|
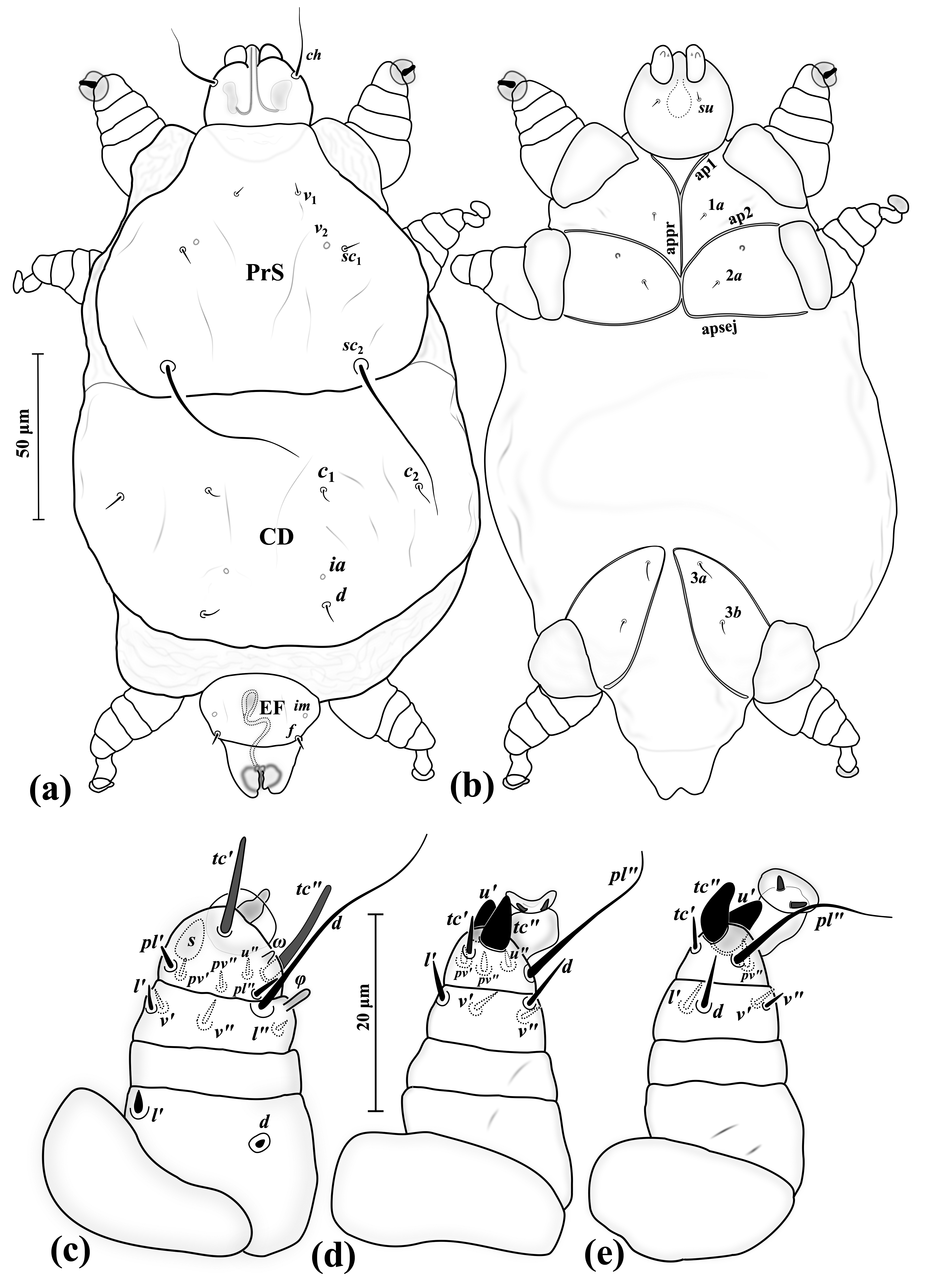
Forelia Liliacea
''Forelia'' is a genus of arachnids belonging to the family Pionidae. The genus was first described by Haller in 1882. The species of this genus are found in Eurasia and Northern America. Species: * '' Forelia liliacea'' * ''Forelia variegator ''Forelia'' is a genus of arachnids belonging to the family Pionidae. The genus was first described by Haller in 1882. The species of this genus are found in Eurasia and Northern America Northern America is the northernmost subregion of ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4659447 Trombidiformes Acari genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnids
Arachnida () is a Class (biology), class of joint-legged invertebrate animals (arthropods), in the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, opiliones, harvestmen, Solifugae, camel spiders, Amblypygi, whip spiders and Thelyphonida, vinegaroons. Almost all adult arachnids have eight Arthropod leg, legs, although the front pair of legs in some species has converted to a sensory function, while in other species, different appendages can grow large enough to take on the appearance of extra pairs of legs. The term is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''aráchnē'', 'spider'), from the myth of the hubristic human weaver Arachne, who was turned into a spider. Almost all Extant taxon, extant arachnids are terrestrial animal, terrestrial, living mainly on land. However, some inhabit freshwater environments and, with the exception of the pelagic zone, marine environments as well. They comprise over 100,000 named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pionidae
Pionidae is a family of prostigs in the order Trombidiformes. There are about 15 genera and at least 90 described species in Pionidae. Genera * '' Forelia'' Haller, 1882 * '' Huitfeldtia'' Thor, 1898 * '' Hydrochoreutes'' C. L. Koch, 1837 * '' Najadicola'' Piersig, 1897 * '' Nautarachna'' Moniez, 1888 * '' Neotiphys'' Habeeb, 1957 * '' Piona'' C. L. Koch, 1842 * '' Pionacercus'' Piersig, 1894 * '' Pionella'' Viets, 1937 * '' Pionopsis'' Piersig, 1894 * '' Pseudofeltria'' Soar, 1904 * '' Schminkea'' * ''Tiphys In Greek mythology, Tiphys (; Ancient Greek: Τῖφυς ''Tîphus'') was the helmsman of the Argonauts.Apollodorus1.9.16/ref> Family Tiphys was the Thespian son of Hagnias or of Phorbas of Elis and Hyrmine, daughter of Epeius. In the latter ac ...'' C. L. Koch, 1836 * '' Twinforksella'' * '' Wettina'' Piersig, 1892 References Further reading * * * * Trombidiformes Acari families {{trombidiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Description
A species description is a formal description of a newly discovered species, usually in the form of a scientific paper. Its purpose is to give a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been described previously or are related. In order for species to be validly described, they need to follow guidelines established over time. Zoological naming requires adherence to the ICZN code, plants, the ICN, viruses ICTV, and so on. The species description often contains photographs or other illustrations of type material along with a note on where they are deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million species have been identified and described, out of some 8.7 million that may actually exist. Millions more have become extinct throughout the existence of life on Earth. Naming process A name of a new species becomes valid (available in zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago and the Russian Far East to the east. The continental landmass is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and Africa to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two continents is a historical social construct, as many of their borders are over land; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data. Eurasia covers around , or around 36.2% of the Earth's total land area. It is also home to the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern America
Northern America is the northernmost subregion of North America. The boundaries may be drawn slightly differently. In one definition, it lies directly north of Middle America (including the Caribbean and Central America).Gonzalez, Joseph. 2004"Northern America: Land of Opportunity"(ch. 6). ''The Complete Idiot's Guide to Geography.'' () New York: Alpha Books; pp. 57–8 Northern America's land frontier with the rest of North America then coincides with the Mexico–United States border. Geopolitically, according to the United Nations' scheme of geographical regions and subregions, Northern America consists of Bermuda, Canada, Greenland, Saint Pierre and Miquelon and the United States (the contiguous United States and Alaska only, excluding Hawaii, Navassa Island, Puerto Rico, the United States Virgin Islands, and other minor U.S. Pacific territories). From a geographical perspective, Mexico would also be part of Northern America as it is on the same land as the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forelia Liliacea
''Forelia'' is a genus of arachnids belonging to the family Pionidae. The genus was first described by Haller in 1882. The species of this genus are found in Eurasia and Northern America. Species: * '' Forelia liliacea'' * ''Forelia variegator ''Forelia'' is a genus of arachnids belonging to the family Pionidae. The genus was first described by Haller in 1882. The species of this genus are found in Eurasia and Northern America Northern America is the northernmost subregion of ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4659447 Trombidiformes Acari genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forelia Variegator
''Forelia'' is a genus of arachnids belonging to the family Pionidae. The genus was first described by Haller in 1882. The species of this genus are found in Eurasia and Northern America Northern America is the northernmost subregion of North America. The boundaries may be drawn slightly differently. In one definition, it lies directly north of Middle America (including the Caribbean and Central America).Gonzalez, Joseph. 20 .... Species: * '' Forelia liliacea'' * '' Forelia variegator'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4659447 Trombidiformes Acari genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trombidiformes
The Trombidiformes are a large, diverse order of mites. Taxonomy In 1998, Trombidiformes was divided into the Sphaerolichida and the Prostigmata. The group has few synapomorphies by which it can be defined, unlike the other major group of acariform mites, Sarcoptiformes. Its members include medically important mites (such as ''Demodex'', the chiggers, and scrub-itch mites) and many agriculturally important species, including the spider mites (Tetranychidae). The superfamily Eriophyoidea, traditionally considered members of the Trombidiformes, have been found to be basal mites in genomic analyses, sister to the clade containing Sarcoptiformes and Trombidiformes. The 2004 classification retained the two suborders, comprising around 125 families and more than 22,000 described species. In the 2011 revised classification, the order now contains 151 families, 2235 genera and 25,821 species, and there were another 10 species with 24 species that present only as fossils. These 151 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |