|
Foley V Hill
''Foley v Hill'' (1848) 2 HLC 28, 9 ER 1002 is a judicial decision of the House of Lords in relation to the fundamental nature of a bank account. Together with '' Joachimson v Swiss Bank Corporation'' 9213 KB 110 it forms part of the foundational cases relating to English banking law and the nature of a bank's relationship with its customer in relation to the account. The case decided that a banker does not hold the sums in a bank account on trust for its customer. Instead the relationship between them is that of debtor and creditor. When the customer deposits money in the account it becomes the bank's money, and the bank's obligation to repay an equivalent sum (and any agreed interest) to the customer or the customer's order. The decision was crucial to the modern evolution of banking. Had the appellant's argument that the bank should be treated as a trustee succeeded then a bank would not be entitled to use the sums deposited with it for lending to other parties because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judicial Functions Of The House Of Lords
Whilst the House of Lords of the United Kingdom is the upper chamber of Parliament and has government ministers, it for many centuries had a judicial function. It functioned as a court of first instance for the trials of peers, for impeachments, and as a court of last resort in the United Kingdom and prior, the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of England. Appeals were technically not to the House of Lords, but rather to the King-in-Parliament. In 1876, the Appellate Jurisdiction Act devolved the appellate functions of the House to an Appellate Committee, composed of Lords of Appeal in Ordinary (informally referred to as Law Lords). They were then appointed by the Lord Chancellor in the same manner as other judges. During the 20th and early 21st century, the judicial functions were gradually removed. Its final trial of a peer was in 1935, and in 1948, the use of special courts for such trials was abolished. The procedure of impeachment became seen as obsolete. In 2009, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill In Equity
Equity is a particular body of law that was developed in the English Court of Chancery. Its general purpose is to provide a remedy for situations where the law is not flexible enough for the usual court system to deliver a fair resolution to a case. The concept of equity is deeply intertwined with its historical origins in the common law system used in England. However, equity is in some ways a separate system from common law: it has its own established rules and principles, and was historically administered by separate courts, called " courts of equity" or "courts of chancery". Equity exists in domestic law, both in civil law and in common law systems, and in international law. The tradition of equity begins in antiquity with the writings of Aristotle (''epieikeia'') and with Roman law (''aequitas''). Later, in civil law systems, equity was integrated in the legal rules, while in common law systems it became an independent body of law. Equity in common law jurisdictions (gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Lords Cases
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.Schoenauer, Norbert (2000). ''6,000 Years of Housing'' (rev. ed.) (New York: W.W. Norton & Company). Houses use a range of different roofing systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses may have doors or locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more bedrooms and bathrooms, a kitchen or cooking area, and a living room. A house may have a separate dining room, or the eating area may be integrated into another room. Some large houses in North America have a recreation room. In traditional agriculture-oriented societies, domestic animals such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Banking Case Law
English usually refers to: * English language * English people English may also refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England ** English national identity, an identity and common culture ** English language in England, a variant of the English language spoken in England * English languages (other) * English studies, the study of English language and literature * ''English'', an Amish term for non-Amish, regardless of ethnicity Individuals * English (surname), a list of notable people with the surname ''English'' * People with the given name ** English McConnell (1882–1928), Irish footballer ** English Fisher (1928–2011), American boxing coach ** English Gardner (b. 1992), American track and field sprinter Places United States * English, Indiana, a town * English, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * English, Brazoria County, Texas, an unincorporated community * Englis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devaynes V Noble
''Devaynes v Noble'' (1816) 35 ER 781, best known for the claim contained in ''Clayton's case'', created a rule, or more precisely common law presumption, in relation to the distribution of money from a bank account. The rule is based upon the deceptively simple notion of ''first-in, first-out'' to determine the effect of payments from an account, and normally applies in English Law in the absence of evidence of any other intention. Payments are presumed to be appropriated to debts in the order in which the debts are incurred. Facts Mr. Clayton had an account with a banking firm, Devaynes, Dawes, Noble, and Co, that was a partnership rather than a joint stock company as modern banks almost always are. The bank's partners were therefore personally liable for the debts of the bank. One of the partners, William Devaynes, died in 1809. The amount then due to Clayton was £1,717. After Mr. Devaynes' death, Clayton made further deposits with the bank and the surviving partners pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breach Of Fiduciary Responsibility
A fiduciary is a person who holds a legal or ethical relationship of trust with one or more other parties (person or group of persons). Typically, a fiduciary prudently takes care of money or other assets for another person. One party, for example, a corporate trust company or the trust department of a bank, acts in a fiduciary capacity to another party, who, for example, has entrusted funds to the fiduciary for safekeeping or investment. Likewise, financial advisers, financial planners, and asset managers, including managers of pension plans, endowments, and other tax-exempt assets, are considered fiduciaries under applicable statutes and laws. In a fiduciary relationship, one person, in a position of vulnerability, justifiably vests confidence, good faith, reliance, and trust in another whose aid, advice, or protection is sought in some matter... In such a relation, good conscience requires the fiduciary to act at all times for the sole benefit and interest of the one who trust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Cottenham LC
Charles Christopher Pepys, 1st Earl of Cottenham, (; 29 April 178129 April 1851) was an English lawyer, judge and politician. He was twice Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain. Background and education Cottenham was born in London, the second son of Sir William Pepys, 1st Baronet, a master in chancery, who was descended from John Pepys, of Cottenham, Cambridgeshire, a great-uncle of Samuel Pepys the diarist. Educated at Harrow School and Trinity College, Cambridge, Pepys was called to the bar of Lincoln's Inn in 1804. Legal and political career Cottenham's progress was slow practising at the Chancery Bar. Not until 22 years after his call was he made a King's Counsel. He sat in Parliament successively for Higham Ferrers and Malton, became Solicitor General in 1834 and Master of the Rolls in the same year. On the formation of Lord Melbourne's second administration in April 1835, the great seal was in commission for a time, but Cottenham, who had been a commissioner, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Wigram
Sir James Wigram, FRS (1793–1866) was an English barrister, politician and judge. Life He was the third son of Lady Eleanor and Sir Robert Wigram, 1st Baronet, and younger brother name of Sir Robert Fitzwygram, 2nd Baronet in 1832; another brother was Joseph Cotton Wigram. Born at his father's residence, Walthamstow House, Essex, on 5 November 1793, James was educated privately and at Trinity College, Cambridge, where he graduated B.A. in 1815, gained a fellowship two years later, and proceeded M.A. in 1818. Admitted a student of Lincoln's Inn on 18 June 1813, he was called to the bar there on 18 November 1819. In practice in the Court of Chancery, Wigram built up a career. In Michaelmas vacation 1834 he was made King's Counsel, and, in 1835 became a bencher of Lincoln's Inn. That year he also was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society. Supported by his wife's family interest, Wigram fought an election for Leominster on Tory principles in 1837, but was defeated at the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Pepys, 1st Earl Of Cottenham By Charles Robert Leslie Cropped
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "free man". The Old English descendant of this word was '' Ċearl'' or ''Ċeorl'', as the name of King Cearl of Mercia, that disappeared after the Norman conquest of England. The name was notably borne by Charlemagne (Charles the Great), and was at the time Latinized as ''Karolus'' (as in ''Vita Karoli Magni''), later also as '' Carolus''. Some Germanic languages, for example Dutch and German, have retained the word in two separate senses. In the particular case of Dutch, ''Karel'' refers to the given name, whereas the noun ''kerel'' means "a bloke, fellow, man". Etymology The name's etymology is a Common Germanic noun ''*karilaz'' meaning "free man", which survives in English as churl (< Old English ''ċeorl''), which developed its de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limitation Act 1623
The Limitation Act 1623 (21 Jac 1 c 16) was an Act of the Parliament of England. The whole Act was repealed by section 1(1) of, and Group 5 of Part I of Schedule 1 to, the Statute Law (Repeals) Act 1986. See also *Limitation Act Limitation Act is a stock short title used for legislation in Malaysia and the United Kingdom which relates to limitation of actions. The Bill for an Act with this short title may have been known as a Limitation Bill during its passage through P ... References * Halsbury's Statutes, Acts of the Parliament of England 1623 in law 1623 in England Statutes of limitations {{England-statute-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Account Of Profits
An account of profits (sometimes referred to as an ''accounting for profits'' or simply an ''accounting'') is a type of equitable remedy most commonly used in cases of breach of fiduciary duty. It is an action taken against a defendant to recover the profits taken as a result of the breach of duty, in order to prevent unjust enrichment. In conducting an account of profits, the plaintiff is treated as if they were conducting the business of the defendant, and made those profits which were attributable to the defendant's wrongful actions. This can be rather complex in practice, because the defendant's accounting records must be examined (sometimes by a forensic accountant) to determine what portion of his gross profits were derived to the wrongful act in question. As a result, mathematical exactness is not called for and reasonable approximation is acceptable. Historically an account was not an equitable remedy, but was an action at common law, and is therefore technically an instru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
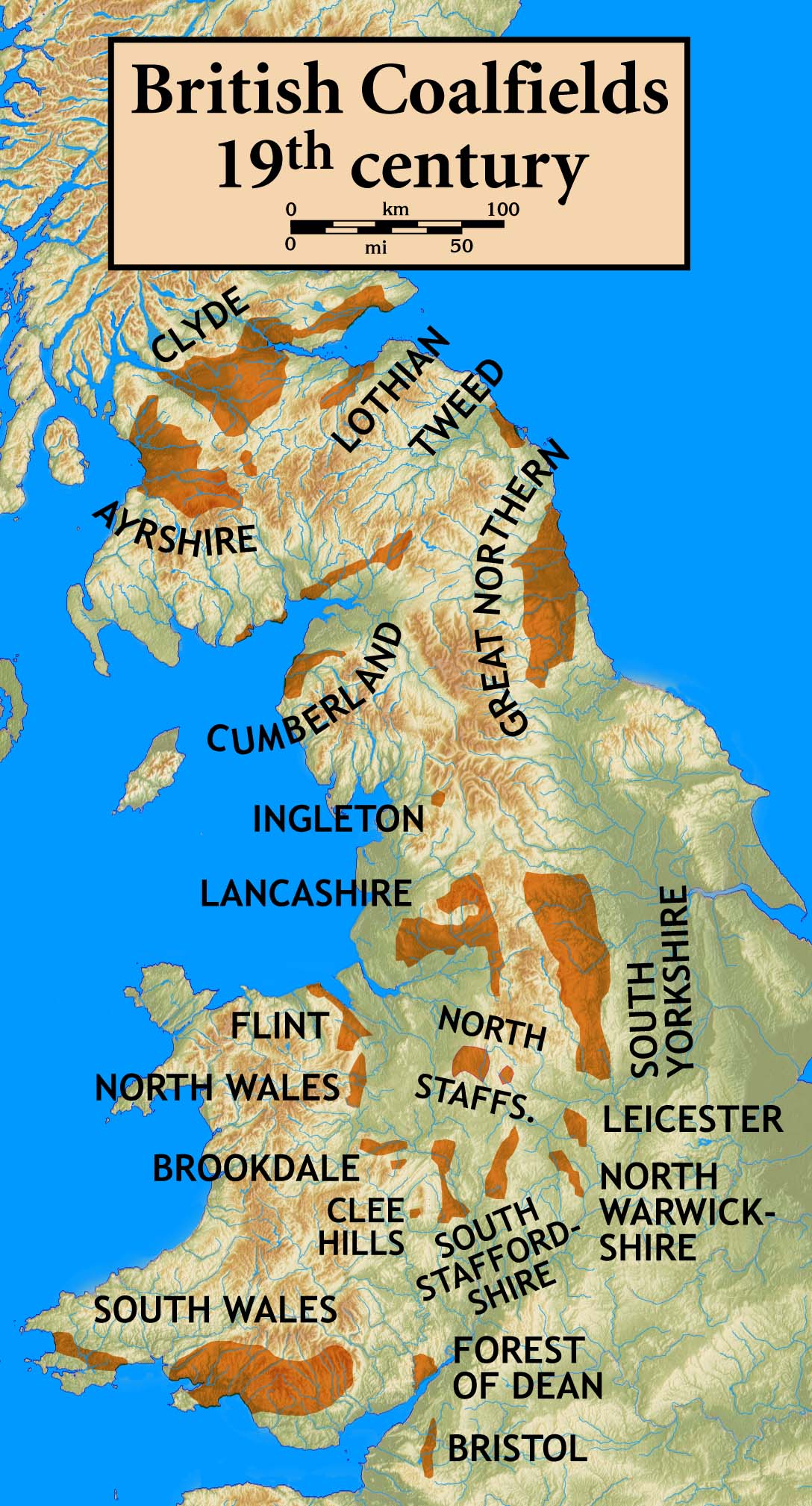
North Staffordshire Coalfield
The North Staffordshire Coalfield was a coalfield in Staffordshire, England, with an area of nearly , virtually all of it within the city of Stoke on Trent and the borough of Newcastle-under-Lyme, apart from three smaller coalfields, Shaffalong and Goldsitch Moss Coalfields near Leek and the Cheadle Coalfield. Coal mining in North Staffordshire began early in the 13th century, but the industry grew during the Industrial Revolution when coal mined in North Staffordshire was used in the local Potteries ceramics and iron industry (ironstone deposits were also found with the coal in certain areas). Before the First World War, 20,000 men worked in the industry and over 50 pits were in operation. After nationalisation in 1947, the industry was gradually reduced in size as smaller pits closed or merged with larger, more modern mines. The industry began its final decline after the 1984-85 miners' strike and the last deep mine, Silverdale, closed on Christmas Eve 1998. Geology Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |