|
Fortress Of Ulm
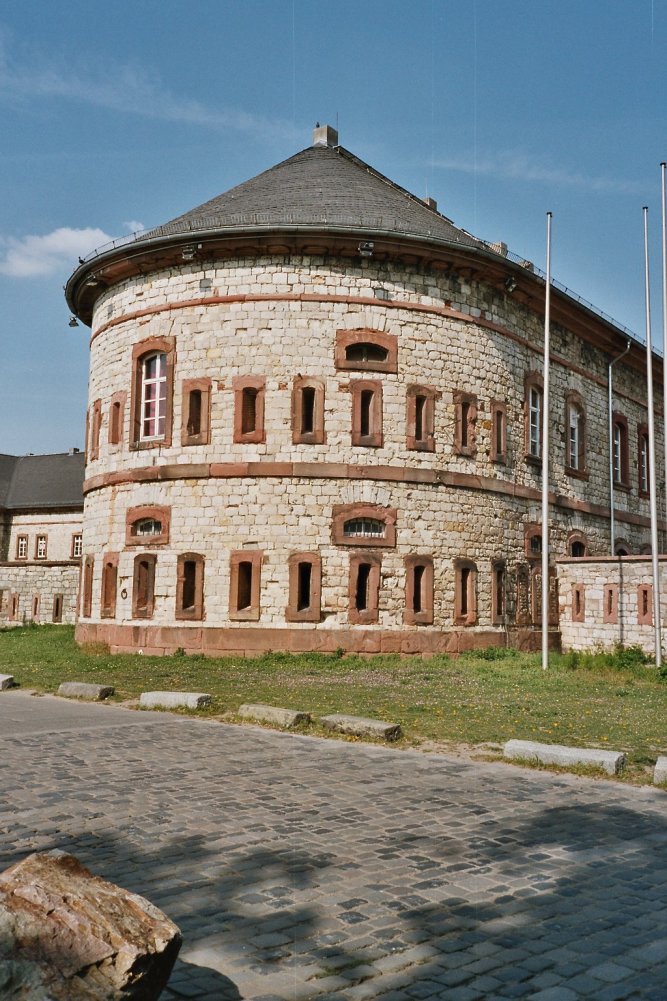
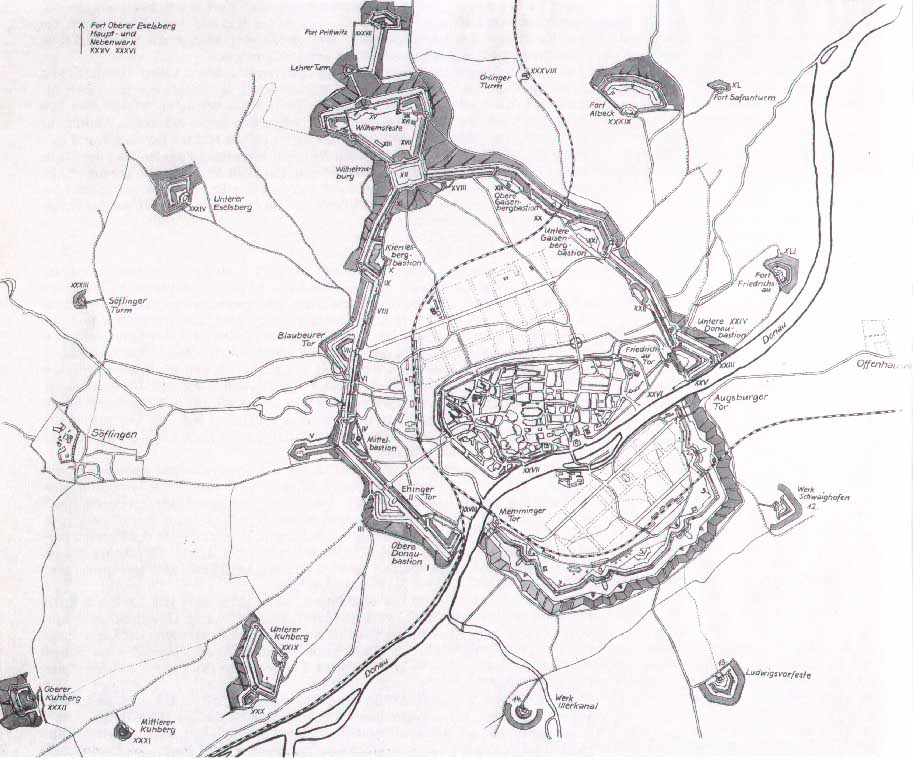
The fortress of Ulm (''Bundesfestung Ulm'') was one of five federal fortresses of the German Confederation around the cities of Ulm and Neu-Ulm. With its 9 km polygonal main circumvallation Ulm had the biggest fortress in Germany in the 19th century and it is still one of the biggest in Europe. After the final defeat of Napoleon in 1815, the victorious powers agreed to defend the states from the inside. The fortresses were one of the few realised projects of the confederation. The fortress Ulm was planned by the Prussian construction manager Moritz Karl Ernst von Prittwitz und Gaffron and built under his supervision between 1842 and 1859. In peacetimes the fortress should hold 5,000 men of the federal army, in wartimes up to 20,000 soldiers. A plan to expand the fortress to hold 100,000 men was never realised. The building costs were valued at 16,5 mio. guilders. The fortress is a closed, polygonal wall system around the cities of Ulm in the Kingdom of Württemberg and Neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Festung Ulm
''Festung'' is a generic German word for a fortress. Although it is not in common usage in English, it is used in a number of historical contexts involving German speakers: * For historical fortresses in Austria, Germany or Switzerland * As part of the reasoning given by the German Army ('' Heer'') for the slow progress of the Siege of Warsaw * For German WWII strongholds which were to be held at all costs, especially towards the end of the war: ** Alpine Fortress or ''Alpenfestung'' ** Atlantic wall or ''Festung Europa — a military propaganda term from the Second World War which referred to the areas of Continental Europe occupied by Nazi Germany. ** Stalingrad (see Battle for Stalingrad) ** Warsaw (Festung Warschau) see also the Warsaw Uprising ** Poznań ( Battle of Posen) ** Kolobrzeg ( Battle of Kolberg) ** Piła (Festung Schneidemühl) ** Wrocław (Festung Breslau) ** Budapest (Battle of Budapest) ** Kaliningrad (Festung Königsberg) * For entire countries such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regensburg
Regensburg or is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the Danube, Naab and Regen rivers. It is capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the state in the south of Germany. With more than 150,000 inhabitants, Regensburg is the fourth-largest city in the State of Bavaria after Munich, Nuremberg and Augsburg. From its foundation as an imperial Roman river fort, the city has been the political, economic and cultural centre of the surrounding region; it is still known in the Romance languages by a cognate of its Latin name of "Ratisbona" (the version "Ratisbon" was long current in English). Later, under the rule of the Holy Roman Empire, it housed the Perpetual Diet of Regensburg. The medieval centre of the city was made a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2006 because of its well-preserved architecture and the city's historical importance for assemblies during the Holy Roman Empire. In 2014, Regensburg was among the top sights and travel attractions in Germany. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Demolished In 1971
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forts
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its 'cyclopean' walls). A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurt Schumacher
Curt Ernst Carl Schumacher, better known as Kurt Schumacher (13 October 1895 – 20 August 1952), was a German politician who became chairman of the Social Democratic Party of Germany from 1946 and the first Leader of the Opposition in the West German Bundestag in 1949; he served in both positions until his death. An opponent of Chancellor Konrad Adenauer's government but an even stronger opponent of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany in East Germany, he was one of the founding fathers of postwar German democracy. He was an opponent of reactionary and revolutionary forces, the Nazi Party and the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) during the Weimar Republic and described the KPD as "red-painted Nazis". Early life and career Schumacher was born in Kulm in West Prussia (now Chełmno in Poland), the son of a small businessman who was a member of the liberal German Free-minded Party and deputy in the municipal assembly. The young man was a brilliant student, but when the First W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentration Camp
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simply mean imprisonment, it tends to refer to preventive confinement rather than confinement ''after'' having been convicted of some crime. Use of these terms is subject to debate and political sensitivities. The word ''internment'' is also occasionally used to describe a neutral country's practice of detaining belligerent armed forces and equipment on its territory during times of war, under the Hague Convention of 1907. Interned persons may be held in prisons or in facilities known as internment camps (also known as concentration camps). The term ''concentration camp'' originates from the Spanish–Cuban Ten Years' War when Spanish forces detained Cuban civilians in camps in order to more easily combat guerrilla forces. Over the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberer Kuhberg Concentration Camp
Oberer Kuhberg concentration camp was a concentration camp built and operated by Nazi Germany on the site of Fort Oberer Kuhberg. History as a fort Fort Oberer Kuhberg was built from 1848 to 1857 as part of the Fortress of Ulm. It was used until the 20th century and is one of the biggest forts in Europe. It was fit to hold 5,000 soldiers in peacetime, and up to 20,000 in wartime. It happens to contains the Ulm Minster, the tallest church in the world. History as a concentration camp It was repurposed as a concentration camp for political dissidents from November 1933 to July 1935. It held more than 600 political prisoners during this time. The purpose of the camp was to intimidate those who opposed the Nazi regime. One notable prisoner was Kurt Schumacher, a politician who became the leader of the Social Democratic Party The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygonal Fort
A polygonal fort is a type of fortification originating in France in the late 18th century and fully developed in Germany in the first half of the 19th century. Unlike earlier forts, polygonal forts had no bastions, which had proved to be vulnerable. As part of ring fortresses, polygonal forts were generally arranged in a ring around the place they were intended to protect, so that each fort could support its neighbours. The concept of the polygonal fort proved to be adaptable to improvements in the artillery which might be used against them, and they continued to be built and rebuilt well into the 20th century. Bastion system deficiencies The bastion system of fortification had dominated military thinking since its introduction in 16th century Italy, until the first decades of the 19th century. The French engineer Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, also devised an effective method to defeat them. Before Vauban, besiegers had driven a sap towards the fort, until they reached the gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Bavaria
The Kingdom of Bavaria (german: Königreich Bayern; ; spelled ''Baiern'' until 1825) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingdom became a federated state of the new empire and was second in size, power, and wealth only to the leading state, the Kingdom of Prussia. The polity's foundation dates back to the ascension of prince-elector Maximilian IV Joseph of the House of Wittelsbach as King of Bavaria in 1805. The crown would go on being held by the Wittelsbachs until the kingdom came to an end in 1918. Most of the border of modern Germany's Free State of Bavaria were established after 1814 with the Treaty of Paris, in which the Kingdom of Bavaria ceded Tyrol and Vorarlberg to the Austrian Empire while receiving Aschaffenburg and Würzburg. In 1918, Bavaria became a republic after the German Revolution, and the kingdom was thus succeeded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortresses Of The German Confederation
Under the terms of the 1815 Peace of Paris, France was obliged to pay for the construction of a line of fortresses to protect the German Confederation against any future aggression by France. All fortresses were located outside Austria and Prussia — the two biggest, bickering powers of the Confederation. Section C. "Defensive System of the Germanic Confederation" of the protocol drawn up at Paris on 3 November 1815, declared Mainz, Luxemburg, and Landau to be fortresses belonging to the Confederation of Germany, and stipulated that a fourth should be constructed on the Upper Rhine. In conformity with this act, a portion of the funds, which France was compelled to pay by way of indemnity for the cost of placing her on a peaceable footing, was thus appropriated: £200,000 were set aside for completing the works at Mainz; £800,000 were assigned to Prussia, to be applied upon its fortresses on the Lower Rhine; another £800,000 were reserved for constructing the new federal fortr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Württemberg
The Kingdom of Württemberg (german: Königreich Württemberg ) was a German state that existed from 1805 to 1918, located within the area that is now Baden-Württemberg. The kingdom was a continuation of the Duchy of Württemberg, which existed from 1495 to 1805. Prior to 1495, Württemberg was a county in the former Duchy of Swabia, which had dissolved after the death of Duke Conradin in 1268. The borders of the Kingdom of Württemberg, as defined in 1813, lay between 47°34' and 49°35' north and 8°15' and 10°30' east. The greatest distance north to south comprised and the greatest east to west was . The border had a total length of and the total area of the state was . The kingdom had borders with Bavaria on the east and south, with Baden in the north, west, and south. The southern part surrounded the Prussian province of Hohenzollern on most of its sides and touched on Lake Constance. History Frederick I Frederick II, the Duke of Württemberg (1754–1816; elev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moritz Karl Ernst Von Prittwitz
Moritz Karl Ernst von Prittwitz German source for this Article (9 February 1795, Gut Kreisewitz in Alzenau, Lower Silesia – 21 October 1885 in Berlin) is a Royal Prussian Lieutenant-General of Infantry, who supervised the building of the large fortress in Ulm. He was later admitted to the Order of St. John as a Knight of Honor. See also * Ernst von Prittwitz und Gaffron Ernst Karl Ferdinand von Prittwitz und Gaffron (20 January 1833 – 24 February 1904) was a Royal Prussian Lieutenant General and Knight of Justice of the Order of Saint John. Family and private life Von Prittwitz was born in Posen, Prussia (mod ... as son of Prittwitz External links * References 1795 births 1885 deaths People from Brzeg County People from the Province of Silesia Lieutenant generals of Prussia {{Germany-mil-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)




