|
Focometer
A focometer is an instrument that measures refractive errors and is intended to provide rural or economically disadvantaged populations spherical eyeglass prescriptions without the need for complicated protocols, expensive equipment, or electricity. The focometer is monocular and hand-held, and is normally used in natural lighting. Patients rotate a collar on the focometer until the best focus is achieved. The individual's refractive power is then read off a linear dioptre scale. The focometer was developed by Drs. Ian Berger and Larry Spitzberg at the University of Houston College of Optometry in Houston, Texas, to provide a simple, inexpensive means for measuring refractive error in human vision. The portable, hand-held instrument is highly appropriate for use in remote and poor areas. Focometers measure spherical refractive errors. Astigmatism can also be measured using a "clock target" with the device. A study has found, however, that the focometer is less effective for ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
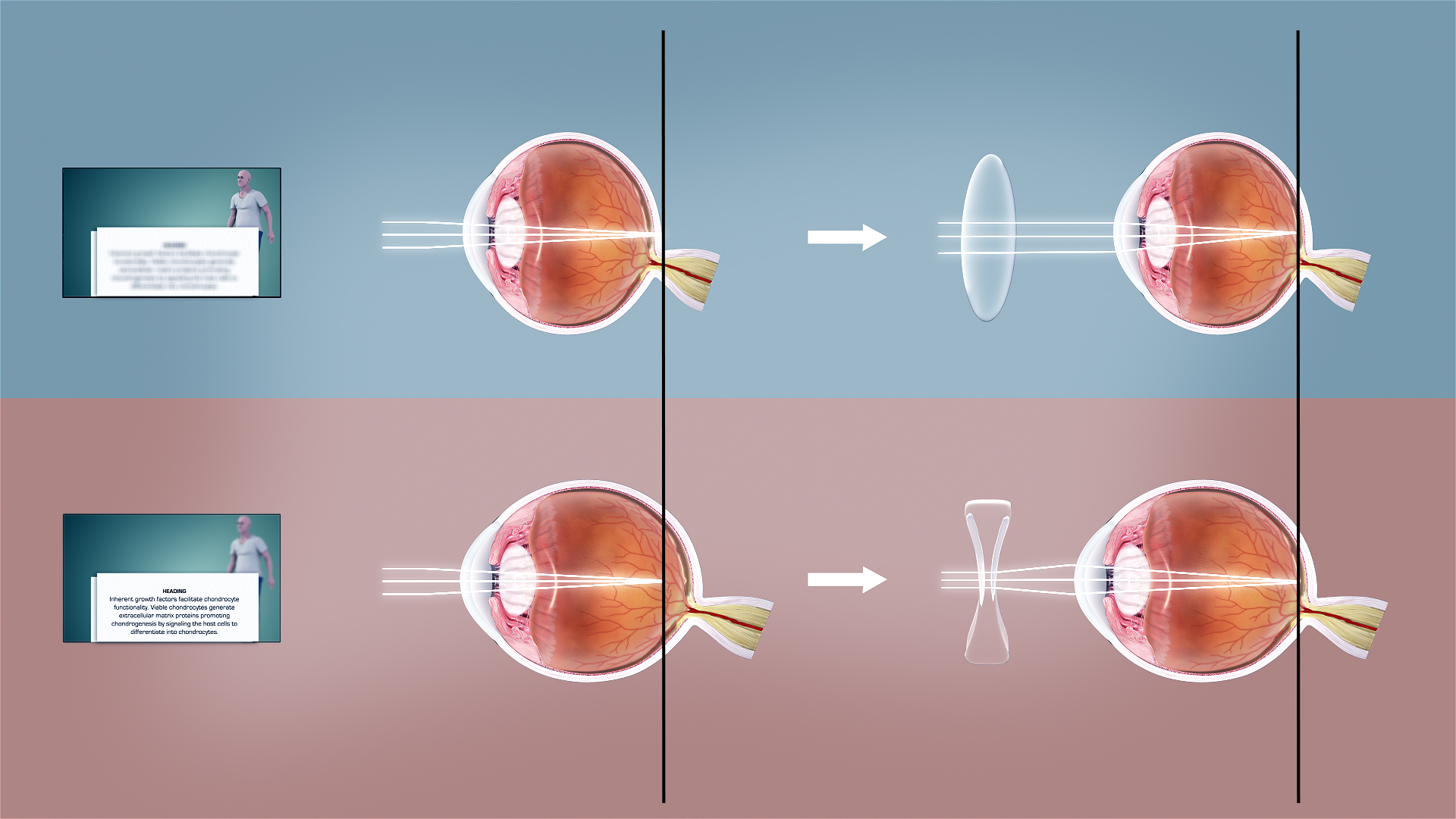
Refractive Error
Refractive error, also known as refraction error, is a problem with focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the eye and or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are near-sightedness, far-sightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Near-sightedness results in far away objects being blurry, far-sightedness and presbyopia result in close objects being blurry, and astigmatism causes objects to appear stretched out or blurry. Other symptoms may include double vision, headaches, and eye strain. Near-sightedness is due to the length of the eyeball being too long, far-sightedness the eyeball too short, astigmatism the cornea being the wrong shape, and presbyopia aging of the lens of the eye such that it cannot change shape sufficiently. Some refractive errors occur more often among those whose parents are affected. Diagnosis is by eye examination. Refractive errors are corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery. Eyeglasses are the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disadvantaged
The "disadvantaged" is a generic term for individuals or groups of people who: * Face special problems such as physical or mental disability * Lack money or economic supportKingdom of Nepal: Economic and Social Inclusion of the Disadvantaged Poor through Livelihood Enhancement with Micro-irrigation (Financed by the Poverty Reduction Cooperation Fund), March 2006 Economically disadvantaged In common usage "the disadvantaged" is a generic term for those "from lower-income backgrounds" or "the Disadvantaged Poor". The "economically disadvantaged" is a term used by government institutions in for example allocating free school meals to "a student who is a member of a household that meets the income eligibility guidelines for free or reduced-price meals (less than or equal to 185% of Federal Poverty Guidelines)" or business grants. The "disadvantaged" is often applied in a third world context and typically relate to women with reduced " upward mobility" suffering social exclusion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyeglass Prescription
An eyeglass prescription is an order written by an eyewear prescriber, such as an optometrist, that specifies the value of all parameters the prescriber has deemed necessary to construct and/or dispense corrective lenses appropriate for a patient. If an eye examination indicates that corrective lenses are appropriate, the prescriber generally provides the patient with an eyewear prescription at the conclusion of the exam. The parameters specified on spectacle prescriptions vary, but typically include the patient's name, power of the lenses, any prism to be included, the pupillary distance, expiration date, and the prescriber's signature. The prescription is typically determined during a refraction, using a phoropter and asking the patient which of two lenses is better, or by automated refractor, or through the technique of retinoscopy. A dispensing optician will take a prescription written by an optometrist and order and/or assemble the frames and lenses to then be dispe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioptre
A dioptre ( British spelling) or diopter ( American spelling) is a unit of measurement with dimension of reciprocal length, equivalent to one reciprocal metre, 1 dioptre = 1 m−1. It is normally used to express the optical power of a lens or curved mirror, which is a physical quantity equal to the reciprocal of the focal length, expressed in metres. For example, a 3-dioptre lens brings parallel rays of light to focus at metre. A flat window has an optical power of zero dioptres, as it does not cause light to converge or diverge. Dioptres are also sometimes used for other reciprocals of distance, particularly radii of curvature and the vergence of optical beams. The main benefit of using optical power rather than focal length is that the thin lens formula has the object distance, image distance, and focal length all as reciprocals. Additionally, when relatively thin lenses are placed close together their powers approximately add. Thus, a thin 2.0-dioptre lens placed close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Houston College Of Optometry
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 in 2020. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the seat and largest city of Harris County and the principal city of the Greater Houston metropolitan area, which is the fifth-most populous metropolitan statistical area in the United States and the second-most populous in Texas after Dallas–Fort Worth. Houston is the southeast anchor of the greater megaregion known as the Texas Triangle. Comprising a land area of , Houston is the ninth-most expansive city in the United States (including consolidated city-counties). It is the largest city in the United States by total area whose government is not consolidated with a county, parish, or borough. Though primarily in Harris County, small portions of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houston, Texas
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 in 2020. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the seat and largest city of Harris County and the principal city of the Greater Houston metropolitan area, which is the fifth-most populous metropolitan statistical area in the United States and the second-most populous in Texas after Dallas–Fort Worth. Houston is the southeast anchor of the greater megaregion known as the Texas Triangle. Comprising a land area of , Houston is the ninth-most expansive city in the United States (including consolidated city-counties). It is the largest city in the United States by total area whose government is not consolidated with a county, parish, or borough. Though primarily in Harris County, small portions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astigmatism (eye)
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. This results in distorted or blurred vision at any distance. Other symptoms can include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at night. Astigmatism often occurs at birth and can change or develop later in life. If it occurs in early life and is left untreated, it may result in amblyopia. The cause of astigmatism is unclear; however, it is believed to be partly related to genetic factors. The underlying mechanism involves an irregular curvature of the cornea and protective reaction changes in the lens of the eye, called lens astigmatism, that has the same mechanism as spasm of accomodation. Diagnosis is by an eye examination called autorefractor keratometry (objective, allows to see lens and cornea components of astigmatism) and subjective refraction, but subjective methods are almost always inaccurate, if lens astigmatism is not fully removed first with a week of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autorefractor
An autorefractor or automated refractor is a computer-controlled machine used during an eye examination to provide an objective measurement of a person's refractive error and prescription for glasses or contact lenses. This is achieved by measuring how light is changed as it enters a person's eye. Technique The majority of autorefractors calculate the vision correction a patient needs (refraction) by using sensors that detect the reflections from a cone of infrared light. These reflections are used to determine the size and shape of a ring in the retina which is located in the posterior part of the eye. By measuring this zone, the autorefractor can determine when a patient's eye properly focuses an image. The instrument changes its magnification until the image comes into focus. The process is repeated in at least three meridians of the eye and the autorefractor calculates the refraction of the eye, sphere, cylinder and axis. Modern autorefractors are based on the idea patented by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)