|
Fort Towson, Oklahoma
Fort Towson is a town in Choctaw County, Oklahoma, United States. The population was 510 at the 2010 census, a 15.1 percent decline from the figure of 611 recorded in 2000. It was named for nearby Fort Towson, which had been established in May 1824 and named for General Nathan Towson, a hero of the War of 1812.Tolman, Keith. ''Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture.'' "Fort Towson." Retrieved September 17, 201/ref> The town of Fort Towson was established in 1902, after the St. Louis, San Francisco and New Orleans Railroad, Arkansas and Choctaw Railway reached eastern Choctaw County.O'Keefe, Marilyn Fleck. ''Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture''. "Fort Towson (Town)." Retrieved September 17, 201/ref> History The fort was first established to protect the southern border of the Indian Territory against Spanish colonies to the south. After Indian Removal and the resettlement of the Choctaw in the area, the fort was revived to protect Doaksville, a mile to the west. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world. Origin and use The word "town" shares an origin with the German word , the Dutch word , and the Old Norse . The original Proto-Germanic word, *''tūnan'', is thought to be an early borrowing from Proto-Celtic *''dūnom'' (cf. Old Irish , Welsh ). The original sense of the word in both Germanic and Celtic was that of a fortress or an enclosure. Cognates of ''town'' in many modern Germanic languages designate a fence or a hedge. In English and Dutch, the meaning of the word took on the sense of the space which these fences enclosed, and through which a track must run. In England, a town was a small community that could not afford or was not allowed to build walls or other larger fortifications, and built a palisade or stockade instead. In the Netherlands, this space was a garden, mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Removal
Indian removal was the United States government policy of forced displacement of self-governing tribes of Native Americans from their ancestral homelands in the eastern United States to lands west of the Mississippi Riverspecifically, to a designated Indian Territory (roughly, present-day Oklahoma). The Indian Removal Act, the key law which authorized the removal of Native tribes, was signed by Andrew Jackson in 1830. Although Jackson took a hard line on Indian removal, the law was enforced primarily during the Martin Van Buren administration. After the passage of the Indian Removal Act in 1830, approximately 60,000 members of the Cherokee, Muscogee (Creek), Seminole, Chickasaw, and Choctaw nations (including thousands of their black slaves) were forcibly removed from their ancestral homelands, with thousands dying during the Trail of Tears. Indian removal, a popular policy among incoming settlers, was a consequence of actions by European settlers in North America during th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo, Oklahoma
Hugo is a city in and the county seat of Choctaw County, Oklahoma, United States. It is located in southeastern Oklahoma, approximately north of the Texas state line. As of the 2010 census, the city population was 5,310. The city was founded in 1901 and named for the French novelist Victor Hugo.Larry O'Dell"Hugo" ''Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture''. Accessed August 25, 2013. In the postwar 20th century, the city served as winter quarters for some circus companies and performers. A cemetery has a section for circus personnel. Nearby is one of the oldest boarding schools west of the Mississippi: Goodland Academy, begun in 1848 as a Presbyterian mission, school and orphanage for Native American children. The town is located in a cultural area of the state known as Little Dixie, as it was settled by Native American tribes, African Americans and European Americans from the southeastern United States. It is within the tourist area designated as Choctaw Country by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond Gary State Park
Raymond Gary State Park is an Oklahoma state park located in southeast Oklahoma. The park borders Raymond Gary Lake Raymond Gary Lake is a reservoir in southeastern Oklahoma, United States, one mile east of the town of Fort Towson in Choctaw County. It was constructed on Gates Creek in 1956 by the Oklahoma Department of Wildlife Conservation. Its primary use ..., which covers and offers opportunities for fishing, boating, swimming, and camping. Park facilities include a fishing dock (handicap accessible), two unlighted boat ramps, picnic sites, recreational vehicle sites, six cabins, a swimming area and children's playground. The park and the adjacent lake were named after Raymond D. Gary who served as Governor of Oklahoma from 1955 to 1959. The park is 1 of 7 Oklahoma State Parks that are in the path of totality for the 2024 solar eclipse, with 3 minutes and 51 seconds of totality. References State parks of Oklahoma Protected areas of Choctaw County, Oklahoma [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond Gary Lake
Raymond Gary Lake is a reservoir in southeastern Oklahoma, United States, one mile east of the town of Fort Towson in Choctaw County. It was constructed on Gates Creek in 1956 by the Oklahoma Department of Wildlife Conservation. Its primary uses are for fishing and general recreation. Retrieved September 18, 2012. The lake and the adjacent Raymond Gary State Park
Raymond Gary State Park is an Oklahoma state park located in southeast Oklahoma. The park borders Raymond Gary Lake
Raymond Gary Lake is a reservoir in southeastern Oklahoma, United States, one mile east of the town of Fort Towson in Choctaw ... were named for [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern North Carolina, southeastern Tennessee, edges of western South Carolina, northern Georgia, and northeastern Alabama. The Cherokee language is part of the Iroquoian language group. In the 19th century, James Mooney, an early American ethnographer, recorded one oral tradition that told of the tribe having migrated south in ancient times from the Great Lakes region, where other Iroquoian peoples have been based. However, anthropologist Thomas R. Whyte, writing in 2007, dated the split among the peoples as occurring earlier. He believes that the origin of the proto-Iroquoian language was likely the Appalachian region, and the split betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stand Watie
Brigadier-General Stand Watie ( chr, ᏕᎦᏔᎦ, translit=Degataga, lit=Stand firm; December 12, 1806September 9, 1871), also known as Standhope Uwatie, Tawkertawker, and Isaac S. Watie, was a Cherokee politician who served as the second principal chief of the Cherokee Nation from 1862 to 1866. The Cherokee Nation allied with the Confederate States during the American Civil War and he was the only Native American Confederate general officer of the war. Watie commanded Indian forces in the Trans-Mississippi Theater, made up mostly of Cherokee, Muskogee, and Seminole. He was the last Confederate States Army general to surrender. Before removal of the Cherokee to Indian Territory in the late 1830s, Watie and his older brother Elias Boudinot were among Cherokee leaders who signed the Treaty of New Echota in 1835. The majority of the tribe opposed their action. In 1839, the brothers were attacked in an assassination attempt, as were other relatives active in the Treaty Party. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Pitchlynn
Peter Perkins Pitchlynn ( cho, Hatchootucknee, italic=no, ) (January 30, 1806 – January 17, 1881) was a Choctaw chief of Choctaw and Anglo-American ancestry. He was principal chief of the Choctaw Republic from 1864-1866 and surrendered to the Union on behalf of the nation at the end of the Civil War. Educated in Choctaw culture and American schools, in 1825 Pitchlynn helped found a school for Choctaw boys: the Choctaw Academy in Kentucky. He also worked to reduce the sale of alcohol in their territory. After removal to Indian Territory in the 1830s, he was appointed by the National Council in 1845 as the Choctaw Delegate (akin to an ambassadorship) to Washington, D.C. At the time, the Nation was proposing to be recognized by the US Congress as a territory. After the war, Pitchlynn returned to Washington, D.C., to represent Choctaw interests and work for concessions from the government for the Choctaw lands sold under pressure to the United States in 1830 during Indian removal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
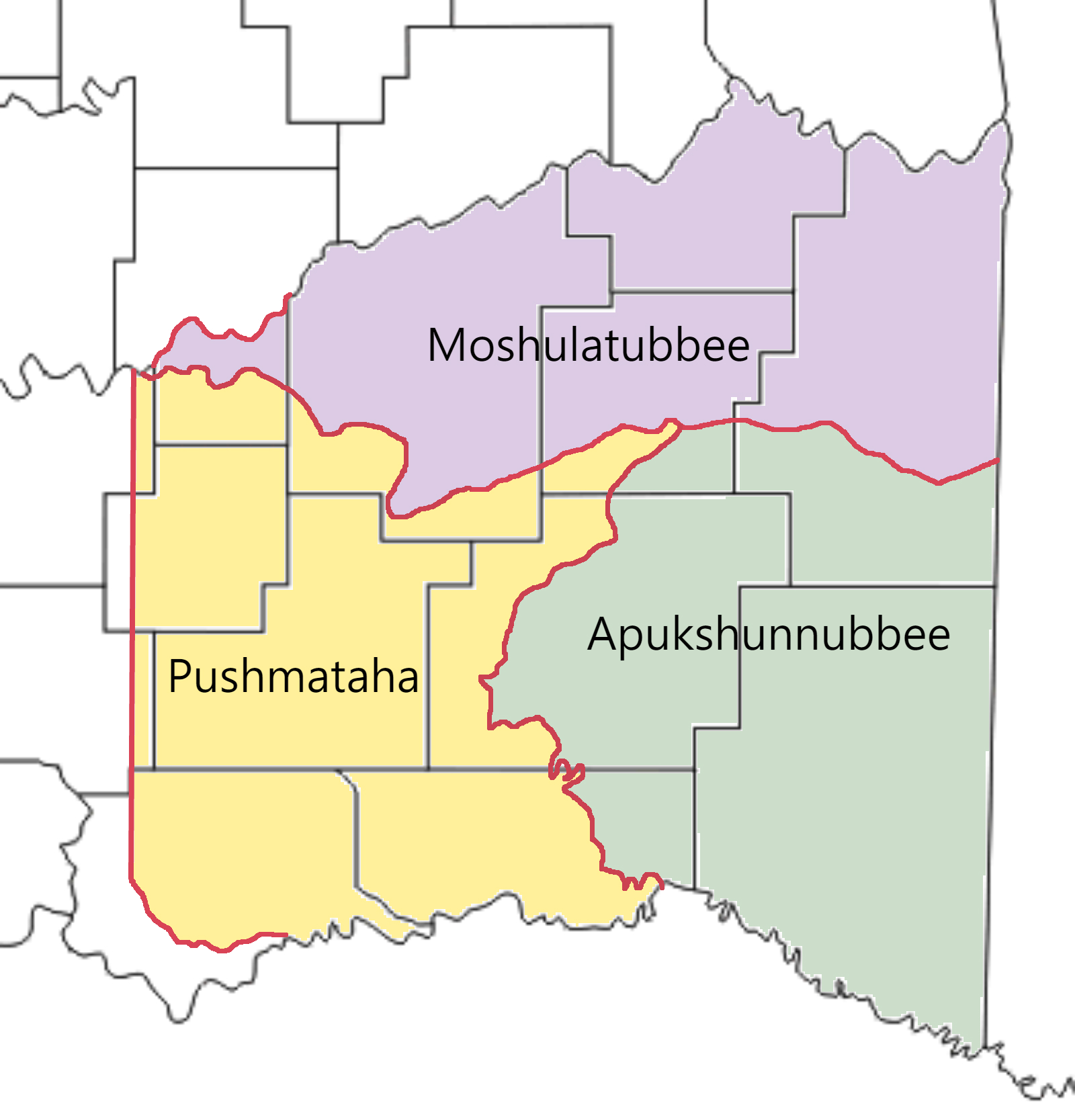
Apukshunnubbee District
Apukshunnubbee District was one of three administrative super-regions comprising the former Choctaw Nation in Indian Territory. Also called the Second District, it encompassed the southeastern one-third of the nation. The Apukshunnubbee District was named in honor of Chief Apukshunnubbee (also spelled Apuckshunubbee), a Choctaw warrior and statesman. He was district chief of the Okla Falaya ("Upper Towns") District in the original Choctaw Nation of the Southeast. Many Choctaw from that area referred to the Apukshunnubbee District as the Okla Falaya District. The other two districts were the Moshulatubbee District and Pushmataha District. History The districts were established when the Choctaw Nation relocated via the Trail of Tears to the Indian Territory—present-day Oklahoma. They were originally intended to be homelands for settlers from the three major clans or divisions of the Choctaw comprising the nation. In practice, the clan affiliations and allegiances rapidly became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towson County, Choctaw Nation
Towson County was a political subdivision of the Choctaw Nation of Indian Territory, prior to Oklahoma being admitted as a state. The county formed part of the Nation's Apukshunnubbee a District, or Second District, one of three administrative super-regions. History Towson County, Choctaw Nation was named for U.S. Army Col. Nathanial Towson (1784–1854), whose name was also commemorated by the territorial-era military post, Fort Towson, and by the present-day adjacent town of Fort Towson. The military post, established in 1824, was named first. Towson County's boundaries were established and designated according to easily recognizable natural landmarks, as were the boundaries of all Choctaw Nation counties. The Red River formed its southern boundary; Little River was its eastern boundary; and the Kiamichi River was its western boundary. A line drawn to connect the Little and Kiamichi rivers formed its northern boundary. Four counties bordered Towson County: Cedar County ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red River Of The South
The Red River, or sometimes the Red River of the South, is a major river in the Southern United States. It was named for its reddish water color from passing through red-bed country in its watershed. It is one of several rivers with that name. Although once a tributary of the Mississippi River, the Red River is now a tributary of the Atchafalaya River, a distributary of the Mississippi that flows separately into the Gulf of Mexico. This confluence is connected to the Mississippi River by the Old River Control Structure. The south bank of the Red River formed part of the US–Mexico border from the Adams–Onís Treaty (in force 1821) until the Texas Annexation and the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. The Red River is the second-largest river basin in the southern Great Plains. It rises in two branches in the Texas Panhandle and flows east, where it serves as the border between the states of Texas and Oklahoma. It forms a short border between Texas and Arkansas before entering Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)