|
Fomepizole
Fomepizole, also known as 4-methylpyrazole, is a medication used to treat methanol poisoning, methanol and ethylene glycol poisoning. It may be used alone or together with hemodialysis. It is given by intravenous, injection into a vein. Common side effects include headache, nausea, sleepiness, and unsteadiness. It is unclear if use during pregnancy is safe for the baby. Fomepizole works by blocking the enzyme that converts methanol and ethylene glycol to their toxic breakdown products. Fomepizole was approved for medical use in the United States in 1997. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical use Fomepizole is used to treat ethylene glycol and methanol poisoning. It acts to inhibit the breakdown of these toxins into their active toxic metabolites. Fomepizole is a competitive inhibition, competitive inhibitor of the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase, found in the liver. This enzyme plays a key role in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene Glycol Poisoning
Ethylene glycol poisoning is poisoning caused by drinking ethylene glycol. Early symptoms include Substance intoxication, intoxication, vomiting and abdominal pain. Later symptoms may include a decreased level of consciousness, headache, and seizures. Long term outcomes may include kidney failure and brain damage. Toxicity and death may occur after drinking even in a small amount as ethylene glycol is more toxic than other Diol, diols. Ethylene glycol is a colorless, odorless, sweet liquid, commonly found in antifreeze. It may be drunk accidentally or intentionally in a suicide attempt. When broken down by the body it results in glycolic acid and oxalic acid which cause most of the toxicity. The diagnosis may be suspected when calcium oxalate crystals are seen in the urine or when acidosis or an increased osmol gap is present in the blood. Diagnosis may be confirmed by measuring ethylene glycol levels in the blood; however, many hospitals do not have the ability to perform this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanol Poisoning
Methanol toxicity (also ''methanol poisoning'') is poisoning from methanol, characteristically via ingestion. Symptoms may include a decreased level of consciousness, poor or no coordination, hypothermia, vomiting, abdominal pain, and a specific smell on the breath. Decreased vision may start as early as twelve hours after exposure. Long-term outcomes may include blindness and kidney failure. Blindness may occur after drinking as little as 10mL; death may occur after drinking quantities over 15 mL (median 100mL, varies depending on body weight). Methanol poisoning most commonly occurs following the drinking of windshield washer fluid. This may be accidental or as part of an attempted suicide. Toxicity may also rarely occur through extensive skin exposure or breathing in fumes. When methanol is broken down by the body it results in formaldehyde, formic acid, and formate which cause much of the toxicity. The diagnosis may be suspected when there is acidosis or an increased osmol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both developed and developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the complementary list. Some medicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harm Minimization
Harm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of public health policies designed to lessen the negative social and/or physical consequences associated with various human behaviors, both legal and illegal. Harm reduction is used to decrease negative consequences of recreational drug use and sexual activity without requiring abstinence, recognizing that those unable or unwilling to stop can still make positive change to protect themselves and others. Harm reduction is most commonly applied to approaches that reduce adverse consequences from drug use, and harm reduction programs now operate across a range of services and in different regions of the world. As of 2020, some 86 countries had one or more programs using a harm reduction approach to substance use, primarily aimed at reducing blood-borne infections resulting from use of contaminated injecting equipment. Needle-exchange programmes reduce the likelihood of people who use heroin and other substances sharing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol Dehydrogenase
Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADH) () are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to NADH. In humans and many other animals, they serve to break down alcohols that otherwise are toxic, and they also participate in generation of useful aldehyde, ketone, or alcohol groups during biosynthesis of various metabolites. In yeast, plants, and many bacteria, some alcohol dehydrogenases catalyze the opposite reaction as part of fermentation to ensure a constant supply of NAD+. Evolution Genetic evidence from comparisons of multiple organisms showed that a glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase, identical to a class III alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH-3/ADH5), is presumed to be the ancestral enzyme for the entire ADH family. Early on in evolution, an effective method for eliminating both endogenous and exogenous formaldehyde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde (IUPAC systematic name ethanal) is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3 CHO, sometimes abbreviated by chemists as MeCHO (Me = methyl). It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the most important aldehydes, occurring widely in nature and being produced on a large scale in industry. Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants. It is also produced by the partial oxidation of ethanol by the liver enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase and is a contributing cause of hangover after alcohol consumption. Pathways of exposure include air, water, land, or groundwater, as well as drink and smoke. Consumption of disulfiram inhibits acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, the enzyme responsible for the metabolism of acetaldehyde, thereby causing it to build up in the body. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has listed acetaldehyde as a Group 1 carcinogen. Acetaldehyde is "one of the mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetaldehyde Dehydrogenase
Acetaldehyde dehydrogenases () are dehydrogenase enzymes which catalyze the conversion of acetaldehyde into acetic acid. The oxidation of acetaldehyde to acetate can be summarized as follows: Acetaldehyde + NAD+ + Coenzyme A ↔ Acetyl-CoA + NADH + H+ In humans, there are three known genes which encode this enzymatic activity, ALDH1A1, ALDH2, and the more recently discovered ALDH1B1 (also known as ALDH5). These enzymes are members of the larger class of aldehyde dehydrogenases. The CAS number for this type of the enzyme is 028-91-5 Structure Cysteine-302 is one of three consecutive Cys residues and is crucial to the enzyme's catalytic function. The residue is alkylated by iodoacetamide in both the cytosolic and mitochondrial isozymes, with modifications to Cys-302 indicative of catalytic activity with other residues. Furthermore, the preceding sequence Gln-Gly-Gln-Cys is conserved in both isozymes for both human and horse, which is consistent with Cys-302 being crucial to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
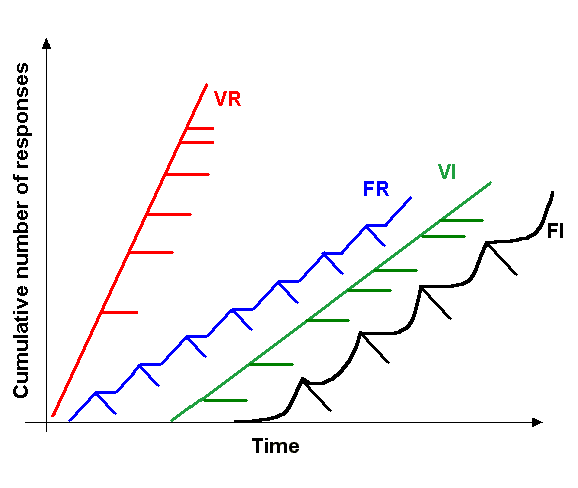
Reinforcement (psychology)
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Negati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disulfiram
Disulfiram is a medication used to support the treatment of chronic alcoholism by producing an acute sensitivity to ethanol (drinking alcohol). Disulfiram works by inhibiting the enzyme acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, causing many of the effects of a hangover to be felt immediately following alcohol consumption. Disulfiram plus alcohol, even small amounts, produces flushing, throbbing in the head and neck, a throbbing headache, respiratory difficulty, nausea, copious vomiting, sweating, thirst, chest pain, palpitation, dyspnea, hyperventilation, fast heart rate, low blood pressure, fainting, marked uneasiness, weakness, vertigo, blurred vision, and confusion. In severe reactions there may be respiratory depression, cardiovascular collapse, abnormal heart rhythms, heart attack, acute congestive heart failure, unconsciousness, convulsions, and death. In the body, alcohol is converted to acetaldehyde, which is then broken down by acetaldehyde dehydrogenase. When the dehydrogenase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consumpti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formic Acid
Formic acid (), systematically named methanoic acid, is the simplest carboxylic acid, and has the chemical formula HCOOH and structure . It is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in some ants. Esters, salts and the anion derived from formic acid are called formates. Industrially, formic acid is produced from methanol. Natural occurrence In nature, formic acid is found in most ants and in stingless bees of the genus ''Oxytrigona''. Wood ants from the genus ''Formica'' can spray formic acid on their prey or to defend the nest. The puss moth caterpillar (''Cerura vinula'') will spray it as well when threatened by predators. It is also found in the trichomes of stinging nettle (''Urtica dioica''). Apart from that, this acid is incorporated in many fruits such as pineapple (0.21mg per 100g), apple (2mg per 100g) and kiwi (1mg per 100g), as well as in many vegetables, namely onion (45mg per 100g), eggplant (1.34 mg per 100g) and, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compliance (medicine)
In medicine, patient compliance (also adherence, capacitance) describes the degree to which a patient correctly follows medical advice. Most commonly, it refers to medication or drug compliance, but it can also apply to other situations such as medical device use, self care, self-directed exercises, or therapy sessions. Both patient and health-care provider affect compliance, and a positive physician-patient relationship is the most important factor in improving compliance. Access to care plays a role in patient adherence, whereby greater wait times to access care contributing to greater absenteeism. The cost of prescription medication also plays a major role. Compliance can be confused with concordance, which is the process by which a patient and clinician make decisions together about treatment. Worldwide, non-compliance is a major obstacle to the effective delivery of health care. 2003 estimates from the World Health Organization indicated that only about 50% of patients with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |