|
Foster–Seeley Discriminator
The Foster–Seeley discriminator is a common type of FM detector circuit, invented in 1936 by Dudley E. FosterDudley E. Foster: biographical information and photo: ''Proceedings of the Institute of Radio Engineers'', vol. 29, page 571 (October 1941). Available on-line at: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/iel5/10933/35665/01694175.pdf and Stuart William Seeley. The Foster–Seeley discriminator was envisioned for automatic frequency control of receivers, but also found application in demodulating an FM signal. The Foster–Seeley discriminator uses a tuned RF transformer to convert frequency changes into amplitude changes. A transformer, tuned to the carrier frequency, is connected to two rectifier diodes. The circuit resembles a full-wave bridge rectifier. If the input equals the carrier frequency, the two halves of the tuned transformer circuit produce the same rectified voltage and the output is zero. As the frequency of the input changes, the balance between the two halve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Modulation
Frequency modulation (FM) is the encoding of information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave. The technology is used in telecommunications, radio broadcasting, signal processing, and Run-length limited#FM: .280.2C1.29 RLL, computing. In Analog signal, analog frequency modulation, such as radio broadcasting, of an audio signal representing voice or music, the instantaneous frequency deviation, i.e. the difference between the frequency of the carrier and its center frequency, has a functional relation to the modulating signal amplitude. Digital data can be encoded and transmitted with a type of frequency modulation known as frequency-shift keying (FSK), in which the instantaneous frequency of the carrier is shifted among a set of frequencies. The frequencies may represent digits, such as '0' and '1'. FSK is widely used in computer modems, such as fax modems, telephone caller ID systems, garage door openers, and other low-frequency transmissions. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier Wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a much higher frequency than the input signal does. The purpose of the carrier is usually either to transmit the information through space as an electromagnetic wave (as in radio communication), or to allow several carriers at different frequencies to share a common physical transmission medium by frequency division multiplexing (as in a cable television system). The term originated in radio communication, where the carrier wave creates the waves which carry the information (modulation) through the air from the transmitter to the receiver. The term is also used for an unmodulated emission in the absence of any modulating signal. In music production, carrier signals can be controlled by a modulating signal to change the sound property of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Circuits
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquiry studying them. There are many disagreements about its precise definition. John Peters argues that the difficulty of defining communication emerges from the fact that communication is both a universal phenomenon and a specific discipline of institutional academic study. One definitional strategy involves limiting what can be included in the category of communication (for example, requiring a "conscious intent" to persuade). By this logic, one possible definition of communication is the act of developing meaning among entities or groups through the use of sufficiently mutually understood signs, symbols, and semiotic conventions. An important distinction is between verbal communication, which happens through the use of a language, and non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase-locked Loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector in a feedback loop. The oscillator's frequency and phase are controlled proportionally by an applied voltage, hence the term voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). The oscillator generates a periodic signal of a specific frequency, and the phase detector compares the phase of that signal with the phase of the input periodic signal, to adjust the oscillator to keep the phases matched. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and output frequencies the same. Consequently, in addition to synchronizing signals, a phase-locked loop can track an input frequency, or it can generate a frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency. These properties are use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrature Detector
In radio, a detector is a device or circuit that extracts information from a modulated radio frequency current or voltage. The term dates from the first three decades of radio (1888-1918). Unlike modern radio stations which transmit sound (an audio signal) on an uninterrupted carrier wave, early radio stations transmitted information by ''radiotelegraphy''. The transmitter was switched on and off to produce long or short periods of radio waves, spelling out text messages in Morse code. Therefore, early radio receivers had only to distinguish between the presence or absence of a radio signal. The device that performed this function in the receiver circuit was called a ''detector''. A variety of different detector devices, such as the coherer, electrolytic detector, magnetic detector and the crystal detector, were used during the wireless telegraphy era until superseded by vacuum tube technology. After sound (amplitude modulation, AM) transmission began around 1920, the term evolved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratio Detector
The ratio detector is a type of detector circuit, commonly used in radio receivers for demodulating frequency modulated (FM) signal. The ratio detector is a variant of the Foster–Seeley discriminator, but one diode conducts in an opposite direction, and using a tertiary winding in the preceding transformer. The output in this case is taken between the sum of the diode voltages and the center tap. The output across the diodes is connected to a large value capacitor, forming a dynamic limiter. The ratio detector has the advantage over the Foster–Seeley discriminator that it does not respond to amplitude modulation (AM) signals, thus potentially saving a limiter stage; however, the output is only 50% of the output of a discriminator for the same input signal. The ratio detector has wider bandwidth, but more distortion than the Foster–Seeley discriminator. Amplitude noise suppression The suppression of the effect of amplitude variation of the incoming signal on the output ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slope Detector
In radio, a detector is a device or circuit that extracts information from a modulated radio frequency current or voltage. The term dates from the first three decades of radio (1888-1918). Unlike modern radio stations which transmit sound (an audio signal) on an uninterrupted carrier wave, early radio stations transmitted information by ''radiotelegraphy''. The transmitter was switched on and off to produce long or short periods of radio waves, spelling out text messages in Morse code. Therefore, early radio receivers had only to distinguish between the presence or absence of a radio signal. The device that performed this function in the receiver circuit was called a ''detector''. A variety of different detector devices, such as the coherer, electrolytic detector, magnetic detector and the crystal detector, were used during the wireless telegraphy era until superseded by vacuum tube technology. After sound (amplitude modulation, AM) transmission began around 1920, the term evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class-A Amplifier
In electronics, power amplifier classes are letter symbols applied to different power amplifier types. The class gives a broad indication of an amplifier's characteristics and performance. The classes are related to the time period that the active amplifier device is passing current, expressed as a fraction of the period of a signal waveform applied to the input. A class A amplifier is conducting through all the period of the signal; Class B only for one-half the input period, class C for much less than half the input period. A Class D amplifier operates its output device in a switching manner; the fraction of the time that the device is conducting is adjusted so a pulse-width modulation output is obtained from the stage. Additional letter classes are defined for special-purpose amplifiers, with additional active elements or particular power supply improvements; sometimes a new letter symbol is used by a manufacturer to promote its proprietary design. Power amplifier classes Powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limiter
In electronics, a limiter is a circuit that allows signals below a specified input power or level to pass unaffected while attenuating (lowering) the peaks of stronger signals that exceed this threshold. Limiting is a type of dynamic range compression. Clipping is an extreme version of limiting. Limiting is any process by which the amplitude of a signal is prevented from exceeding a predetermined value. Limiters are common as a safety device in live sound and broadcast applications to prevent sudden volume peaks from occurring. Limiters are also used as protective features in some components of sound reinforcement systems (e.g., powered mixing boards and power amplifiers) and in some bass amplifiers, to prevent unwanted distortion or loudspeaker damage. Types Limiting can refer to a range of treatments designed to limit the maximum level of a signal. Treatments in order of decreasing severity range from clipping, in which a signal is passed through normally but sheared off when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
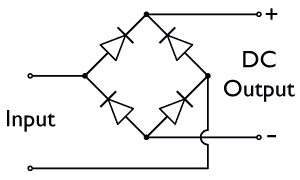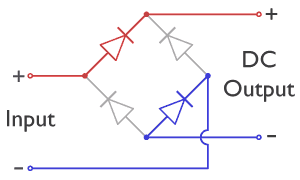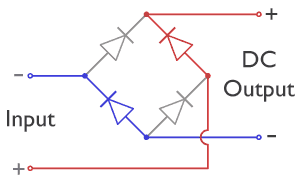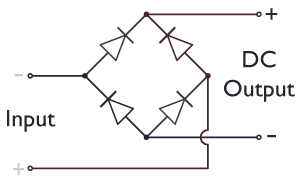
Bridge Rectifier
A diode bridge is a bridge rectifier circuit of four diodes that is used in the process of converting alternating current (AC) from the input terminals to direct current (DC, i.e. fixed polarity) on the output terminals. Its function is to convert the negative-going AC pulses into positive going pulses, after which a low-pass filter can be used to smooth the result into DC. When used in its most common application, for conversion of an alternating-current (AC) input into a direct-current (DC) output, it is known as a bridge rectifier. A bridge rectifier provides full-wave rectification from a two-wire AC input, resulting in lower cost and weight as compared to a rectifier with a three-wire input from a transformer with a center-tapped secondary winding. The essential feature of a diode bridge is that the polarity of the output is the same regardless of the polarity at the input. The diode bridge circuit was invented by Polish electrotechnician Karol Pollak and patented in De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detector (radio)
In radio, a detector is a device or circuit that extracts information from a modulated radio frequency current or voltage. The term dates from the first three decades of radio (1888-1918). Unlike modern radio stations which transmit sound (an audio signal) on an uninterrupted carrier wave, early radio stations transmitted information by ''radiotelegraphy''. The transmitter was switched On-off_keying, on and off to produce long or short periods of radio waves, spelling out text messages in Morse code. Therefore, early radio receiver, radio receivers had only to distinguish between the presence or absence of a radio signal. The device that performed this function in the receiver circuit was called a ''detector''. A variety of different detector devices, such as the coherer, electrolytic detector, magnetic detector and the crystal detector, were used during the wireless telegraphy era until superseded by vacuum tube technology. After sound (amplitude modulation, AM) transmission began ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A diode vacuum tube or thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also used. Among many uses, diodes are found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |