|
Fotheringhay Motte, 2009
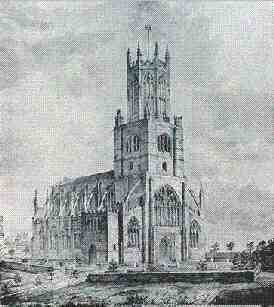
Fotheringhay is a village and civil parish in Northamptonshire, England, north-east of Oundle and around west of Peterborough. It is most noted for being the site of Fotheringhay (or Fotheringay) Castle which was razed in 1627. There is nothing left of the castle to be seen today other than the motte on which it was built that provides excellent views of the River Nene. The Nene Way long distance footpath runs through the village. As the home of the great Yorkist line, the village was, for a considerable part of the 15th and 16th centuries, of national standing. The death of Richard III at Bosworth Field altered its history irrevocably. As the historian John Nicholls stated, "Fotheringhay has been distinguished beyond any other place in Britain, except the Capital, by the aggravated misfortunes of Royalty." At the time of the 2001 census, the parish's population was 123 people, reducing to 119 at the 2011 census. History The first written mention of a settlement here wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Northamptonshire
North Northamptonshire is one of two local authority areas in Northamptonshire, England. It is a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area forming about one half of the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Northamptonshire. It was created in 2021. Its notable towns are Kettering, Corby, Wellingborough, Rushden, Raunds, Desborough, Rothwell, Northamptonshire, Rothwell, Irthlingborough, Thrapston and Oundle. The council is based at the Corby Cube in Corby. It has a string of lakes along the River Nene, Nene Valley Conservation Park, associated Nene Valley Railway, heritage railway, the village of Fotheringhay which has tombs of the House of York as well as a towering church supported by flying buttresses. This division has a well-preserved medieval castle in private hands next to Corby – Rockingham Castle – and about 20 other notable : country houses in Northamptonshire, country houses, many of which have visitor gardens or days. History N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Leland (antiquary)
John Leland or Leyland (13 September, – 18 April 1552) was an English poet and antiquary.Carley (2006), "Leland, John (''ca''. 1503–1552)" Leland has been described as "the father of English local history and bibliography". His ''Itinerary'' provided a unique source of observations and raw materials for many subsequent antiquaries, and introduced the county as the basic unit for studying the local history of England, an idea that has been influential ever since. Early life and education Most evidence for Leland's life and career comes from his own writings, especially his poetry. He was born in London on 13 September, most probably in about 1503, and had an older brother, also named John. Having lost both his parents at an early age, he and his brother were raised by Thomas Myles. Leland was educated at St Paul's School, London, under its first headmaster, William Lily. It was here that he already met some of his future benefactors, notably William Paget. Leland wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hewer
William Hewer (1642 – 3 December 1715), sometimes known as Will Hewer, was one of Samuel Pepys' manservants, and later Pepys's clerk, before embarking on an administrative career of his own. Hewer is mentioned several times in Pepys' diary and was ultimately the executor of Pepys' will. Pepys' manservant Hewer was employed by Samuel Pepys as a manservant and office clerk for Pepys' work as the new Clerk of the Acts to the Navy Board. By November 1663, Hewer was able to move out of Pepys' house and have his own lodgings. Hewer was initially introduced to Pepys by Hewer's uncle Robert Blackborne, whose sister was Hewer's mother, and who was a longtime Pepys friend with whom he worked at the Admiralty. It has been said that the biggest favor Blackborne did for Pepys was the introduction of his nephew Hewer to Pepys in 1660. Hewer in Pepys' diary Hewer is frequently mentioned in Pepys' diary as a trusted friend as well as an assistant. As their relationship developed, it becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Savile, 2nd Marquess Of Halifax
William Savile, 2nd Marquess of Halifax (1665 – 31 August 1700) was the son of George Savile, 1st Viscount Halifax and Dorothy Savile, Viscountess Halifax (née Spencer). He was educated in Geneva in 1677 and matriculated at Christ Church, Oxford in 1681, but did not take a degree. He travelled on the continent in 1684–1687, returning on his brother's death. From that time, he was known as Lord Elland, from his father's subsidiary title of Baron Savile of Elland. He was elected Member of Parliament for Newark-on-Trent from 1689 to 1695. He was a Tory and voted in 1689 that the throne was not vacant. He had four daughters including: *By his first wife, Elizabeth Grimston, the daughter of Sir Samuel Grimston, whom he married on 24 November 1687: **Lady Anne Savile (1691 – 18 July 1717) who married Charles Bruce, 4th Earl of Elgin (1682–1747) *By his second wife, Lady Mary Finch, who was the first cousin of his first wife, daughter of Daniel Finch, 7th Earl of Winc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Savile, 1st Marquess Of Halifax
George Savile, 1st Marquess of Halifax, (11 November 1633 – 5 April 1695), was an English statesman, writer, and politician who sat in the House of Commons in 1660, and in the House of Lords after he was raised to the peerage in 1668. Background and early life, 1633–1667 Savile was born in Thornhill, in the West Riding of Yorkshire, the eldest son of Sir William Savile, 3rd Baronet, and his wife Anne Coventry, eldest daughter of Lord Keeper Thomas Coventry, 1st Baron Coventry. His father distinguished himself in the civil war in the royalist cause and died in 1644. Savile was also the nephew of Sir William Coventry, who is said to have influenced his political opinions, and of Lord Shaftesbury, afterwards his most bitter opponent, and great-nephew of the Earl of Strafford. He was the great-grandson of Sir George Savile of Lupset and Thornhill (created baronet in 1611). He was educated at Shrewsbury School in 1643 while his mother was staying with a sister in Shropshire. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Newport
Earl of Newport, in the Isle of Wight, was a title in the Peerage of England. It was created in 1628 for Mountjoy Blount, 1st Baron Mountjoy, an illegitimate son of Charles Blount, 1st Earl of Devonshire. He had already been created Baron Mountjoy, of Mountjoy Fort in the County of Tyrone, in the Peerage of Ireland in 1618, and Baron Mountjoy, of Thurveston in the County of Derby, in the Peerage of England in 1627. The latter title was originally created with precedence ahead of those barons created between 20 May and 5 June 1627. This precedence was later revoked by the House of Lords. The first Earl's three surviving sons were "all idiots", and some confusion exists as to their names and dates of death. Parish registers indicate that the second Earl, named either George or Mountjoy, died at Newport House in London, and was buried at St Martin-in-the-Fields in March 1675; his brother Thomas, the third Earl, was buried at Weyhill in May 1675; and their youngest brother Henry was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balliol College, Oxford
Balliol College () is one of the constituent colleges of the University of Oxford in England. One of Oxford's oldest colleges, it was founded around 1263 by John I de Balliol, a landowner from Barnard Castle in County Durham, who provided the foundation and endowment for the college. When de Balliol died in 1268, his widow, Dervorguilla, a woman whose wealth far exceeded that of her husband, continued his work in setting up the college, providing a further endowment and writing the statutes. She is considered a co-founder of the college. The college's alumni include four former Prime Ministers of the United Kingdom ( H. H. Asquith, Harold Macmillan, Edward Heath, and Boris Johnson), Harald V of Norway, Empress Masako of Japan, five Nobel laureates, several Lords of Appeal in Ordinary, and numerous literary and philosophical figures, including Shoghi Effendi, Adam Smith, Gerard Manley Hopkins, and Aldous Huxley. John Wycliffe, who translated the Bible into English, was m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward VI Of England
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and King of Ireland, Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. Edward was the son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour and the first English monarch to be raised as a Protestant. During his reign, the realm was governed by a regent, regency council because he never reached maturity. The council was first led by his uncle Edward Seymour, 1st Duke of Somerset (1547–1549), and then by John Dudley, 1st Earl of Warwick (1550–1553), who from 1551 was Duke of Northumberland. Edward's reign was marked by economic problems and social unrest that in 1549 erupted into riot and rebellion. An expensive war with Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, at first successful, ended with military withdrawal from Scotland and Boulogne-sur-Mer in exchange for peace. The transformation of the Church of England into a recognisably Protestant body also occurred under Edward, who took ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relic Sunday
Relick Sunday (or Relic Sunday) is a moveable feast in the Christian calendar celebrated in mid July on the third Sunday after Midsummer's day. The feast celebrated Christian relics of all kinds, in which offerings were given to relics. A second usage of the term used in medieval times occurred across England, persisting most notably in Northamptonshire, when the Sunday after the feast of Saint Thomas Becket Thomas Becket (), also known as Saint Thomas of Canterbury, Thomas of London and later Thomas à Becket (21 December 1119 or 1120 – 29 December 1170), was an English nobleman who served as Lord Chancellor from 1155 to 1162, and then ... (29 December) was commonly known as Relick Sunday. This meant that it was celebrated annually between 30 December and 5 January. A manuscript from the late fifteenth century carrying a sermon entitled ''In festo Reliquarum'' describes its commemoration:London, British Library, Harley MS 2247, f. 169v. Punctuation and spelling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michaelmas
Michaelmas ( ; also known as the Feast of Saints Michael, Gabriel, and Raphael, the Feast of the Archangels, or the Feast of Saint Michael and All Angels) is a Christian festival observed in some Western liturgical calendars on 29 September, and on 8 November in the Eastern tradition. Michaelmas has been one of the four quarter days of the English and Irish financial, judicial, and academic year. In Christian angelology, the Archangel Michael is the greatest of all the angels; he is particularly honored for defeating Lucifer in the war in heaven. History In the fifth century, a basilica near Rome was dedicated in honour of Saint Michael the Archangel on 30 September, beginning with celebrations on the eve of that day. 29 September is now kept in honour of Saint Michael and all Angels throughout some western churches. The name Michaelmas comes from a shortening of "Michael's Mass", in the same style as Christmas (Christ's Mass) and Candlemas (Candle Mass, the Mass where t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Finch, 2nd Earl Of Nottingham
Daniel Finch, 2nd Earl of Nottingham, 7th Earl of Winchilsea, PC (2 July 16471 January 1730) was an English Tory statesman who supported the Hanoverian Succession in 1714. Origins He was born on 2 July 1647, the son of Heneage Finch, 1st Earl of Nottingham (1620-1682), Lord Chancellor of England, by his wife Elizabeth Harvey, a daughter of Daniel Harvey. Education Little is known about his upbringing. He entered Westminster School in 1658, where he boarded for three years at the house of Dr. Richard Busby, the headmaster and his father's former tutor at Christ Church, Oxford. Daniel also went to Christ Church and the excellence of his studies made his father doubt their authenticity. He matriculated at Christ Church as a Gentleman Commoner on 26 July 1662. In April 1663 his father wrote to him, advising that he "loose not the reputation which I am told you have gayn'd of diligence and sobriety". His father also advised him a month after he had arrived in Oxford "to frequent t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamford, Lincolnshire
Stamford is a town and civil parish in the South Kesteven District of Lincolnshire, England. The population at the 2011 census was 19,701 and estimated at 20,645 in 2019. The town has 17th- and 18th-century stone buildings, older timber-framed buildings and five medieval parish churches. It is a frequent film location. In 2013 it was rated a top place to live in a survey by ''The Sunday Times''. Its name has been passed on to Stamford, Connecticut, founded in 1641. History Roman and Medieval Stamford The Romans built Ermine Street across what is now Burghley Park and forded the River Welland to the west of Stamford, eventually reaching Lincoln. They also built a town to the north at Great Casterton on the River Gwash. In 61 CE Boudica followed the Roman legion Legio IX Hispana across the river. The Anglo-Saxons later chose Stamford as the main town, being on a larger river than the Gwash. The place-name Stamford is first attested in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, where it ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpeg)





