|
Fort Terry
Fort Terry was a coastal fortification on Plum Island, a small island just off Orient Point, New York, United States. This strategic position afforded it a commanding view over the Atlantic entrance to the commercially vital Long Island Sound. It was established in 1897 and used intermittently through the end of World War II. In 1952, it became a military animal and biological warfare (BW) research facility, moving to civilian control in 1954 as the Plum Island Animal Disease Center. However, the biological warfare mission continued under civilian control until 1969, when the US ended offensive BW research. The island is now being considered for sale or conversion to a wildlife refuge. Fort Terry was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2021. History Early history First “owned” by the Corchaug and Montaukett Indian tribes the Plum Island was sold to Samuel Wyllys for a coat, a barrel of biscuits and 100 fishhooks. The original fort was constructed after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harbor Defenses Of Long Island Sound
The Harbor Defenses of Long Island Sound was a United States Army Coast Artillery Corps harbor defense command. It coordinated the coast defenses of Long Island Sound and Connecticut from 1895 to 1950, beginning with the Endicott program. These included both coast artillery forts (all but two on islands in the sound) and underwater minefields. The area defended included the approach via the Sound to New York City, the port cities and manufacturing centers of New London, New Haven, and Bridgeport, and eventually included the submarine base and shipyard in Groton. The command originated circa 1900 as an Artillery District, was renamed Coast Defenses of Long Island Sound in 1913, and again renamed Harbor Defenses of Long Island Sound in 1925.Stanton, pp. 455-481Rinaldi, pp. 165-166Berhow, pp. 430-434 History Early Long Island Sound forts Colonial period Connecticut appears to have had few coastal fortifications in the colonial era. Unnamed forts are referred to in New Haven at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newsday
''Newsday'' is an American daily newspaper that primarily serves Nassau and Suffolk counties on Long Island, although it is also sold throughout the New York metropolitan area. The slogan of the newspaper is "Newsday, Your Eye on LI", and formerly it was "Newsday, the Long Island Newspaper". The newspaper's headquarters is in Melville, New York, in Suffolk County. ''Newsday'' has won 19 Pulitzer Prizes and has been a finalist for 20 more. As of 2019, its weekday circulation of 250,000 was the 8th-highest in the United States, and the highest among suburban newspapers. By January 2014, ''Newsday''s total average circulation was 437,000 on weekdays, 434,000 on Saturdays and 495,000 on Sundays. As of June 2022, the paper had an average print circulation of 97,182. History Founded by Alicia Patterson and her husband, Harry Guggenheim, the publication was first produced on September 3, 1940 from Hempstead. For many years until a major redesign in the 1970s, ''Newsday'' copied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Steele
Frederick Steele (January 14, 1819 – January 12, 1868) was a career military officer in the United States Army, serving as a major general in the Union Army during the American Civil War. He was most noted for retaking much of secessionist Arkansas for the Union cause, escaping the besieged port-city of Camden through successful deception tactics, and defeating Sterling Price and E. Kirby Smith at Jenkins Ferry. Early life Steele, son of Nathaniel & Dameras (Johnson) Steele, was born in Delhi, New York. He was an 1843 graduate of West Point, and later served in the Mexican–American War, where he participated in many engagements. Steele was meritoriously mentioned for distinguished bravery, and was promoted to first lieutenant in June 1848. He served in California during the Yuma War until 1853, and then to Fort Ridgely in Minnesota Territory and then Kansas Territory, and Nebraska Territory until the Civil War. He received his captain's commission on February 5, 1855. Civi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbette
Barbettes are several types of gun emplacement in terrestrial fortifications or on naval ships. In recent naval usage, a barbette is a protective circular armour support for a heavy gun turret. This evolved from earlier forms of gun protection that eventually led to the pre-dreadnought. The name ''barbette'' ultimately comes from fortification - it originally meant a raised platform or mound, as in the French phrase ''en barbette'', which refers to the practice of firing a cannon over a parapet rather than through an embrasure in a fortification's casemate. The former gives better angles of fire but less protection than the latter. The disappearing gun was a variation on the barbette gun; it consisted of a heavy gun on a carriage that would retract behind a parapet or into a gunpit for reloading. Barbettes were primarily used in coastal defences, but saw some use in a handful of warships, and some inland fortifications. The term is also used for certain aircraft gun mounts. Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12-inch Coast Defense Mortar
The 12-inch coast defense mortar was a weapon of caliber emplaced during the 1890s and early 20th century to defend US harbors from seaborne attack. In 1886, when the Endicott Board set forth its initial plan for upgrading the coast defenses of the United States, it relied primarily on mortars, not guns, to defend American harbors. "Sea-Coast Mortar Fire", Report of a Board, in ''Journal of the United States Artillery'', Vol. 7, No. 3, 1897. Over the years, provision was made for fortifications that would mount some 476 of these weapons, although not all of these tubes were installed. Ninety-one of these weapons were remounted as railway artillery in 1918-1919, but this was too late to see action in World War I. The railway mortars were only deployed in small quantities, and none overseas. The fixed mortars in the Philippines saw action in the Japanese invasion in World War II. All of the fixed mortars (except four) in the United States were scrapped by 1944, as new weapons replac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Stoneman
George Stoneman Jr. (August 8, 1822 – September 5, 1894) was a United States Army cavalry officer and politician who served as the fifteenth Governor of California from 1883 to 1887. He was trained at West Point, where his roommate was Stonewall Jackson, and graduated in 1846. Stoneman served in the Army for thirty-six years, though he was relieved of command in 1871. During this time, he was involved in multiple conflicts, including the Mexican–American War, where he did not see any combat, the Yuma War, and the American Civil War. In 1861, Stoneman was promoted to Brigadier General, and was later put in command of the Army of the Potomac's 3rd Infantry Corps, and subsequently the newly-created cavalry corps. At the Battle of Chancellorsville in 1863, under the command of Joseph Hooker, Stoneman failed in an ambitious attempt to penetrate behind enemy lines, getting bogged down at an important river crossing. Hooker placed much of the blame for the Union army's defeat on Ston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Tyler
Fort Tyler was a coastal fortification on Gardiners Point Island, a small island off Gardiners Island, in Gardiners Bay, at the eastern tip of Long Island, New York City, New York. The fort was constructed in 1898, during the Spanish American War, to protect Long Island from the danger of bombardment from Spanish Naval vessels. The fort was equipped with two 8-inch (203mm) rifles and two 5-inch (127mm) rifles. The fort was abandoned in 1920 and POTUS, President Franklin Roosevelt made it a bird reserve in 1938. During World War II, United States Navy, United States Naval forces used the fort as a target. The fort may contain unexploded ordnance, so landing is prohibited. References {{coord missing, New York (state) Forts in New York (state), Tyler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodman Gun
Drawing comparing Model 1844 8-inch columbiad and Model 1861 10-inch "Rodman" columbiad. The powder chamber on the older columbiad is highlighted by the red box. The Rodman gun is any of a series of American Civil War–era columbiads designed by Union artilleryman Thomas Jackson Rodman (1815–1871). The guns were designed to fire both shot and shell. These heavy guns were intended to be mounted in seacoast fortifications. They were built in 8-inch, 10-inch, 13-inch, 15-inch, and 20-inch bore. Other than size, the guns were all nearly identical in design, with a curving bottle shape, large flat cascabels with ratchets or sockets for the elevating mechanism. Rodman guns were true guns that did not have a howitzer-like powder chamber, as did many earlier columbiads. Rodman guns differed from all previous artillery because they were hollow cast, a new technology that Rodman developed that resulted in cast-iron guns that were much stronger than their predecessors. Casting file:R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
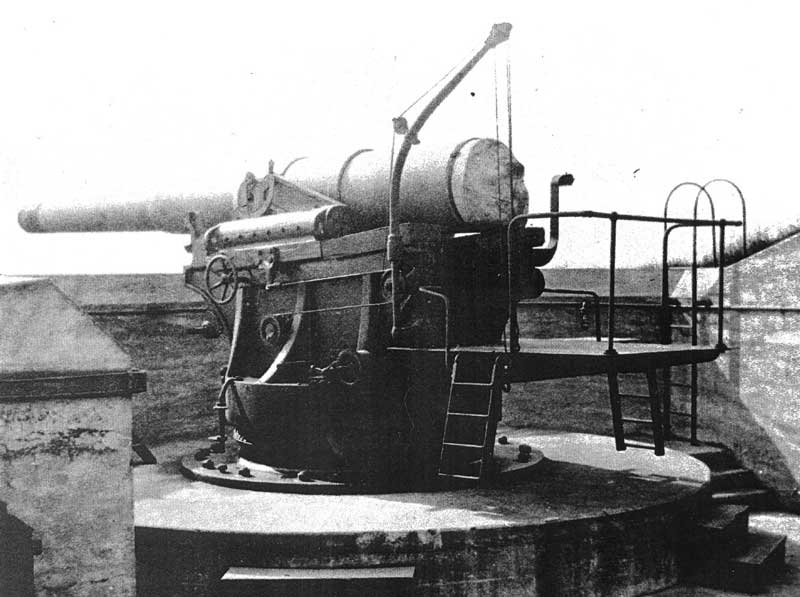
8-inch M1888
The 8-inch gun M1888 (203 mm) was a U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps gun, initially deployed 1898–1908 in about 75 fixed emplacements, usually on a disappearing carriage. During World War I, 37 or 47 of these weapons (references vary) were removed from fixed emplacements or from storage to create a railway gun version, the 8-inch Gun M1888MIA1 Barbette carriage M1918 on railway car M1918MI, converted from the fixed coast defense mountings and used during World War I and World War II. History The M1888 gun was a coastal artillery gun initially deployed as part of the Endicott system of fortifications. The first nine were deployed on the M1892 barbette carriage in 1898, but the improved M1894 and M1896 disappearing carriages soon became available, and approximately 64 additional weapons were deployed on these carriages by 1908. An "emergency" converted Rodman carriage was also used during the Spanish–American War in 1898 to quickly arm 21 emplacements with the moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandy Hook Proving Ground
The Sandy Hook Proving Ground was a military facility along the Atlantic coast of New Jersey established by the Secretary of War on August 7, 1874, to serve as the United States Army's first proving ground for the testing of ordnance and materiel. The facility was located at Sandy Hook, a narrow coastal spit of land, approximately in length and 0.5 miles (varying between 0.1 and 1 miles) wide, in Middletown Township in Monmouth County. The facility was operated in conjunction with the adjoining Fort Hancock. Essentially abandoned in 1919 for a larger facility, the area was left to degrade and most of the structures still remain today. The proving ground and parts of Fort Hancock are now property of the National Park Service and mostly closed to the public. Background The Civil War, just ten years earlier, had introduced several new innovations in weaponry. Rifled cannon fired pointed-nosed projectiles farther and faster than cannonballs and ironclad warships with mounted guns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QF 4
QF may stand for: * Qantas, an airline of Australia (IATA code QF) * Qatar Foundation, a private, chartered, non-profit organization in the state of Qatar * Quality factor, in physics and engineering, a measure of the "quality" of a resonant system * Quick-firing gun, a sort of artillery piece * Quiverfull, a movement of Christians who eschew all forms of birth control * A gun breech that uses metallic cartridges (see British ordnance terms#QF) * Quds Force The Quds Force ( fa, نیروی قدس, niru-ye qods, Jerusalem Force) is one of five branches of Iran's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) specializing in unconventional warfare and military intelligence operations. U.S. Army's Iraq War ... an expeditionary warfare unit of IRGC {{disambig fr:QF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence , image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg , image_size = 300px , caption = (clockwise from top left) , date = April 21 – August 13, 1898() , place = , casus = , result = American victory *Treaty of Paris (1898), Treaty of Paris of 1898 *Founding of the First Philippine Republic and beginning of the Philippine–American War * German–Spanish Treaty (1899), Spain sells to Germany the last colonies in the Pacific in 1899 and end of the Spanish Empire in Spanish colonization of the Americas, America and Asia. , territory = Spain relinquishes sovereignty over Cuba; cedes Puerto Rico, Guam and the Philippine Islands to the United States. $20 million paid to Spain by the United States for infrastructure owned by Spain. , combatant1 = United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |