|
Flutemazepam
Flutemazepam, initially first synthesized in 1965, but wasn't further developed and described until a team at Stabilimenti Chimici Farmaceutici Riuniti SpA in the mid 1970s. It is the fluorinated analogue of temazepam that has powerful hypnotic, sedative, amnesiac, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It is most closely related in structure to temazepam, being the fluoro instead of chloro analogue. As a result, flutemazepam has been shown to have similar pharmacological properties to temazepam and nimetazepam. It has been found to be effective for the treatment of the most severe states of anxiety, panic attacks, and severe insomnia. Furthermore, it is highly potent with 1 mg of flutemazepam being equivalent to 10 mg of diazepam. Flutemazepam is highly effective for acute psychotic states, especially stimulant psychosis, violent behaviour, and aggression. It was first synthesized and described in 1965 by Leo Sternbach. In a test which compared a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
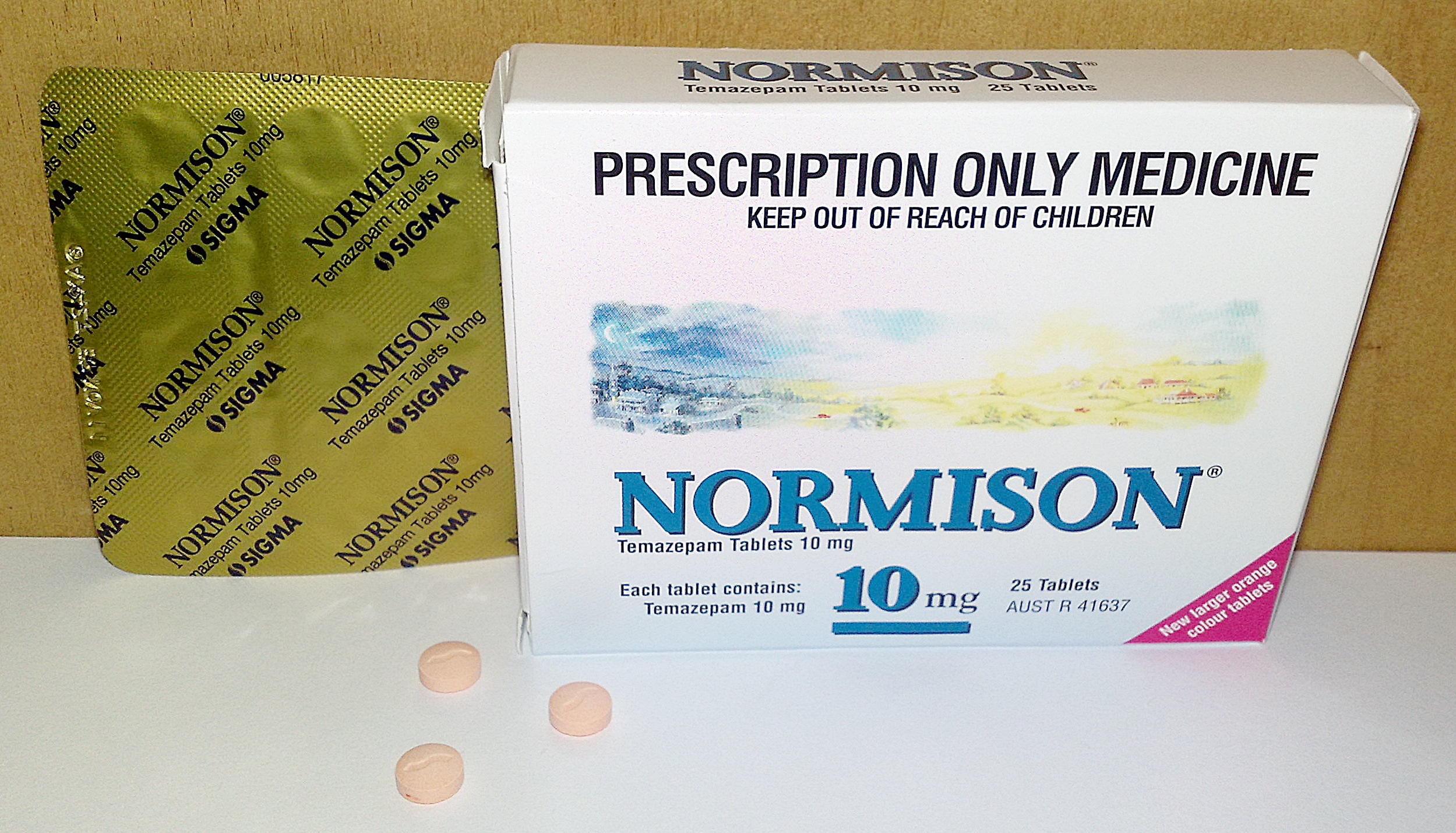
Temazepam
Temazepam (sold under the brand names Restoril among others) is a medication of the benzodiazepine class which is generally used to treat severe or debilitating insomnia. It is taken by mouth. Temazepam is rapidly absorbed, and significant hypnotic effects begin in less than 30 minutes and can last for up to eight hours. Many studies, some going as far back as the early 1980s out of Australia and the United Kingdom, both of which have had serious temazepam abuse epidemics and related mortality, have all mostly corroborated each other and proven that the potential for abuse and physical dependence is very high, even in comparison to many other benzodiazepines. As a result, prescriptions for hypnotics such as temazepam have seen a dramatic decrease since 2010, while anxiolytics such as alprazolam (Xanax), clonazepam (Rivitrol, Klonopin), and lorazepam (Ativan) have increased or remained stable. Temazepam and similar hypnotics, such as triazolam (Halcion) are generally reserved for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), was discovered accidentally by Leo Sternbach in 1955 and was made available in 1960 by Hoffmann–La Roche, who soon followed with diazepam (Valium) in 1963. By 1977, benzodiazepines were the most prescribed medications globally; the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), among other factors, decreased rates of prescription, but they remain frequently used worldwide. Benzodiazepines are depressants that enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the GABAA receptor, resulting in sedative, hypnotic ( sleep-inducing), anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties. High doses o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactams
A lactam is a cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino alkanoic acid. The term is a portmanteau of the words ''lactone'' + ''amide''. Nomenclature Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size: * α-Lactam (3-atom rings) * β-Lactam (4-atom rings) * γ-Lactam (5-atom rings) * δ-Lactam (6-atom rings) * ε-Lactam (7-atom rings) This ring-size nomenclature stems from the fact that a hydrolyzed α-Lactam leads to an α-amino acid and a β-Lactam to a β-amino acid, ''etc''. Synthesis General synthetic methods exist for the organic synthesis of lactams. Beckmann rearrangement Lactams form by the acid-catalyzed rearrangement of oximes in the Beckmann rearrangement. Schmidt reaction Lactams form from cyclic ketones and hydrazoic acid in the Schmidt reaction. Cyclization of amino acids Lactams can be formed from cyclisation of amino acids via the coupling between an amine and a carboxylic acid within the same molecule. Lactamization is most efficient in this wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroarenes
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide (also known as haloarene) is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. The haloarene are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications. Preparation The two main preparatory routes to aryl halides are direct halogenation and via diazonium salts. Direct halogenation In the Friedel-Crafts halogenation, Lewis acids serve as catalysts. Many metal chlorides are used, examples include iron(III) chloride or aluminium chloride. The most important aryl halide, chlorobenzene is produced by this route. Monochlorination of benzene is always accompanied by formation of the dichlorobenzene derivatives. Arenes with electron donating groups react with halogens even in the absence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), was discovered accidentally by Leo Sternbach in 1955 and was made available in 1960 by Hoffmann–La Roche, who soon followed with diazepam (Valium) in 1963. By 1977, benzodiazepines were the most prescribed medications globally; the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), among other factors, decreased rates of prescription, but they remain frequently used worldwide. Benzodiazepines are depressants that enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the GABAA receptor, resulting in sedative, hypnotic ( sleep-inducing), anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties. High doses of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temazepam
Temazepam (sold under the brand names Restoril among others) is a medication of the benzodiazepine class which is generally used to treat severe or debilitating insomnia. It is taken by mouth. Temazepam is rapidly absorbed, and significant hypnotic effects begin in less than 30 minutes and can last for up to eight hours. Many studies, some going as far back as the early 1980s out of Australia and the United Kingdom, both of which have had serious temazepam abuse epidemics and related mortality, have all mostly corroborated each other and proven that the potential for abuse and physical dependence is very high, even in comparison to many other benzodiazepines. As a result, prescriptions for hypnotics such as temazepam have seen a dramatic decrease since 2010, while anxiolytics such as alprazolam (Xanax), clonazepam (Rivitrol, Klonopin), and lorazepam (Ativan) have increased or remained stable. Temazepam and similar hypnotics, such as triazolam (Halcion) are generally reserved for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitemazepam
Nitemazepam (or 3-hydroxynimetazepam) is a benzodiazepine derivative which was first synthesised in the 1970s but was never marketed. It is the 7-nitro instead of 7-chloro analogue of temazepam, and also the 3-hydroxy derivative of nimetazepam, and an active metabolite. It has in more recent years been sold as a designer drug A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Des ..., first being definitively identified in Europe in 2017. It is metabolized to 7-aminonitemazepam, nimetazepam, 3-hydroxynitemazepam, temazepam, and nimetazepam glucuronide. References {{GABAAR PAMs Nitrobenzodiazepines Designer drugs GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators Lactims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorazepam
Lorazepam, sold under the brand name Ativan among others, is a benzodiazepine medication. It is used to treat anxiety disorders, trouble sleeping, severe agitation, active seizures including status epilepticus, alcohol withdrawal, and chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. It is also used during surgery to interfere with memory formation and to sedate those who are being mechanically ventilated. It is also used, along with other treatments, for acute coronary syndrome due to cocaine use. It can be given by mouth or as an injection into a muscle or vein. When given by injection onset of effects is between one and thirty minutes and effects last for up to a day. Common side effects include weakness, sleepiness, low blood pressure, and a decreased effort to breathe. When given intravenously the person should be closely monitored. Among those who are depressed there may be an increased risk of suicide. With long-term use, larger doses may be required for the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypnotic
Hypnotic (from Greek ''Hypnos'', sleep), or soporific drugs, commonly known as sleeping pills, are a class of (and umbrella term for) psychoactive drugs whose primary function is to induce sleep (or surgical anesthesiaWhen used in anesthesia to produce and maintain unconsciousness, "sleep" is metaphorical as there are no regular sleep stages or cyclical natural states; patients rarely recover from anesthesia feeling refreshed and with renewed energy. The word is also used in art.) and to treat insomnia (sleeplessness). This group of drugs is related to sedatives''. ''Whereas the term sedative describes drugs that serve to calm or relieve anxiety, the term hypnotic generally describes drugs whose main purpose is to initiate, sustain, or lengthen sleep. Because these two functions frequently overlap, and because drugs in this class generally produce dose-dependent effects (ranging from anxiolysis to loss of consciousness), they are often referred to collectively as sedative-h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Sternbach
Leo Sternbach (May 7, 1908 – September 28, 2005) was a Polish American chemist who is credited with first synthesizing benzodiazepines, the main class of tranquilizers. Background and family Sternbach was born on May 7, 1908, in Opatija, Kingdom of Hungary, Austro-Hungarian Empire, to an upper middle class Jewish family. He had a younger brother, Giusi. Ha-Kol (Glasilo Židovske zajednice u Hrvatskoj); Sanja Dukić; Povratak velikana u rodnu Opatiju; stranica 40, 41; broj 94, svibanj / lipanj 2006. His father Michael Abracham Sternbach was from the Polish city of Przemyśl in Galicia (then part of Austria-Hungary), and his mother Piroska (née Cohn) Sternbach was from Orosháza, Hungary. Sternbach's parents met and married in Opatija where they both lived. The family lived in modest conditions, in a rented four-room apartment on the third floor of the "Vila Jadran" (Villa Adriatic), near the pharmacy owned by Sternbach's father. Sternbach attended a private German school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |