|
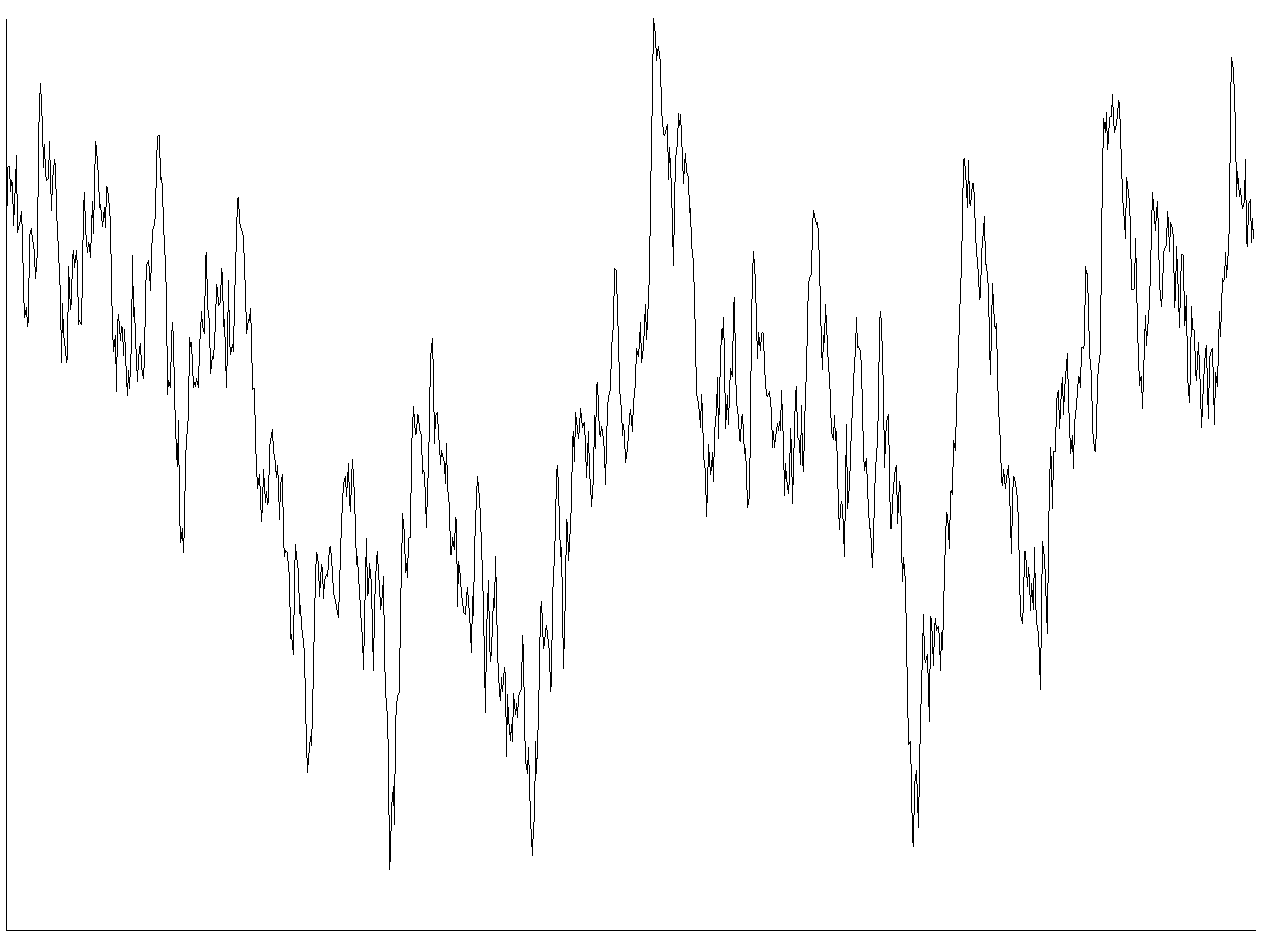
Fluctuation-enhanced Sensing
Fluctuation-enhanced sensing (FES) is a specific type of chemical or biological sensing where the stochastic component, ''noise'', of the sensor signal is analyzed. The stages following the sensor in a FES system typically contain filters and preamplifier(s) to extract and amplify the stochastic signal components, which are usually microscopic temporal fluctuations that are orders of magnitude weaker than the sensor signal. Then selected statistical properties of the amplified ''noise'' are analyzed, and a corresponding pattern is generated as the stochastic fingerprint of the sensed agent. Often the power density spectrum of the stochastic signal is used as output pattern however FES has been proven effective with more advanced methods, too, such as higher-order statistics. History During the 1990s, several authors (for example, Bruno Neri and coworkers, Peter Gottwald and Bela Szentpali) had proposed using the spectrum of measured noise to obtain information about ambient chemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise (electronics)
In electronics, noise is an unwanted disturbance in an electrical signal. Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly as it is produced by several different effects. In particular, noise is inherent in physics, and central to thermodynamics. Any conductor with electrical resistance will generate thermal noise inherently. The final elimination of thermal noise in electronics can only be achieved cryogenically, and even then quantum noise would remain inherent. Electronic noise is a common component of noise in signal processing. In communication systems, noise is an error or undesired random disturbance of a useful information signal in a communication channel. The noise is a summation of unwanted or disturbing energy from natural and sometimes man-made sources. Noise is, however, typically distinguished from interference, for example in the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) and signal-to-noise plus interference ratio (SNIR) measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Higher-order Statistics
In statistics, the term higher-order statistics (HOS) refers to functions which use the third or higher power of a sample, as opposed to more conventional techniques of lower-order statistics, which use constant, linear, and quadratic terms (zeroth, first, and second powers). The third and higher moments, as used in the skewness and kurtosis, are examples of HOS, whereas the first and second moments, as used in the arithmetic mean (first), and variance (second) are examples of low-order statistics. HOS are particularly used in the estimation of shape parameters, such as skewness and kurtosis, as when measuring the deviation of a distribution from the normal distribution. In statistical theory, one long-established approach to higher-order statistics, for univariate and multivariate distributions is through the use of cumulants and joint cumulants.Kendall, MG., Stuart, A. (1969) ''The Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 1: Distribution Theory, 3rd Edition'', Griffin. (Chapte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Nose
An electronic nose is an electronic sensing device intended to detect odors or flavors. The expression "electronic sensing" refers to the capability of reproducing human senses using sensor arrays and pattern recognition systems. Since 1982, research has been conducted to develop technologies, commonly referred to as electronic noses, that could detect and recognize odors and flavors. The stages of the recognition process are similar to human olfaction and are performed for identification, comparison, quantification and other applications, including data storage and retrieval. Some such devices are used for industrial purposes. Other techniques to analyze odors In all industries, odor assessment is usually performed by human sensory analysis, by chemosensors, or by gas chromatography. The latter technique gives information about volatile organic compounds but the correlation between analytical results and mean odor perception is not direct due to potential interactions between s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claes-Göran Granqvist
Claes-Göran Sture Granqvist (born 25 December 1946, Helsingborg, Sweden) is a materials physicist and Professor of Solid State Physics at Uppsala University in Sweden. Granqvist is considered a pioneer and expert in photochromic materials and energy-efficient building materials such as glass, paint, and wood. Granqvist is a Fellow of SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics and a Member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Science and the Royal Swedish Academy of Engineering Sciences. He has served as Chairman of the Nobel Committee for Physics of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. Education Granqvist received the PhD degree in physics at Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, in 1974. Career In 1975, Granqvist was a Postdoctoral associate at Cornell University, USA. In the period of 1976–89, he held various research positions at Chalmers University of Technology. From 1989–93 he was a Full Professor of Experimental Physics at Gothenburg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uppsala University
Uppsala University ( sv, Uppsala universitet) is a public university, public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the List of universities in Sweden, oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation. The university rose to significance during the rise of Swedish Empire, Sweden as a great power at the end of the 16th century and was then given a relative financial stability with a large donation from King Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden, Gustavus Adolphus in the early 17th century. Uppsala also has an important historical place in Swedish national culture, identity and for the Swedish establishment: in historiography, literature, politics, and music. Many aspects of Swedish academic culture in general, such as the white student cap, originated in Uppsala. It shares some peculiarities, such as the student nation system, with Lund University and the University of Helsinki. Uppsala belongs to the Coimbra Group of European universities a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Revo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensing Of Phage-triggered Ion Cascades
Sensing of phage-triggered ion cascades (SEPTIC) is a prompt bacterium identification method based on fluctuation-enhanced sensing in fluid medium. The advantages of SEPTIC are the specificity and speed (needs only a few minutes) offered by the characteristics of phage infection, the sensitivity due to fluctuation-enhanced sensing, and durability originating from the robustness of phages. An idealistic SEPTIC device may be as small as a pen and maybe able to identify a library of different bacteria within a few minutes measurement window. The mechanism SEPTIC utilizes bacteriophages as indicators to trigger an ionic response by the bacteria during phage infection. Microscopic metal electrodes detect the random fluctuations of the electrochemical potential due to the stochastic fluctuations of the ionic concentration gradient caused by the phage infection of bacteria. The electrode pair in the electrolyte with different local ion concentrations at the vicinity of electrodes form an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas A&M University
Texas A&M University (Texas A&M, A&M, or TAMU) is a public, land-grant, research university in College Station, Texas. It was founded in 1876 and became the flagship institution of the Texas A&M University System in 1948. As of late 2021, Texas A&M has the largest student body in the United States, and is the only university in Texas to hold simultaneous designations as a land, sea, and space grant institution. In 2001, it was inducted into the Association of American Universities. The university's students, alumni, and sports teams are known as Aggies, and its athletes compete in eighteen varsity sports as a member of the Southeastern Conference. The university was the first public higher-education institution in Texas; it opened for classes on October 4, 1876, as the Agricultural and Mechanical College of Texas (A.M.C.) under the provisions of the 1862 Morrill Land-Grant Act. In the following decades, the college grew in size and scope, expanding to its largest enrol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Szeged
, mottoeng = Truth. Bravery. Freedom. , established = , type = Public research university , founder = Emperor Franz Joseph I , affiliation = European University Association, Science Without Borders, Confucius Institute , budget = US$220 million , chancellor = Judit Fendler , rector = László Rovó , students = 22,693 , undergrad = 17,384 , postgrad = 2,668 , doctoral = 714 , other = 3,997 (international) , city = Szeged , country = Hungary , coordinates = , campus = Urban , language = Hungarian, English , colours = Blue , website = , academic_staff = 1,968 , administrative_staff = 2,200 The University of Szeged ( hu, Szegedi Tudományegyetem, ) is a public research university in Szeged, Hungary. Established as the Jesuit Academy of Kolozsvár in present-day Cluj-Napoca in 1581, the institution was re-established as a university in 1872 by Emperor Franz Joseph I. The university relocated to Szeged in 1921, making it one of the oldest research universitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Heszler
Peter Heszler (November 1, 1958, Miskolc – August 15, 2009, Szeged) was a Hungarian physicist. He is well known for, among others, his research on laser-assisted nanoparticle synthesis. His research included nanotechnology, condensed matter physics, materials science, fluctuations and noise, laser science and chemical sensors, including fluctuation-enhanced sensing. One of his early famous papers was the exact denial of a non-existing phenomenon called quantum 1/f noise. The denial was based on quantum electrodynamics and proved that the quantum 1/f noise effect does not exist and its theoretical model is incorrect. In the quantum 1/f noise model, the photons and their vacuum states were omitted from the equations and such errors yielded faulty mathematical predictions for fluctuations that cannot exist because they are forbidden by the basic orthogonality rules of quantum electrodynamics. Perhaps, his most important breakthroughs are the discovery and application of emiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janusz Smulko
Janusz Smulko (born April 25, 1964 in Kolno, Poland) is a Polish electronics engineer, full professor of Gdańsk University of Technology. Research Interests: reliability assessment of electronic devices (electrochromic materials, supercapacitors, varistors, thin metal foil capacitors), fluctuation-enhanced sensing (various systems and sensors), gas sensing, Raman spectroscopy, noise in biological systems, signal processing. Since September 2016 – Vice-Rector for Scientific Research, Gdańsk University of Technology, Poland. Education Janusz Smulko graduated in 1989 with honors from the Faculty of Electronics at Gdańsk University of Technology, specialising in measuring instruments. In 1989 he took second place in the Red Rose competition for the best student in the Pomerania Region, Poland. Career Since the beginning of his career he has been associated with Gdańsk University of Technology: research assistant (1989-1996), Assistant Professor (1996-2012), Associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |