|
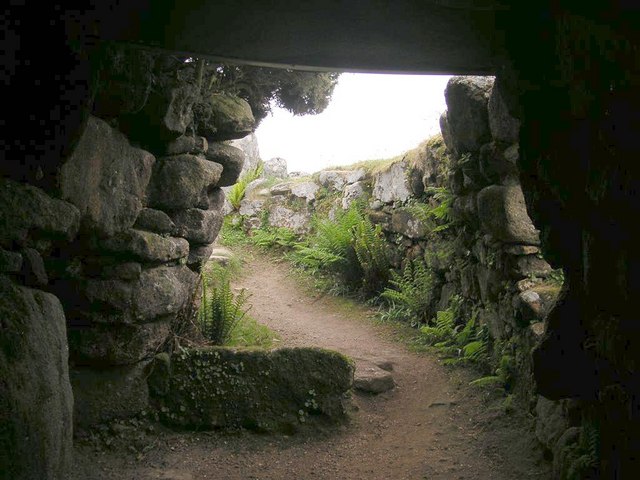
Fogou
A fogou or fougou (pronounced "foo-goo") is an underground, dry-stone structure found on Iron Age or Romano-British-defended settlement sites in Cornwall. The original purpose of a fogou is uncertain today. Colloquially called , , , giant holts, or holes in various dialects, fogous have similarities with souterrains or earth-houses of northern Europe and particularly Scotland, including Orkney. Fewer than 15 confirmed fogous have been found. Construction Fogous consist of a buried, usually corbelled stone wall, tapering at the top and capped by stone slabs. They were mainly constructed by excavating a sloping trench about wide and deep, lining it with drystone walling as stated, which was battered inwards and roofed with flat slabs; soil from excavation was heaped on top as at Pendeen Vau or incorporated in the rampart of the enclosure as at Halliggye Fogou, Trelowarren.Fox, Aileen (1973). ''South-West England 3500 BC – AD 600''. Pub. David & Charles. . p. 178. Functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halliggye Fogou
Halliggye Fogou is one of many fogous in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The site is under the guardianship of English Heritage, and managed by the Trelowarren Estate, where the fogou is located. Entry to the fogou is free but there is a charge to enter the rest of the Trelowarren Estate. The Halliggye Fogou consists of a long narrow tunnel leading to three sectioned chambers, and a window-like entrance which was dug in Victorian times by supposed treasure hunters (this has since been filled in). The complex of passages has a roof and walls of stone, and is the largest and best-preserved of several mysterious tunnels associated with Cornish Iron Age settlements. It was described by Sir Richard Vyvyan in his "Account of the ‘fogou’ or cave at Halligey, Trelowarren", in the ''Journal of the Royal Institution of Cornwall'' (1885, viii. 256–58) In 1861, J. T. Blight wrote a comprehensive description and drafted plans of the fogou in conjunction with Sir Richard Vyvyan, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carn Euny
, alternate_name = , image = CarnEuny1.jpg , alt = Fragments of stone round-houses , caption = Carn Euny ancient village , map_type = Southwest Cornwall , map_alt = , map_size = , location = Brane, Cornwall , region = , coordinates = , type = Ancient village , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = , material = , built = c. 200 BC , abandoned = c. 400 AD , epochs = Iron Age/Roman , cultures = Romano-British , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = , excavations = , archaeologists = , condition = Ruins , ownership = Cornwall Heritage Trust , public_access = Yes , website = , notes = Carn Euny (from kw, Karn Uni)Place-names in the Standard Written Form (SWF) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pendeen Vau
Pendeen Vau is a fogou on the Cornish coast of England, near the village of Pendeen. It is situated at Pendeen (Manor) farm, once the home of the renowned historian William Borlase William Borlase (2 February 169631 August 1772), Cornish antiquary, geologist and naturalist. From 1722, he was Rector of Ludgvan, Cornwall, where he died. He is remembered for his works ''The Antiquities of Cornwall'' (1754; 2nd ed., 1769) ... about half a mile from Pendeen Lighthouse. As the fogou is on private land, it is only accessible by asking permission at Pendeen Manor farm. Notes Archaeological sites in Cornwall Fogous {{Cornwall-archaeology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fougou
Fougou, Guinea is a town and sub-prefecture in the Dalaba Prefecture in the Mamou Region Mamou Region ( Pular: 𞤁𞤭𞥅𞤱𞤢𞤤 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤥𞤵𞤲) is located in central Guinea. It is bordered by the country of Sierra Leone and the Guinean regions of Faranah Region, Faranah, Labé, and Kindia. Administrative divis ... of northern Guinea. References {{coord, 11, 54, N, 12, 18, W, display=title, region:GN_type:city_source:GNS-enwiki Populated places in the Mamou Region Sub-prefectures of Guinea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
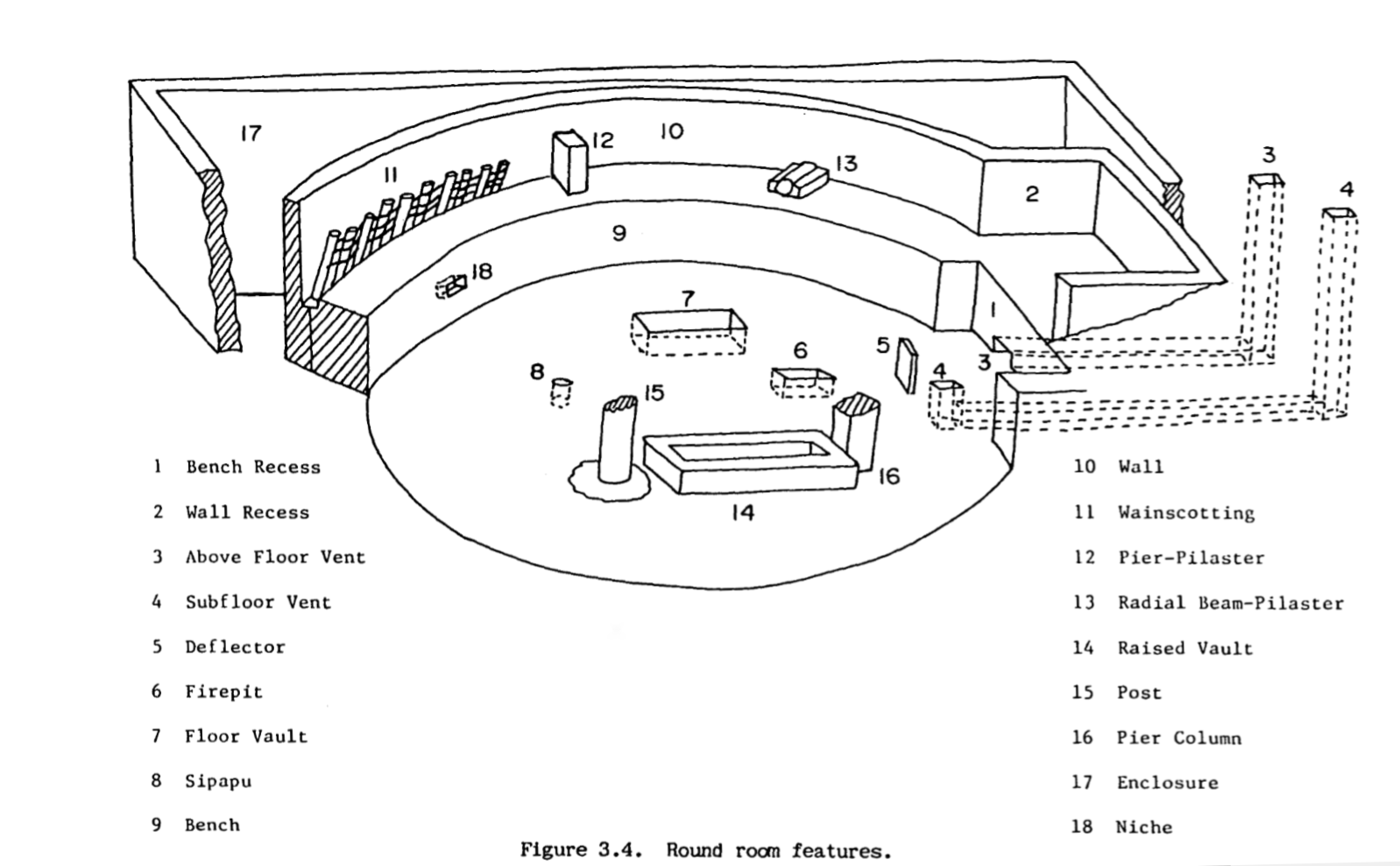
Kiva
A kiva is a space used by Puebloans for rites and political meetings, many of them associated with the kachina belief system. Among the modern Hopi and most other Pueblo peoples, "kiva" means a large room that is circular and underground, and used for spiritual ceremonies. Similar subterranean rooms are found among ruins in the North-American South-West, indicating uses by the ancient peoples of the region including the ancestral Puebloans, the Mogollon, and the Hohokam. Those used by the ancient Pueblos of the Pueblo I Period and following, designated by the Pecos Classification system developed by archaeologists, were usually round and evolved from simpler pit-houses. For the Ancestral Puebloans, these rooms are believed to have had a variety of functions, including domestic residence along with social and ceremonial purposes. Evolution During the late 8th century, Mesa Verdeans started building square pit structures that archeologists call protokivas. They were typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia (Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat dela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treveneague
Treveneague is an area near Goldsithney, Penzance, in the civil parish of St Hilary. It was originally composed of two places, North Treveneague and South Treveneague. The Grade II listed early 19th century North Treveneague Farmhouse and Farm Buildings North of Treveneague Farmhouse are located here. In the 1860s, an Iron Age fogou was discovered at Treveneague, the location of the fogou was located using Geophysics during a 1996 Time Team ''Time Team'' is a British television programme that originally aired on Channel 4 from 16 January 1994 to 7 September 2014. It returned online in 2022 for two episodes released on YouTube. Created by television producer Tim ... episode. References Penzance {{Penwith-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrosphere
Petrosphere (from Greek πέτρα (''petra''), "stone", and σφαῖρα (''sphaira''), "ball") may refer to: * Stone balls, a diverse class of archaeological artefact ** Particularly carved stone balls Carved stone balls are petrospheres dated from the late Neolithic, to possibly as late as the Iron Age, mainly found in Scotland, but also elsewhere in Britain and Ireland. They are usually round and rarely oval, and of fairly uniform size ..., prehistoric artefacts found in the British Isles * Petrosphere (geology), a planet's crust and mantle {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Ireland (800–1169)
The history of Ireland 800–1169 covers the period in the history of Ireland from the first Viking raids to the Norman invasion. The first two centuries of this period are characterised by Viking raids and the subsequent Norse settlements along the coast. Viking ports were established at Dublin, Wexford, Waterford, Cork and Limerick, which became the first large towns in Ireland. Ireland consisted of many semi-independent territories ( túatha), and attempts were made by various factions to gain political control over the whole of the island. For the first two centuries of this period, this was mainly a rivalry between putative High Kings of Ireland from the northern and southern branches of the Uí Néill. The one who came closest to being de facto king over the whole of Ireland, however, was Brian Boru, the first high king in this period not belonging to the Uí Néill. Following Brian's death at the Battle of Clontarf in 1014, the political situation became more complex with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strathnaver
Strathnaver or Strath Naver ( gd, Srath Nabhair) is the fertile strath of the River Naver, a famous salmon river that flows from Loch Naver to the north coast of Scotland. The term has a broader use as the name of an ancient province also known as the Mackay Country ( gd, Dùthaich MhicAoidh), once controlled by the Clan Mackay and extending over most of northwest Sutherland. Geography Loch Naver lies at the head of the strath, in the shadow of Ben Klibreck. The loch is long and deep. The Altnaharra Hotel at the western end of the loch has been used by anglers since the early 19th century. The loch is fed by two rivers ( Mudale and Vagastie) and several burns. Just below the loch, the Naver is joined by the River Mallart coming down from Loch Choire. It then flows through the Naver Forest and under the road bridge at Syre. The Langdale Burn and Carnachy Burn are other major tributaries as the strath widens out and flows into the sea at Bettyhill. Most of Strathnaver l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puebloans
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Zuni, and Hopi are the best-known. Pueblo people speak languages from four different language families, and each Pueblo is further divided culturally by kinship systems and agricultural practices, although all cultivate varieties of maize. Pueblo peoples have lived in the American Southwest for millennia and descend from Ancestral Pueblo peoples. The term ''Anasazi'' is sometimes used to refer to ancestral Pueblo people but it is now largely minimized. ''Anasazi'' is a Navajo word that means ''Ancient Ones'' or ''Ancient Enemy'', hence Pueblo peoples' rejection of it (see exonym). ''Pueblo'' is a Spanish term for "village." When Spaniards entered the area, beginning in the 16th-century with the founding of Nuevo México, they came across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barn
A barn is an agricultural building usually on farms and used for various purposes. In North America, a barn refers to structures that house livestock, including cattle and horses, as well as equipment and fodder, and often grain.Allen G. Noble, ''Traditional Buildings: A Global Survey of Structural Forms and Cultural Functions'' (New York: Tauris, 2007), 30. As a result, the term barn is often qualified e.g. tobacco barn, dairy barn, cow house, sheep barn, potato barn. In the British Isles, the term barn is restricted mainly to storage structures for unthreshed cereals and fodder, the terms byre or shippon being applied to cow shelters, whereas horses are kept in buildings known as stables. In mainland Europe, however, barns were often part of integrated structures known as byre-dwellings (or housebarns in US literature). In addition, barns may be used for equipment storage, as a covered workplace, and for activities such as threshing. Etymology The word ''barn'' comes f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |