|
Flying-spot Scanner
A flying-spot scanner (FSS) uses a scanning source of a spot of light, such as a high-resolution, high-light-output, low-persistence cathode ray tube (CRT), to scan an image. Usually the image to be scanned is on photographic film, such as motion picture film, or a slide or photographic plate. The output of the scanner is usually a television signal. Basic principle In the case of the CRT-based scanner, as an electron beam is drawn across the face of the CRT it creates a scan that has the correct number of lines and aspect ratio for the format of the signal. The image of this scan is focused with a lens onto the film frame. Its light passes through the image being scanned and is converted to a proportional electrical signal by photomultiplier tube(s), one for each color (red, green, blue), that detects the variations in intensity of the beam spot as it scans across the film, and are converted to proportional electrical signals, one for each of the color channels. Telecines that u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reversal Film
In photography, reversal film or slide film is a type of photographic film that produces a positive image on a transparent base. Instead of negatives and prints, reversal film is processed to produce transparencies or diapositives (abbreviated as "diafilm" or "dia" in some languages like German or Hungarian). Reversal film is produced in various sizes, from 35 mm to roll film to 8×10 inch sheet film. A slide is a specially mounted individual transparency intended for projection onto a screen using a slide projector. This allows the photograph to be viewed by a large audience at once. The most common form is the 35 mm slide, with the image framed in a 2×2 inch cardboard or plastic mount. Some specialized labs produce photographic slides from digital camera images in formats such as JPEG, from computer-generated presentation graphics, and from a wide variety of physical source material such as fingerprints, microscopic sections, paper documents, astronomical imag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Television
The concept of television was the work of many individuals in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The first practical transmissions of moving images over a radio system used mechanical rotating perforated disks to scan a scene into a time-varying signal that could be reconstructed at a receiver back into an approximation of the original image. Development of television was interrupted by the Second World War. After the end of the war, all-electronic methods of scanning and displaying images became standard. Several different standards for addition of color to transmitted images were developed with different regions using technically incompatible signal standards. Television broadcasting expanded rapidly after World War II, becoming an important mass media, mass medium for advertising, propaganda, and entertainment. Television broadcasts can be distributed over the air by VHF and UHF radio signals from terrestrial transmitting stations, by microwave signals from Earth orbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
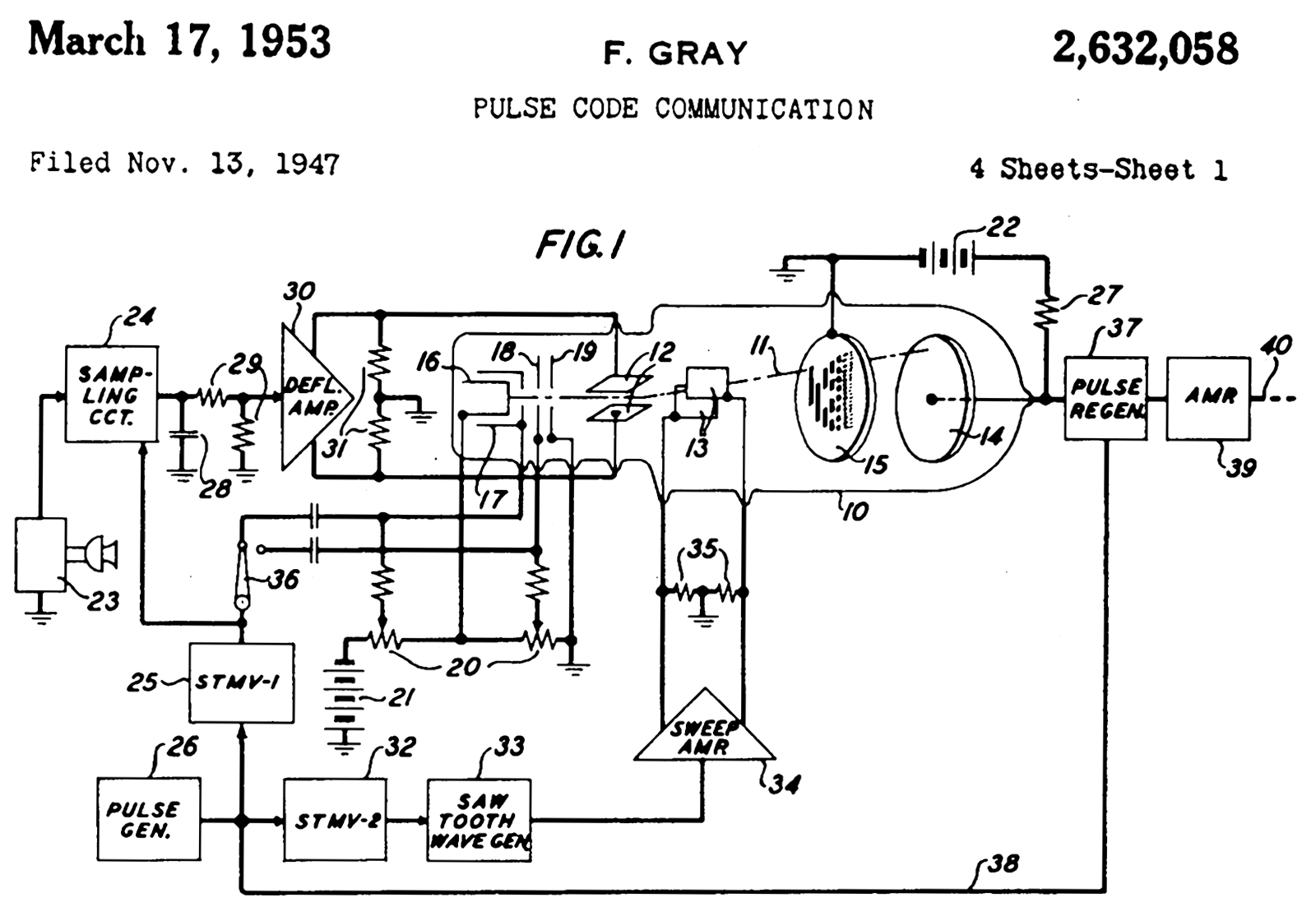
Frank Gray (researcher)
Frank Gray (13 September 1887 – 23 May 1969) was a physicist and researcher at Bell Labs who made numerous innovations in television, both mechanical and electronic, and is remembered for the Gray code. The Gray code, or reflected binary code (RBC), appearing in Gray's 1953 patent, is a binary numeral system often used in electronics, but with many applications in mathematics. Gray conducted pioneering research on the development of television; he proposed an early form of "flying spot scanner" for early TV systems in 1927, and helped develop a two-way mechanically scanned TV system in 1930. With Pierre Mertz, Gray wrote the classic paper on the mathematics of raster scan systems in 1934. He later participated in the early days of the digital revolution, with Raymond W. Sears, William M. Goodall, John Robinson Pierce, and others at Bell Labs, by providing the binary code used by Sears in his Pulse-code modulation#History, PCM tube, a beam deflection tube of the type that Sear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and professional digital cameras, act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cintel
Cintel was a British digital cinema company founded in 1927 by John Logie Baird and based in Ware, Hertfordshire. The early company was called ''Cinema Television Ltd''. Cinema Television was sold to J Arthur Rank Organization renamed Rank Cintel in 1958. It specialized in the design and manufacture of professional post-production equipment, for transcribing film into video or data formats. It was formerly part of the Rank Organisation. Along with a line of telecines, Rank Cintel made 3 tube RGB color video projectors in the 1960s. Their main products were based on either cathode ray tube (CRT) Flying-spot scanner or charge coupled device (CCD) technology and include, like the diTTo, diTTo Evolution & dataMill film scanners, Millennium II, Millennium HD & C-Reality & DSX telecines, imageMill 1 & 2 image processing system. The CRT tubes were made by Rank and Brimar. In September 2002 Cintel purchased ITK - Innovation TK Ltd. ITK held a number of patents for features used in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fernseh
The Fernseh AG television company was registered in Berlin on July 3, 1929, by John Logie Baird, Robert Bosch, Zeiss Ikon and D.S. Loewe as partners. John Baird owned Baird Television Ltd. in London, Zeiss Ikon was a camera company in Dresden, D.S. Loewe owned a company in Berlin and Robert Bosch owned a company, Robert Bosch GmbH, in Stuttgart. with an initial capital of 100,000 Reichsmark. Fernseh AG did research and manufacturing of television equipment. Etymology The company name "Fernseh AG" is a compound of ''Fernsehen'' ‘television’ and ''Aktiengesellschaft (AG)'' ‘joint-stock company’. The company was mainly known by its German abbreviation "FESE". See section see also on this page for other uses. Early years In 1929 Fernseh AG's original board of directors included: Emanuel Goldberg, Oliver George Hutchinson (for Baird), David Ludwig Loewe, and Erich Carl Rassbach (for Bosch) and Eberhard Falkenstein who did the legal work. Carl Zeiss's company worked alongside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motion Picture Film Scanner
A motion picture film scanner is a device used in digital filmmaking to scan original film for storage as high-resolution digital intermediate files. A film scanner scans original film stock: negative or positive print or reversal/IP. Units may scan gauges from 8 mm to 70 mm (8 mm, Super 8, 9.5 mm, 16 mm, Super 16, 35 mm, Super 35, 65 mm and 70 mm) with very high resolution scanning at 2K, 4K, 8K, or 16K resolutions. (2K is approximately 2048×1080 pixels and 4K is approximately 4096×2160 pixels). Some models of film scanner are intermittent pull-down film scanners which scan each frame individually, locked down in a pin-registered film gate, taking roughly a second per frame. Continuous-scan film scanners, where the film frames are scanned as the film is continuously moved past the imaging pick up device, are typically evolved from earlier telecine mechanisms, and can act as such at lower resolutions. The scanner scans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slide Projector
A slide projector is an opto-mechanical device for showing photographic slides. 35 mm slide projectors, direct descendants of the larger-format magic lantern, first came into widespread use during the 1950s as a form of occasional home entertainment; family members and friends would gather to view slide shows. Reversal film was much in use, and supplied slides snapped during vacations and at family events. Slide projectors were also widely used in educational and other institutional settings. Photographic film slides and projectors have mostly been replaced by image files on digital storage media shown on a projection screen by using a video projector or simply displayed on a large-screen video monitor. History A continuous-slide lantern was patented in 1881. It included a dissolving views apparatus.Sloane, T. O'Conor. ''Facts Worth Knowing Selected Mainly from the Scientific American for Household, Workshop, and Farm Embracing Practical and Useful Information fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Film
Test film are rolls or loops or slides of photographic film used for testing the quality of equipment. Equipment to be tested could include: telecine, motion picture film scanner, Movie projectors, Image scanners, film-out gear, Film recorders and Film scanners. Test films comes in all film formats: 16mm, 35mm, Super 8, 8mm, 65mm, 70mm and IMAX, both motion pictures and still photography. China girl China girl or leader ladies or LAD girl or laboratory aim density (LAD) test film, is common name for a color chart test film with a color or black-and-white set up chart and a woman. This would be used stand alone or placed on a film leader, that is at the start of the first roll of film. LAD patch is neutral gray, with visual density of 1.0. With the LAD patch is usually a white and black patch for white balancing FILMS. Color patches of blue, green, and red are used to check saturated colors. Grayscale chips are used to check for neutral color balance and correct contrast. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Station Identification
Station identification (ident, network ID or channel ID or bumper) is the practice of radio and television stations and broadcast network, networks identifying themselves on-air, typically by means of a call sign or brand name (sometimes known, particularly in the United States, as a "sounder" or "stinger", more generally as a station or network ID). This may be to satisfy requirements of licensing authorities, a form of branding, or a combination of both. As such, it is closely related to production logos, used in television and cinema alike. Station identification used to be done regularly by an announcer at the halfway point during the presentation of a television program, or in between programs. Asia Idents are known as a ''montage'' in Thailand and the Malay world (except Indonesia), and as an ''interlude'' in Cambodia and Vietnam. Philippines Station identifications in the Philippines differ from the vernacular meaning in most of the world. They describe what would be r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |