|
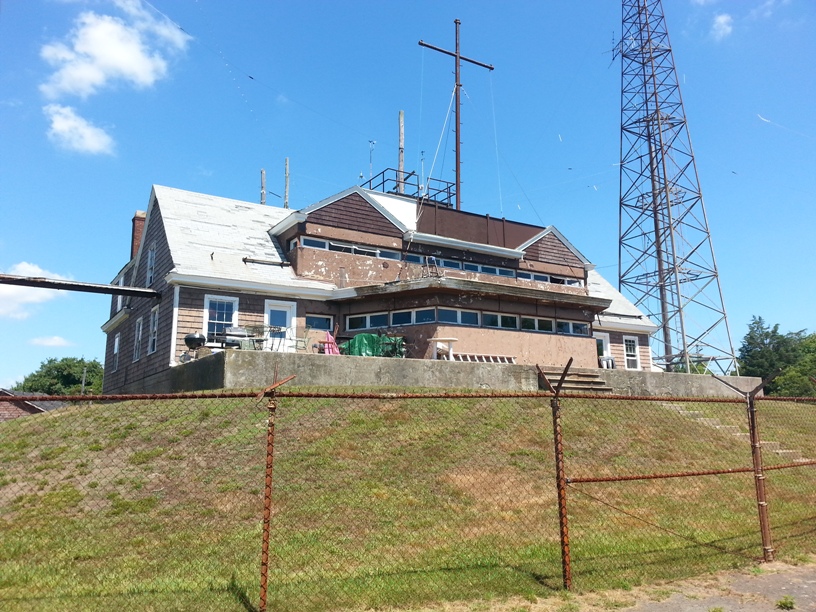
Fort Getty
Fort Getty is a town park in Jamestown, Rhode Island, on Conanicut Island in Narragansett Bay. From 1900 through World War II it was a military fort. The Town of Jamestown later received the property and opened it as a park, primarily a campground. History Fort Getty's construction began in 1901 to defend the West Passage of Narragansett Bay as part of the Coast Defenses of Narragansett Bay (renamed Harbor Defenses in 1925). The fort was named for Colonel George W. Getty, who had a distinguished career in the Mexican–American War, American Civil War, and afterward. The fort's three gun batteries were completed by 1905 but for some reason were not accepted until 1910. They were Battery Tousard with three 12-inch M1900 guns (305 mm) on disappearing carriages, Battery House with two 6-inch M1900 guns (152 mm) on pedestal mounts, and Battery Whiting with two 3-inch M1903 guns (76 mm) on pedestal mounts. Battery Tousard was named for Louis de Tousard, an engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disappearing Gun
A disappearing gun, a gun mounted on a ''disappearing carriage'', is an obsolete type of artillery which enabled a gun to hide from direct fire and observation. The overwhelming majority of carriage designs enabled the gun to rotate backwards and down behind a parapet, or into a pit protected by a wall, after it was fired; a small number were simply barbette mounts on a retractable platform. Either way, retraction lowered the gun from view and direct fire by the enemy while it was being reloaded. It also made reloading easier, since it lowered the breech to a level just above the loading platform, and shells could be rolled right up to the open breech for loading and ramming. Other benefits over non-disappearing types were a higher rate of repetitive fire and less fatigue for the gun crew. Some disappearing carriages were complicated mechanisms, protection from aircraft observation and attack was difficult, and almost all restricted the elevation of the gun. With a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
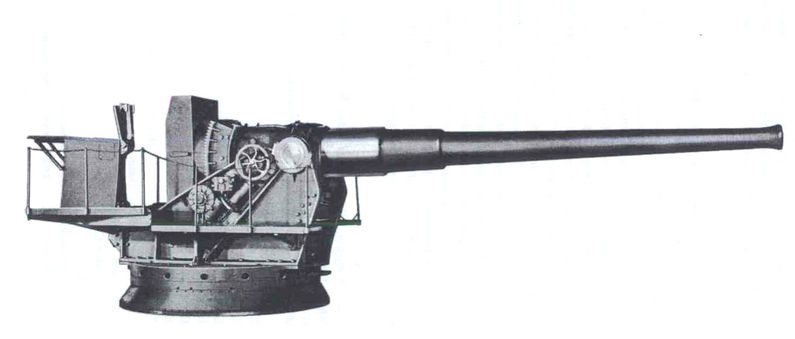
3-inch Gun M1903
The 3-inch gun M1903 and its predecessors the M1898 and M1902 were rapid fire breech-loading artillery guns with a 360-degree traverse. In some references they are called "15-pounders" due to their projectile weight. They were originally emplaced from 1899 to 1917 and served until shortly after World War II. These 3-inch guns were placed to provide fire to protect underwater mines and nets against minesweepers, and also to protect against motor torpedo boats. In some documentation they are called "mine defense guns". The 3-inch guns were mounted on pedestal mounts (or a retractable "masking parapet" mount for the M1898) that bolted into a concrete emplacement that provided cover and safety for the gun's crew. History The 3-inch mine defense guns were part of a comprehensive plan of new fortifications specified by the Board of Fortifications of 1885. The new forts initially included guns up to 12-inch (305 mm) on disappearing carriages, to conceal the fort from obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seacoast Defense In The United States
Seacoast defense was a major concern for the United States from its independence until World War II. Before Military aviation, airplanes, many of America's enemies could only reach it from the sea, making coastal forts an economical alternative to Standing army, standing armies or a large navy. After the 1940s, it was recognized that fixed fortifications were obsolete and ineffective against aircraft and missiles. However, in prior eras foreign fleets were a realistic threat, and substantial fortifications were built at key locations, especially protecting major harbors. The defenses heavily depended on fortifications but also included Submarine mines in United States harbor defense, submarine minefields, nets and boom (navigational barrier), booms, ships, and airplanes. Therefore, all of the armed forces participated in seacoast defense, but the United States Army Corps of Engineers, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers played the central role in constructing fixed defenses. Designs evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Island (Rhode Island)
Dutch Island is an island lying west of Conanicut Island at an entrance to Narragansett Bay in Rhode Island, United States. It is part of the town of Jamestown, Rhode Island, and has a land area of 0.4156 km² (102.7 acres). It was uninhabited as of the United States Census, 2000. The island was fortified from the American Civil War through World War II and was known as Fort Greble from 1898 to 1947. History Dutch Island's Indian name was ''Quotenis'' or ''Quetenesse''. Abraham Pietersen van Deusen of the Dutch West India Company established a trading post on the island around 1636 to trade with the Narragansett Indians, trading Dutch goods, cloths, implements, and liquors for the Indians' furs, fish, and venison. Several years later, the Dutch built Fort Ninigret in Charlestown. In 1654, English colonists purchased the island from the Indians. In 1825, the federal government acquired at the southern end of the island, and Dutch Island Light was established on January 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner-of-war Camp
A prisoner-of-war camp (often abbreviated as POW camp) is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured by a belligerent power in time of war. There are significant differences among POW camps, internment camps, and military prisons. Purpose-built prisoner-of-war camps appeared at Norman Cross in England in 1797 during the French Revolutionary Wars and HM Prison Dartmoor, constructed during the Napoleonic Wars, and they have been in use in all the main conflicts of the last 200 years. The main camps are used for marines, sailors, soldiers, and more recently, airmen of an enemy power who have been captured by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. Civilians, such as Merchant navy, merchant mariners and war correspondents, have also been imprisoned in some conflicts. With the adoption of the Geneva Convention on Prisoners of War (1929), Geneva Convention on the Prisoners of War in 1929, later superseded by the Third Geneva Convention, prisoner-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Burnside
Beavertail State Park is a public recreation area encompassing at the southern end of Conanicut Island in Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island. The state park's main attraction is the active Beavertail Lighthouse, the current tower of which dates from 1856. During World War II, the park area was part of Fort Burnside, one of several coastal fortifications designed to protect Narragansett Bay. The park's scenic shoreline offers hiking, picnicking, and saltwater fishing. History Lighthouse A 58-foot wooden tower built in 1749, under the direction of architect Peter Harrison of Newport, burned down in 1753. It was replaced by a fieldstone tower which was in use until 1856, when the present tower and keeper's quarters were completed. The assistant keeper's house, which was built in 1898, now houses the Beavertail Lighthouse Museum. Coastal fortifications In 1776, during the American Revolution, the Beaver Tail Fort was built in conjunction with the Conanicut Battery near Beaver Head. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Varnum
Camp Varnum is a Rhode Island Army National Guard training facility in the Boston Neck area of Narragansett, Rhode Island. During World War II it was Fort Varnum, a coastal defense fort. History Fort Varnum was built as part of a general modernization of US coast defenses begun in 1940 with the outbreak of war in Europe and the Fall of France. The fort is named for General James Mitchell Varnum of the Revolutionary War. It was built to relocate previously-emplaced weapons to a more useful location nearer the entrance to Narragansett Bay. The fort was sited to reinforce new 6-inch gun batteries at Fort Greene in Point Judith and Fort Burnside in Jamestown. Berhow, p. 205 The fort was intended to protect the West Passage of Narragansett Bay as part of the Harbor Defenses of Narragansett Bay. Fort Varnum's main armament was Battery House, two 6-inch M1900 guns on pedestal mounts, completed in 1942. The battery was a relocation of Battery House at Fort Getty in Jamestown. Two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Greene (Narragansett, Rhode Island)
Fort Greene is a United States Army Reserve installation in the Point Judith area of Narragansett, Rhode Island. During World War II this was a coastal defense fort, and together with Fort Church in Little Compton, it superseded all previous heavy gun defenses in the Harbor Defenses of Narragansett Bay. It is named for General Nathanael Greene of the Revolutionary War, who was born in Rhode Island. History Fort Greene was built as part of a general modernization of US coast defenses, begun in 1940 with the outbreak of war in Europe and the Fall of France. The goal was to replace all previous heavy weapons, most of which were over 35 years old, with long-range ex-Navy 16"/50 caliber Mark 2 guns. Lighter weapons would be replaced by 6-inch guns on high-angle shielded barbette carriages. Ammunition magazines and the 16-inch guns would be in casemated bunkers to protect against air attack. The fort was intended to protect the approaches to Narragansett Bay as part of the Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Church (Rhode Island)
Fort Church was a World War II United States Army coastal defence and fortification, coastal defense fort in Little Compton, Rhode Island. Together with Fort Greene (Rhode Island), Fort Greene near Point Judith, it superseded all previous heavy gun defenses in the Harbor Defenses of Narragansett Bay. History Fort Church was built as part of a general modernization of US coast defenses that began in 1940 with the outbreak of war in Europe and the Fall of France. The fort was named for Colonel Benjamin Church (ranger), Benjamin Church (1639–1718), considered a forerunner of the United States Army Rangers and buried in Little Compton. The goal was to replace all previous heavy weapons, many of which were over 35 years old, with long-range 16"/50 caliber Mark 2 guns. Lighter weapons would be replaced by 6-inch gun M1, 6-inch guns on high-angle shielded barbette carriages. Ammunition magazine (artillery), magazines and the 16-inch guns would be in casemated bunkers to protect agai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Greble (Rhode Island)
Dutch Island is an island lying west of Conanicut Island at an entrance to Narragansett Bay in Rhode Island, United States. It is part of the town of Jamestown, Rhode Island, and has a land area of 0.4156 km² (102.7 acres). It was uninhabited as of the United States Census, 2000. The island was fortified from the American Civil War through World War II and was known as Fort Greble from 1898 to 1947. History Dutch Island's Indian name was ''Quotenis'' or ''Quetenesse''. Abraham Pietersen van Deusen of the Dutch West India Company established a trading post on the island around 1636 to trade with the Narragansett Indians, trading Dutch goods, cloths, implements, and liquors for the Indians' furs, fish, and venison. Several years later, the Dutch built Fort Ninigret in Charlestown. In 1654, English colonists purchased the island from the Indians. In 1825, the federal government acquired at the southern end of the island, and Dutch Island Light was established on January 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Gun_on_Moncrieff_disappearing_mount%2C_at_Scaur_Hill_Fort%2C_Bermuda.jpg)