|
Forster, South Australia
Forster is a locality in the Murraylands region of South Australia. It lies on the inside of a bend on the east/left bank of the Murray River north of Walker Flat. Forster previously had a Methodist Church in the locality. Reverend Clem Hawke (later father of Prime Minister Bob Hawke) was Methodist home missionary there in 1919. It also had a Lutheran Church Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol .... The original church building built in 1904 was burnt down in 1920 and replaced in 1921. References Towns in South Australia {{SouthAustralia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelaide
Adelaide ( ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater Adelaide (including the Adelaide Hills) or the Adelaide city centre. The demonym ''Adelaidean'' is used to denote the city and the residents of Adelaide. The Native title in Australia#Traditional owner, Traditional Owners of the Adelaide region are the Kaurna people. The area of the city centre and surrounding parklands is called ' in the Kaurna language. Adelaide is situated on the Adelaide Plains north of the Fleurieu Peninsula, between the Gulf St Vincent in the west and the Mount Lofty Ranges in the east. Its metropolitan area extends from the coast to the Adelaide Hills, foothills of the Mount Lofty Ranges, and stretches from Gawler in the north to Sellicks Beach in the south. Named in honour of Queen Adelaide, the city was founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral District Of Chaffey
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office. Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated since the 17th century. Elections may fill offices in the legislature, sometimes in the executive and judiciary, and for regional and local government. This process is also used in many other private and business organisations, from clubs to voluntary associations and corporations. The global use of elections as a tool for selecting representatives in modern representative democracies is in contrast with the practice in the democratic archetype, ancient Athens, where the elections were considered an oligarchic institution and most political offices were filled using sortition, also known as allotment, by which officeholders were chosen by lot. Electoral reform describes the process of introducing fair electoral systems where they a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division Of Barker
The Division of Barker is an Divisions of the Australian House of Representatives, Australian Electoral Division in the south-east of South Australia. The division was established on 2 October 1903, when South Australia's original Division of South Australia, single multi-member division was split into seven single-member divisions. It is named for Collet Barker, an early explorer of the region at the mouth of the Murray River. The 63,886 km² seat currently stretches from Morgan, South Australia, Morgan in the north to Port MacDonnell, South Australia, Port MacDonnell in the south, taking in the Murray Mallee, the Riverland, the Murraylands and most of the Barossa Valley, and includes the towns of Barmera, South Australia, Barmera, Berri, South Australia, Berri, Bordertown, South Australia, Bordertown, Coonawarra, South Australia, Coonawarra, Keith, South Australia, Keith, Kingston SE, South Australia, Kingston SE, Loxton, South Australia, Loxton, Lucindale, South Australia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nildottie, South Australia
Nildottie is a locality in the Australian state of South Australia located on the east side of the Murray River about east of the state capital of Adelaide and about north-east of the municipal seat in Mannum. Nildottie's boundaries were created on 27 March 2003 for the "long established name" and include the sites of the Kroehns Landing Shack Site and Scrubby Flat Shack Site. On 22 December 2011, Nildottie was enlarged by the addition of land on its northern side after the locality of Greenways Landing was abolished following a request from residents and local government. The name is derived from the Aboriginal word 'ngurltartang', which means 'smoke signal hill'. The 2016 Australian census which was conducted in August 2016 reports that Nildottie had 189 people living within its boundaries. Nildottie is located within the federal division of Barker, the state electoral district of Chaffey and the local government area of the Mid Murray Council The Mid Murray Council ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walker Flat, South Australia
Walker Flat (previously Walkers Flat) is a small town on the Murray River in South Australia. It is one of the crossings of the river by cable ferry. The school opened in 1948 but has since closed. Walker Flat is located approximately from the Adelaide city centre. The Ankara youth camp owned by the Seventh-day Adventist Church is on the bank of the river near the ferry. See also *List of crossings of the Murray River The Murray River in south-eastern Australia has been a significant barrier to land-based travel and trade. This article lists and briefly describes all of the recognised crossing points. Many of these had also developed as river ports for trans ... Notes External links Towns in South Australia Murray River {{SouthAustralia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
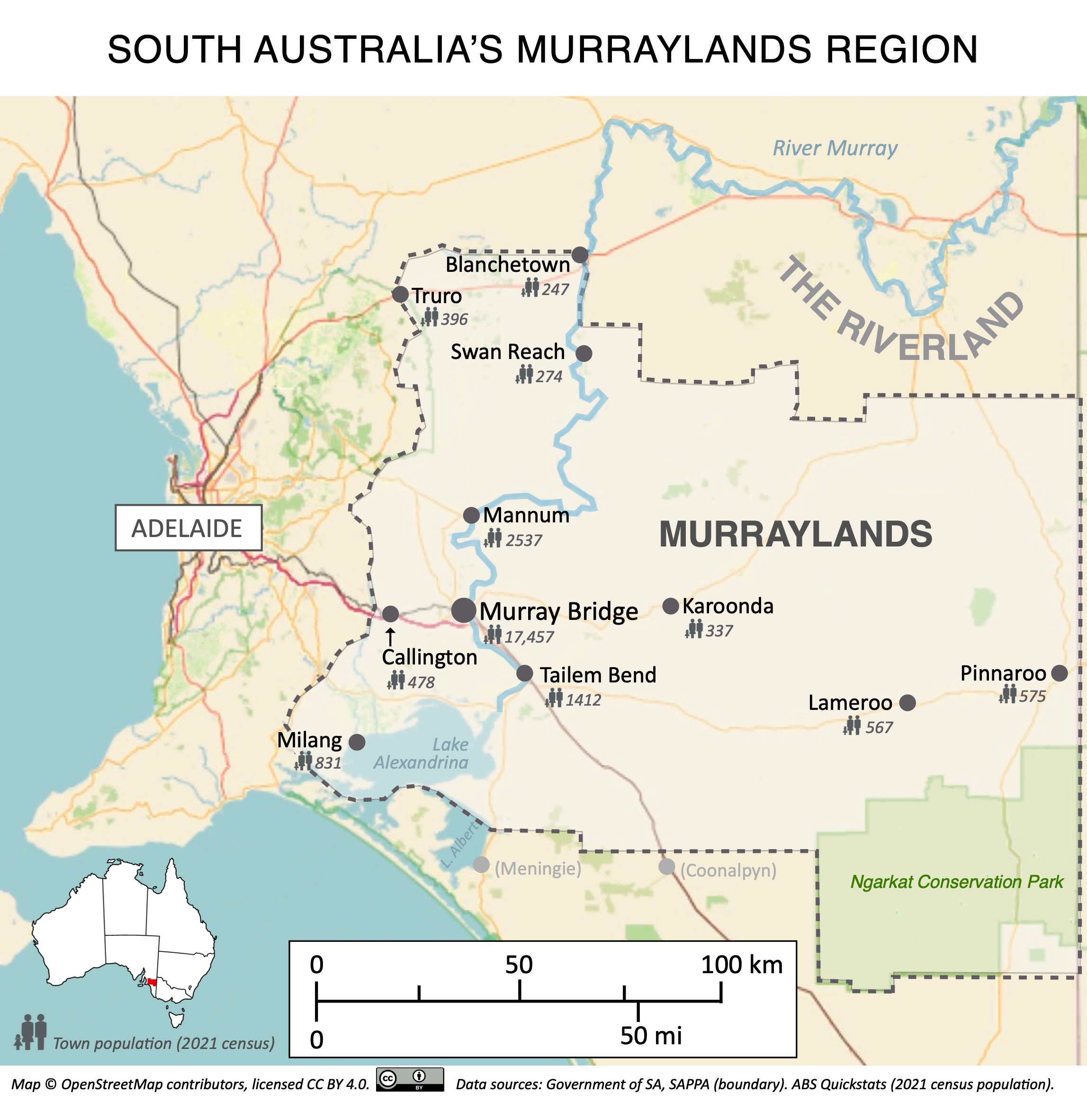
Murraylands
The Murraylands is a geographical region of the Australian state of South Australia (SA); its name reflects that of the river running through it. Lying due east of South Australia's capital city, Adelaide, it extends from the eastern slopes of the Mount Lofty Ranges to the border with the state of Victoria, a distance of about . The north-to-south distance is about . The region's economy is centred on agriculture (especially vegetables, grains and livestock), and tourism, especially along its frontage of the River Murray. The main towns in the region, in order of population at the 2016 census, are:A few kilometres outside the boundaries are Coonalpyn in the south and Meningie in the south-west, with populations of 1118 and 313 respectively; they are not included in this article. * Murray Bridge (16,560) * Tailem Bend (1660) * Mannum (2640) * Milang (880) * Lameroo (850) * Pinnaroo (710) * Callington (610) * Truro (550) * Karoonda (510) * Blanchetown (310) * Swan Rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, and second smallest state by population. It has a total of 1.8 million people. Its population is the second most highly centralised in Australia, after Western Australia, with more than 77 percent of South Australians living in the capital Adelaide, or its environs. Other population centres in the state are relatively small; Mount Gambier, the second-largest centre, has a population of 33,233. South Australia shares borders with all of the other mainland states, as well as the Northern Territory; it is bordered to the west by Western Australia, to the north by the Northern Territory, to the north-east by Queensland, to the east by New South Wales, to the south-east by Victoria, and to the south by the Great Australian B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murray River
The Murray River (in South Australia: River Murray) ( Ngarrindjeri: ''Millewa'', Yorta Yorta: ''Tongala'') is a river in Southeastern Australia. It is Australia's longest river at extent. Its tributaries include five of the next six longest rivers of Australia (the Murrumbidgee, Darling, Lachlan, Warrego and Paroo Rivers). Together with that of the Murray, the catchments of these rivers form the Murray–Darling basin, which covers about one-seventh the area of Australia. It is widely considered Australia's most important irrigated region. The Murray rises in the Australian Alps, draining the western side of Australia's highest mountains, then meanders northwest across Australia's inland plains, forming the border between the states of New South Wales and Victoria as it flows into South Australia. From an east–west direction it turns south at Morgan for its final , reaching the eastern edge of Lake Alexandrina, which fluctuates in salinity. The water then flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methodist Church
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related Christian denomination, denominations of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother Charles Wesley were also significant early leaders in the movement. They were named ''Methodists'' for "the methodical way in which they carried out their Christian faith". Methodism originated as a Christian revival, revival movement within the 18th-century Church of England and became a separate denomination after Wesley's death. The movement spread throughout the British Empire, the United States, and beyond because of vigorous Christian mission, missionary work, today claiming approximately 80 million adherents worldwide. Wesleyan theology, which is upheld by the Methodist churches, focuses on sanctification and the transforming effect of faith on the character of a Christians, Christian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clem Hawke
Arthur Clarence "Clem" Hawke (5 March 1898 – 23 December 1989) was the General Secretary of the Australian Labor Party in South Australia 1919–20, and a Congregationalist minister. He was the father of Bob Hawke, Prime Minister of Australia 1983–91; and brother of Bert Hawke, MHA for Burra Burra, South Australia 1924–27 and Premier of Western Australia 1953–59. History Born in Kapunda, South Australia, he was a son of miner James Renfrey Hawke (25 September 186213 September 1930) and his wife Elizabeth Ann Hawke (''née'' Pascoe; 31 December 186227 December 1946). Hawke left school at age 12 and worked at a number of jobs including blacksmithing while studying at the School of Mines in Kapunda. He trained for the ministry at Brighton under Dr. William George Torr and served as Methodist home missionary at Forster in the South Australian Riverland, Port Neill and Kalangadoo. In 1919 he became General Secretary of the Australian Labor Party in South Australia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bob Hawke
Robert James Lee Hawke (9 December 1929 – 16 May 2019) was an Australian politician and union organiser who served as the 23rd prime minister of Australia from 1983 to 1991, holding office as the leader of the Australian Labor Party (ALP). Previously he served as the president of the Australian Council of Trade Unions from 1969 to 1980 and president of the Labor Party national executive from 1973 to 1980. Hawke was born in Border Town, South Australia. He attended the University of Western Australia and went on to study at University College, Oxford as a Rhodes Scholar, during which time he set a world record for downing a yard of ale in 11 seconds. In 1956, Hawke joined the Australian Council of Trade Unions (ACTU) as a research officer. Having risen to become responsible for national wage case arbitration, he was elected as president of the ACTU in 1969, where he achieved a high public profile. In 1973, he was appointed as president of the Labor Party. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
