|
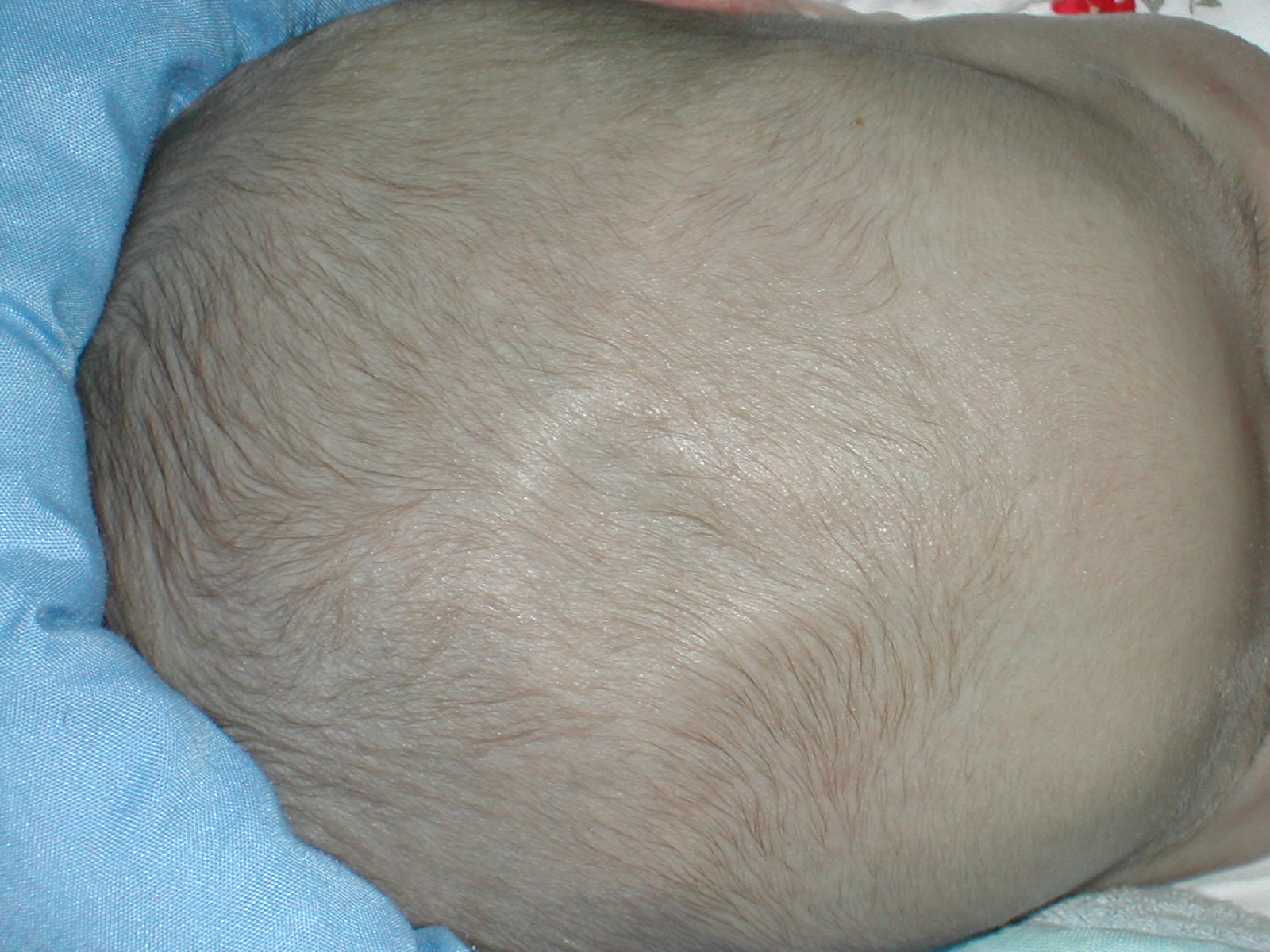
Fontanel
A fontanelle (or fontanel) (colloquially, soft spot) is an anatomical feature of the infant human skull comprising soft membranous gaps ( sutures) between the cranial bones that make up the calvaria of a fetus or an infant. Fontanelles allow for stretching and deformation of the neurocranium both during birth and later as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow. Premature complete ossification of the sutures is called craniosynostosis. After infancy, the anterior fontanelle is known as the bregma. Structure An infant's skull consists of five main bones: two frontal bones, two parietal bones, and one occipital bone. These are joined by fibrous sutures, which allow movement that facilitates childbirth and brain growth. * Posterior fontanelle is triangle-shaped. It lies at the junction between the sagittal suture and lambdoid suture. At birth, the skull features a small posterior fontanelle with an open area covered by a tough membrane, where the two p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Fontanelle
The anterior fontanelle (bregmatic fontanelle, frontal fontanelle) is the largest fontanelle, and is placed at the junction of the sagittal suture, coronal suture, and frontal suture; it is lozenge-shaped, and measures about 4 cm in its antero-posterior and 2.5 cm in its transverse diameter. The fontanelle allows the skull to deform during birth to ease its passage through the birth canal and for expansion of the brain after birth. The anterior fontanelle typically closes between the ages of 12 and 18 months. Clinical significance The anterior fontanelle is useful clinically. Examination of an infant includes palpating the anterior fontanelle. A sunken fontanelle indicates dehydration whereas a very tense or bulging anterior fontanelle indicates raised intracranial pressure Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium ( facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bregma
The bregma is the anatomical point on the skull at which the coronal suture is intersected perpendicularly by the sagittal suture. Structure The bregma is located at the intersection of the coronal suture and the sagittal suture on the superior middle portion of the calvaria. It is the point where the frontal bone and the two parietal bones meet. Development The bregma is known as the anterior fontanelle during infancy. The anterior fontanelle is membranous and closes in the first 18-36 months of life. Clinical significance Cleidocranial dysostosis In the birth defect cleidocranial dysostosis, the anterior fontanelle never closes to form the bregma. Surgical landmark The bregma is often used as a reference point for stereotactic surgery of the brain. It may be identified by blunt scraping of the surface of the skull and washing to make the meeting point of the sutures clearer. Neonatal examination Examination of an infant includes palpating the anterior fontanell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Fontanelle
The posterior fontanelle (lambdoid fontanelle, occipital fontanelle) is a gap between bones in the human skull (known as fontanelle), triangular in form and situated at the junction of the sagittal suture and lambdoidal suture. It generally closes in 6–8 weeks from birth. The cranial point in adults corresponding the fontanelle is called 'lambda' A delay in closure is associated with congenital hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as .... See also * Lambda (anatomy) References Skull {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleidocranial Dysostosis
Cleidocranial dysostosis (CCD), also called cleidocranial dysplasia, is a birth defect that mostly affects the bones and teeth. The collarbones are typically either poorly developed or absent, which allows the shoulders to be brought close together. The front of the skull often does not close until later, and those affected are often shorter than average. Other symptoms may include a prominent forehead, wide set eyes, abnormal teeth, and a flat nose. Symptoms vary among people; however, intelligence is typically unaffected. The condition is either inherited from a person's parents or occurs as a new mutation. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. It is due to a defect in the RUNX2 gene which is involved in bone formation. Diagnosis is suspected based on symptoms and X-rays with confirmation by genetic testing. Other conditions that can produce similar symptoms include mandibuloacral dysplasia, pyknodysostosis, osteogenesis imperfecta, and Hajdu-Cheney syndrome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietal Bone
The parietal bones () are two bones in the skull which, when joined at a fibrous joint, form the sides and roof of the cranium. In humans, each bone is roughly quadrilateral in form, and has two surfaces, four borders, and four angles. It is named from the Latin ''paries'' (''-ietis''), wall. Surfaces External The external surface ig. 1is convex, smooth, and marked near the center by an eminence, the parietal eminence (''tuber parietale''), which indicates the point where ossification commenced. Crossing the middle of the bone in an arched direction are two curved lines, the superior and inferior temporal lines; the former gives attachment to the temporal fascia, and the latter indicates the upper limit of the muscular origin of the temporal muscle. Above these lines the bone is covered by a tough layer of fibrous tissue – the epicranial aponeurosis; below them it forms part of the temporal fossa, and affords attachment to the temporal muscle. At the back part and clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infant
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of other organisms. A newborn is, in colloquial use, an infant who is only hours, days, or up to one month old. In medical contexts, a newborn or neonate (from Latin, ''neonatus'', newborn) is an infant in the first 28 days after birth; the term applies to premature, full term, and postmature infants. Before birth, the offspring is called a fetus. The term ''infant'' is typically applied to very young children under one year of age; however, definitions may vary and may include children up to two years of age. When a human child learns to walk, they are called a toddler instead. Other uses In British English, an '' infant school'' is for children aged between four and seven. As a legal term, ''infancy'' is mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracranial Pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adult. The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF. Changes in ICP are attributed to volume changes in one or more of the constituents contained in the cranium. CSF pressure has been shown to be influenced by abrupt changes in intrathoracic pressure during coughing (which is induced by contraction of the diaphragm and abdominal wall muscles, the latter of which also increases intra-abdominal pressure), the valsalva maneuver, and communication with the vasculature (venous and arterial systems). Intracranial hypertension (IH), also called increased ICP (IICP) or raised intracranial pressure (RICP), is elevation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g. distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. Its aim is usually to find a source of disease or to exclude pathology. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequencies which are significantly higher than the range of human hearing (>20,000 Hz). Ultrasonic images, also known as sonograms, are created by sending pulses of ultrasound into tissue usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calvaria (skull)
The calvaria is the top part of the skull. It is the upper part of the neurocranium and covers the cranial cavity containing the brain. It forms the main component of the skull roof. The calvaria is made up of the superior portions of the frontal bone, occipital bone, and parietal bones. In the human skull, the sutures between the bones normally remain flexible during the first few years of postnatal development, and fontanelles are palpable. Premature complete ossification of these sutures is called craniosynostosis. In Latin, the word ''calvaria'' is used as a feminine noun with plural ''calvariae''; however, many medical texts list the word as ''calvarium'', a neuter Latin noun with plural ''calvaria''. Structure The outer surface of the skull possesses a number of landmarks. The point at which the frontal bone and the two parietal bones meet is known as "Bregma". The point at which the two parietal bones and the occipital bone meet is known as "Lambda". Not only do the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda (anatomy)
The lambda is the meeting point of the sagittal suture and the lambdoid suture. This is also the point of the occipital angle. It is named after the Greek letter lambda. Structure The lambda is the meeting point of the sagittal suture and the lambdoid suture. It may be the exact midpoint of the lambdoid suture, but often deviates slightly from the midline. This is also the point of the occipital angle. Development In the foetus, the lambda is membranous, and is called the posterior fontanelle. Etymology The lambda is named after the Greek letter lambda Lambda (}, ''lám(b)da'') is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed . Lambda gave ris ..., whose lowercase form (λ) resembles the junction formed by the sutures. References External links * Skull {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |