his first law of motion. After some other definitions, Newton states in his first law of motion: The word "perseveres" is a direct translation from Newton's Latin. Other, less forceful terms such as "to continue" or "to remain" are commonly found in modern textbooks. The modern use follows from some changes in Newton's original mechanics (as stated in the ''Principia'') made by Euler, d'Alembert, and other Cartesians. The term inertia comes from the Latin word ''iners'', meaning idle, sluggish. The term inertia may also refer to the resistance of any physical object to a change in its velocity. This includes changes to the object's speed or direction of motion. An aspect of this property is the tendency of objects to keep moving in a straight li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.gif)